|
Manimekalai
''Maṇimēkalai'' ( ta, மணிமேகலை, ), also spelled ''Manimekhalai'' or ''Manimekalai'', is a Tamil-Buddhist epic composed by Kulavāṇikaṉ Seethalai Sataṉar probably around the 6th century. It is an "anti-love story", a sequel to the "love story" in the earliest Tamil epic ''Silappadikaram'', with some characters from it and their next generation. The epic consists of 4,861 lines in ''akaval'' meter, arranged in 30 cantos. The title ''Manimekalai'' is also the name of the daughter of Kovalan and Madhavi, who follows in her mother's footsteps as a dancer and a Buddhist nun. The epic tells her story. Her physical beauty and artistic achievements seduces the Chola prince Udayakumara. He pursues her. She, a nun of Mahayana Buddhism persuasion, feels a commitment to free herself from human ties. She rejects his advances, yet finds herself drawn to him. She hides, prays and seeks the help of her mother, her Buddhist teacher Aravana Adikal and angels. They teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Five Great Epics Of Tamil Literature
The Five Great Epics ( ta, ஐம்பெரும்காப்பியங்கள் ''Aimperumkāppiyaṅkaḷ'') are five Tamil epics according to later Tamil literary tradition. They are '' Silappatikāram'', ''Manimekalai'', ''Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi'', ''Valayapathi'' and '' Kuṇṭalakēci''. Three of the five great epics of Tamil literature are attributed to Tamil Jains, while two are attributed to Tamil Buddhists. ''Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi'', '' Cilappatikāram'', and ''Valayapathi'' were written by Tamil Jains, while ''Manimekalai'' and '' Kuṇṭalakēci'' were authored by Buddhists. The first mention of the ''Aimperumkappiyam'' (lit. Five large epics) occurs in Mayilainathar's commentary of ''Nannūl''. However, Mayilainathar does not mention their titles. The titles are first mentioned in the late-18th-to-early-19th-century work ''Thiruthanikaiula''. Earlier works like the 17th-century poem ''Tamil vidu thoothu'' mention the great epics as ''Panchkavyams''. Amon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chithalai Chathanar
Satthanar or Chithalai Satthanar ( ta, சாத்தனார் or சீத்தலைச் சாத்தனார், ''cītalai cāttanār'') was the Tamil poet who composed the epic Manimekalai. A total of 11 verses of the Sangam literature have been attributed to Satthanar, including verse 10 of the Tiruvalluva Maalai. Etymology Pronounced ''Sa-tha-naar,'' the name is derived from ( ta, சாத்து, ''sāttu'') meaning Buddhist monk. Applying this principle to the name Maturai Kulavāṇikan Cāttan, the author of Manimekalai, we see that the two appellations Maturai and Kulavanikan were prefixed to his name in order to distinguish him from another poet of Maturai with the same name and from a third who lived elsewhere. Several examples could be cited of this system of nomenclature which prevailed during the early days. Biography Satthanar hailed from a place known as Seerthandalai, later came to be known as Seethalai. He was a grain merchant at Madurai and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
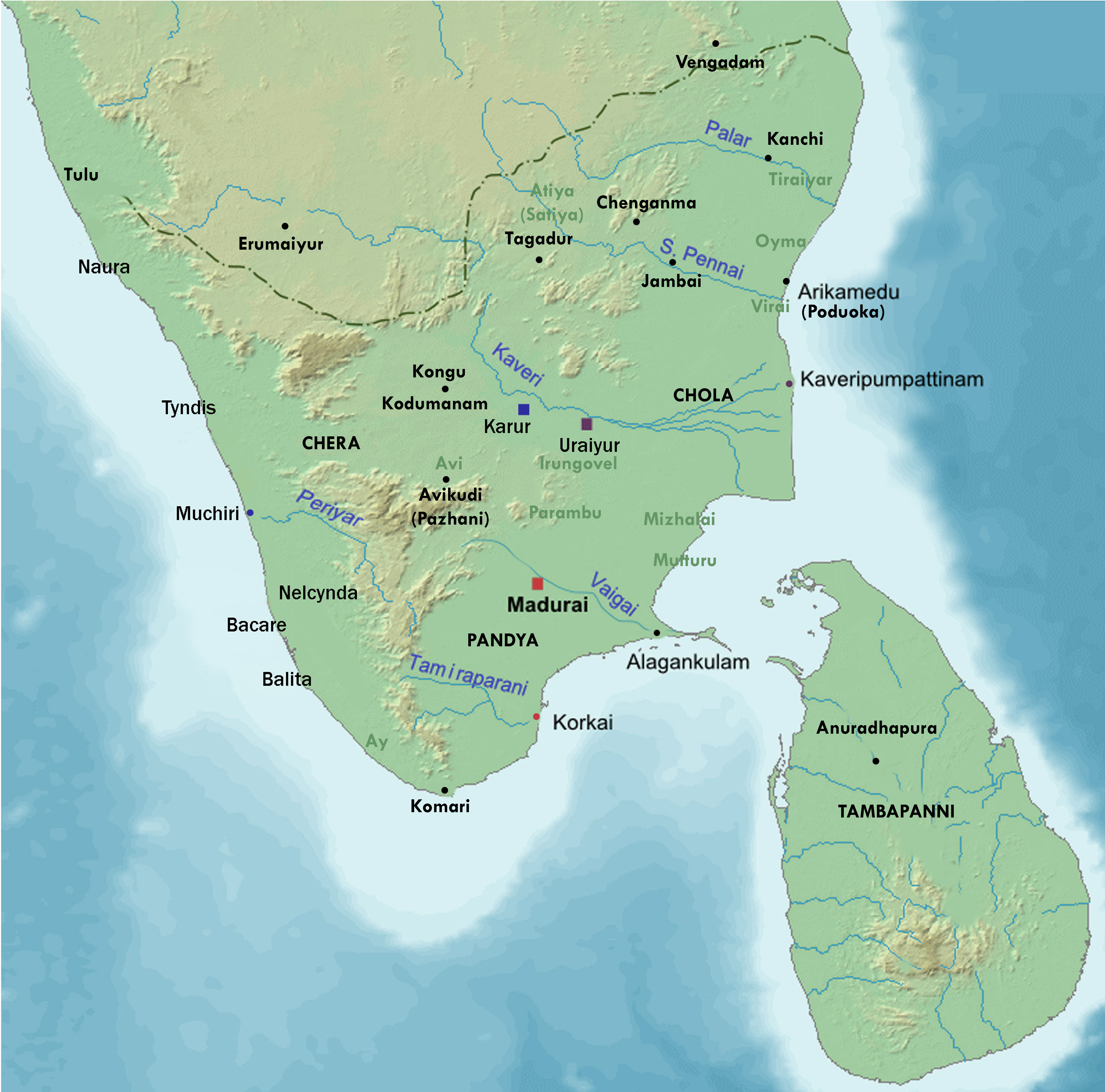
Silappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം, IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappadikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം,IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time, Ko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannaki
