|
Lys-N
Lys-N is a metalloendopeptidase found in the mushroom ''Grifola frondosa'' that cleaves proteins on the amino side of lysine residues. Mass spectrometry Lys-N is becoming a popular protease used for protein digestion in proteomics experiments. The combination Lys-N proteolytic peptides and mass spectrometry sequencing with ETD creates tandem mass spectra composed mostly of amino terminal peptide fragment ions. This fragmentation pattern facilitates the applicability of these spectra for de novo peptide sequencing. See also * Endoproteinase Lys-C * Mass spectrometry * Tandem mass spectrometry * Bottom-up proteomics References External links * The MEROPS MEROPS is an online database for peptidases (also known as proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes) and their inhibitors. The classification scheme for peptidases was published by Rawlings & Barrett in 1993, and that for protein inhibitor ... online database for peptidases and their inhibitorsM35.004Coverage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoproteinase Lys-C
Endoproteinase Lys-C is a protease that cleaves proteins on the C-terminal side of lysine residues. This enzyme is naturally found in the bacterium ''Lysobacter enzymogenes'' and is commonly used in protein sequencing. Lys-C activity is optimal in the pH range 7.0 - 9.0. See also *Trypsin *Lys-N Lys-N is a metalloendopeptidase found in the mushroom ''Grifola frondosa'' that cleaves proteins on the amino side of lysine residues. Mass spectrometry Lys-N is becoming a popular protease used for protein digestion in proteomics experiments. Th ... References Bacterial enzymes Proteases EC 3.4 Post-translational modification Proteomics §gtfgf {{Enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloendopeptidase
A metalloendopeptidase is an enzyme that functions as a metalloproteinase endopeptidase Endopeptidase or endoproteinase are proteolytic peptidases that break peptide bonds of nonterminal amino acids (i.e. within the molecule), in contrast to exopeptidases, which break peptide bonds from end-pieces of terminal amino acids. For this .... References External links * EC 3.4.24 {{enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grifola Frondosa
''Grifola frondosa'' (also known as hen-of-the-woods, in Japanese, ram's head or sheep's head) is a polypore mushroom that grows at the base of trees, particularly old growth oaks or maples. It is typically found in late summer to early autumn. It is native to China, Europe, and North America. Description Like the sulphur shelf mushroom, ''G. frondosa'' is a perennial fungus that often grows in the same place for several years in succession. It occurs most prolifically in the northeastern regions of the United States, but has been found as far west as Idaho. ''G. frondosa'' grows from an underground tuber-like structure known as a sclerotium, about the size of a potato. The fruiting body, occurring as large as , rarely , is a cluster consisting of multiple grayish-brown caps which are often curled or spoon-shaped, with wavy margins and broad. The undersurface of each cap bears about one to three pores per millimeter, with the tubes rarely deeper than . The milky-white stip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a basic, charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the ''S'' configuration. The human body cannot synthesize lysine. It is essential in humans and must therefore be obtained from the diet. In organisms that synthesise lysine, two main biosynthetic pathways exist, the diaminopimelate and α-aminoadipate pathways, which employ distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. In addition, other kinds of proteins include antibodies that protect an organism from infection, and hormones that send important signals throughout the body. The proteome is the entire set of proteins produced or modified by an organism or system. Proteomics enables the identification of ever-increasing numbers of proteins. This varies with time and distinct requirements, or stresses, that a cell or organism undergoes. Proteomics is an interdisciplinary domain that has benefited greatly from the genetic information of various genome projects, including the Human Genome Project. It covers the exploration of proteomes from the overall level of protein composition, structure, and activity, and is an important component of functional genomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolytic
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause disease. Proteolysis can also be used as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, and it may also be used in industry, for example in food pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron-transfer Dissociation
Electron-transfer dissociation (ETD) is a method of fragmenting multiply-charged gaseous macromolecules in a mass spectrometer between the stages of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). Similar to electron-capture dissociation, ETD induces fragmentation of large, multiply-charged cations by transferring electrons to them. ETD is used extensively with polymers and biological molecules such as proteins and peptides for sequence analysis. Transferring an electron causes peptide backbone cleavage into c- and z-ions while leaving labile post translational modifications (PTM) intact. The technique only works well for higher charge state peptide or polymer ions (z>2). However, relative to collision-induced dissociation (CID), ETD is advantageous for the fragmentation of longer peptides or even entire proteins. This makes the technique important for top-down proteomics. The method was developed by Hunt and coworkers at the University of Virginia. History Electron-capture dissociation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Tandem mass spectrometry, also known as MS/MS or MS2, is a technique in instrumental analysis where two or more mass analyzers are coupled together using an additional reaction step to increase their abilities to analyse chemical samples. A common use of tandem MS is the analysis of biomolecules, such as proteins and peptides. The molecules of a given sample are ionized and the first spectrometer (designated MS1) separates these ions by their mass-to-charge ratio (often given as m/z or m/Q). Ions of a particular m/z-ratio coming from MS1 are selected and then made to split into smaller fragment ions, e.g. by collision-induced dissociation, ion-molecule reaction, or photodissociation. These fragments are then introduced into the second mass spectrometer (MS2), which in turn separates the fragments by their m/z-ratio and detects them. The fragmentation step makes it possible to identify and separate ions that have very similar m/z-ratios in regular mass spectrometers. Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Novo Peptide Sequencing
In mass spectrometry, de novo peptide sequencing is the method in which a peptide amino acid sequence is determined from tandem mass spectrometry. Knowing the amino acid sequence of peptides from a protein digest is essential for studying the biological function of the protein. In the old days, this was accomplished by the Edman degradation procedure. Today, analysis by a tandem mass spectrometer is a more common method to solve the sequencing of peptides. Generally, there are two approaches: database search and de novo sequencing. Database search is a simple version as the mass spectra data of the unknown peptide is submitted and run to find a match with a known peptide sequence, the peptide with the highest matching score will be selected. This approach fails to recognize novel peptides since it can only match to existing sequences in the database. De novo sequencing is an assignment of fragment ions from a mass spectrum. Different algorithms are used for interpretation and most in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
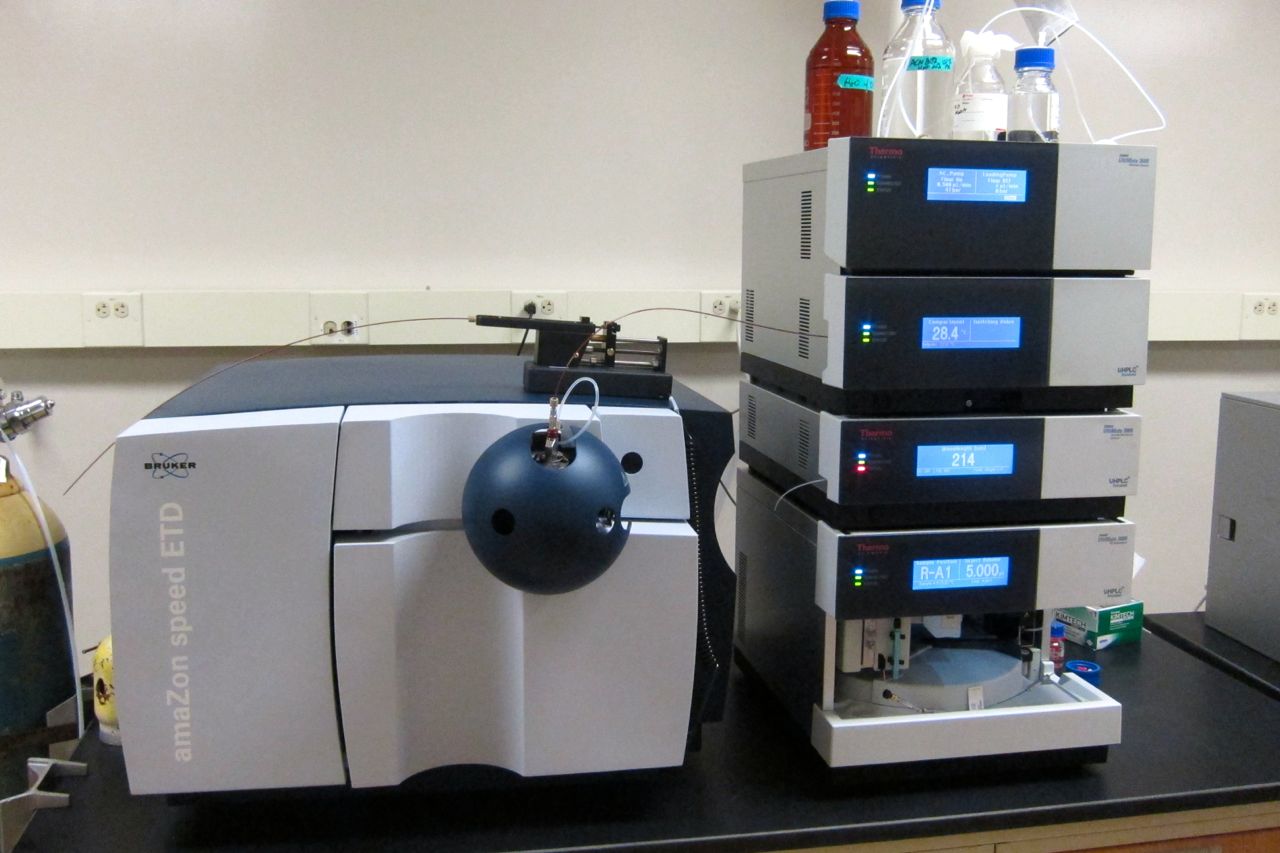
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom-up Proteomics
Bottom-up proteomics is a common method to identify proteins and characterize their amino acid sequences and post-translational modifications by proteolytic digestion of proteins prior to analysis by mass spectrometry. The major alternative workflow used in proteomics is called top-down proteomics where intact proteins are purified prior to digestion and/or fragmentation either within the mass spectrometer or by 2D electrophoresis. Essentially, bottom-up proteomics is a relatively simple and reliable means of determining the protein make-up of a given sample of cells, tissues, etc. In bottom-up proteomics, the crude protein extract is enzymatically digested, followed by one or more dimensions of separation of the peptides by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry, a technique known as shotgun proteomics. By comparing the masses of the proteolytic peptides or their tandem mass spectra with those predicted from a sequence database or annotated peptide spectral in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)