Kannagi ( ta, கண்ணகி) sometimes spelled Kannaki, is a legendary Tamil woman who forms the central character of the Tamil epic '' Cilappatikaram''. Kannagi is described as the chaste woman who stays with her husband despite his unfaithfulness, their attempt to rebuild their marriage after her husband had lost everything but repented, how her husband is falsely framed then punished without the due checks and processes of justice. Kannagi proves and protests the injustice, then curses the king and city of Madurai leading to the death of the unjust Pandyan King of Madurai, who had wrongfully put her husband Kovalan to death. The society that had made her suffer, suffers in retribution as the city Madurai is burnt to the ground because of her curse. In the Chera (Kerala) and Tamil tradition, Kannagi has been deified as the symbol – sometimes as goddess – of chastity, with sculptures or reliefs in Hindu temples iconographically reminding the visitor of her breaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kovalan
Kovalan ( ta, கோவலன்) is a central character in Ilango Adigal's ''Silappatikaram,'' one of the ancient Tamil epics. Family Father : Machattuvan Wife : Kannagi Lover : Madhavi Daughter : Manimekalai (Mother: Madhavi) Narrative Puharkkandam Kovalan, the son of a wealthy merchant, Machattuvan, married Kannagi, the daughter of another merchant, Manayakan. At the time of his marriage, he was sixteen years old. They lived together happily in the city of Kaveripattinam, until Kovalan met the courtesan Madhavi and fell in love with her. In his infatuation, he completely forgot his wife and spent his time and parental wealth with Madhavi. During the annual festival in the honour of Indra, there was a misunderstanding between Kovalan and Madhavi. As a result, the penniless Kovalan returned to Kannagi, who welcomed him whole-heartedly. Realising his mistake, he decided to start a new life by migrating to Madurai with Kannagi. Accompanied by a Buddhist nun, they s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages extending up to the 3rd century CE. ''Ramayana'' is one of the two important epics of Hinduism, the other being the ''Mahābhārata''. The epic, traditionally ascribed to the Maharishi Valmiki, narrates the life of Sita, the Princess of Janakpur, and Rama, a legendary prince of Ayodhya city in the kingdom of Kosala. The epic follows his fourteen-year exile to the forest urged by his father King Dasharatha, on the request of Rama's stepmother Kaikeyi; his travels across forests in the Indian subcontinent with his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana, the kidnapping of Sita by Ravana – the king of Lanka, that resulted in war; and Rama's eventual return to Ayodhya to be crowned king amidst jubilation and celebration. The ''Ramayana'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimekhala
Manimekhala ( pi, Maṇīmekhalā) is a goddess in the Hindu-Buddhist mythology. She is regarded as a guardian of the seas, namely the Indian Ocean and the South China Sea as part of the mythology of Southeast Asia. She was placed by Cātummahārājika to protect virtuous beings from shipwreck. She appears in several Buddhist stories including the Mahanipata Jataka (Mahajanaka Jataka), in which she rescues Prince Mahajanaka from a shipwreck. Anne Elizabeth Monius. Imagining a place for Buddhism: literary culture and religious community in Tamil-speaking South India. Oxford University Press US, 2001, pages 111-112 Etymology In Pali, ' refers to a girdle or belt of jewels. In Southeast Asia, she is known by various indigenized appellations, including as Mani Maykhala () in Burmese, as Moni Mekhala () or Neang Mekhala () in Khmer; as Mani Mekkhala () in Thai. In Mainland Southeast Asia Archaeological evidence of Manimekhala in the form of reliefs has been found in Zothoke, Myan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism. Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within the Trimurti, the triple deity of supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva. Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme being who creates, protects, and transforms the universe. In the Shaktism tradition, the Goddess, or Adi Shakti, is described as the supreme Para Brahman, yet Vishnu is revered along with Shiva and Brahma. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power ( Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the highest form of Ishvara is with qualities ( Saguna), and have certain form, but is limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saṃsāra (Buddhism)
Saṃsāra ( sa, संसार, pi, saṃsāra; also ''samsara'') in Buddhism and Hinduism is the beginningless cycle of repeated birth, mundane existence and dying again. Samsara is considered to be '' dukkha'', suffering, and in general unsatisfactory and painful, perpetuated by desire and '' avidya'' (ignorance), and the resulting karma. Rebirths occur in six realms of existence, namely three good realms (heavenly, demi-god, human) and three evil realms (animal, ghosts, hellish). Samsara ends if a person attains nirvana, the "blowing out" of the desires and the gaining of true insight into impermanence and non-self reality. Characteristics In Buddhism, ''saṃsāra'' is the "suffering-laden, continuous cycle of life, death, and rebirth, without beginning or end". In several suttas of the Samyutta Nikaya's chapter XV in particular it's said "From an inconstruable beginning comes transmigration. A beginning point is not evident, though beings hindered by ignorance and fett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharani
Dharanis ( IAST: ), also known as ''Parittas'', are Buddhist chants, mnemonic codes, incantations, or recitations, usually the mantras consisting of Sanskrit or Pali phrases. Believed to be protective and with powers to generate merit for the Buddhist devotee, they constitute a major part of historic Buddhist literature. Many of these chants are in Sanskrit and Pali, written in scripts such as Siddhaṃ as well as transliterated into Chinese, Korean, Japanese, Sinhala, Thai and other regional scripts. They are similar to and reflect a continuity of the Vedic chants and mantras. Dharanis are found in the ancient texts of all major traditions of Buddhism. They are a major part of the Pali canon preserved by the Theravada tradition. Mahayana sutras such as the Lotus Sutra and the Heart Sutra include or conclude with dharani. Some Buddhist texts, such as ''Pancarakṣa'' found in the homes of many Buddhist tantra tradition followers, are entirely dedicated to dharani. They are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world. * * * * The city has a syncretic tradition of Muslim artisanship that underpins its religious tourism. * * * * * Located in the middle-Ganges valley in the southeastern part of the state of Uttar Pradesh, Varanasi lies on the left bank of the river. It is to the southeast of India's capital New Delhi and to the east of the state capital, Lucknow. It lies downstream of Allahabad (officially Prayagraj), where the confluence with the Yamuna river is another major Hindu pilgrimage site. Varanasi is one of the world's oldest continually inhabited cities. Kashi, its ancient name, was associated with a kingdom of the same name of 2,500 years ago. The Lion capital of Ashoka at nearby Sarnath has been interpreted to be a commemoration of the Buddha's first sermon the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |