|
Lobosa
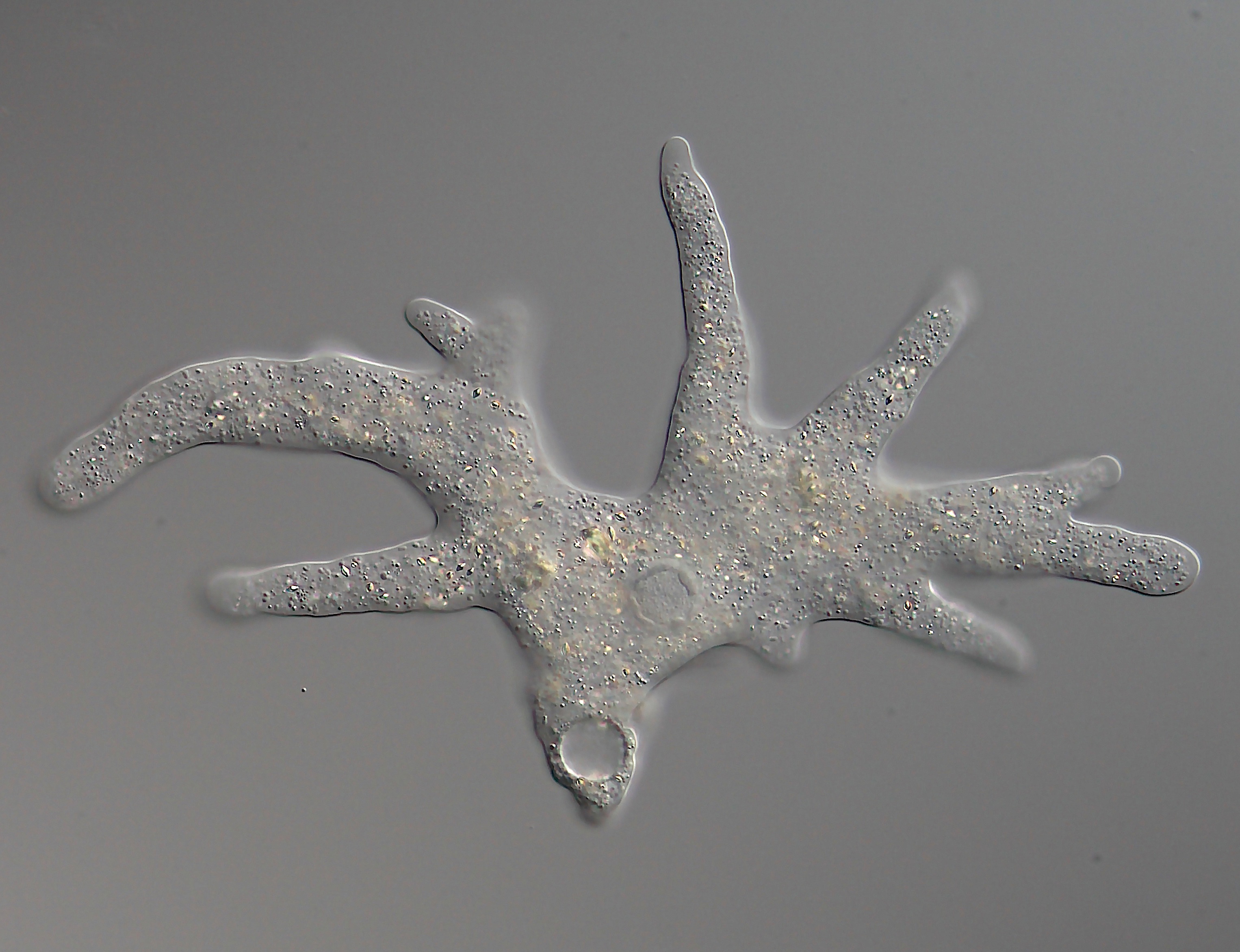
Lobosa is a taxonomic group of amoebae in the phylum Amoebozoa. Most lobosans possess broad, bluntly rounded pseudopods, although one genus in the group, the recently discovered ''Sapocribrum,'' has slender and threadlike (filose) pseudopodia. In current classification schemes, Lobosa is a subphylum, composed mainly of amoebae that have lobose pseudopods but lack cilia or flagella. Characteristics The group was originally proposed in 1861 by William B. Carpenter, who created it as a taxonomic order containing the single family Amoebina. Carpenter's Lobosa consisted of amoeboid organisms whose endoplasm (endosarc) flows into lobe-like "pseudopodian prolongations." This type of pseudopod, which was understood to be typical of the genus Amoeba "and its allies," differed from the filose (thread-like) or reticulose (netlike) pseudopods of the Foraminifera. The name Lobosa was chosen for these amoebae "as expressing the lobe-like character of their pseudopodial extensions". As cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycopoda
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known amoeboid organisms, such as ''Chaos'', '' Entamoeba'', '' Pelomyxa'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutosa
Cutosea () is a small group of marine amoeboid protists proposed in 2016. It is a monotypic class of Amoebozoa containing the order Squamocutida (). Cutosean organisms are characterized by a cell coat of microscales separated from the cell membrane. Four genera, '' Armaparvus'', '' Idionectes'', '' Sapocribrum'' and '' Squamamoeba'', belong to this group, distributed in three families. Characteristics The cells of cutosean amoebae are surrounded by a continuous thin, somewhat flexible envelope, unique in structure because it is not attached to the cytoplasmic membrane. Below this envelope, they present oval microscales surrounded by a dense matrix. The small scales are not visible under a light microscope. The envelope is penetrated by one or many small pores, which allow subpseudopodia to occasionally protrude from the cell membrane, for a very slow locomotion. Locomoting cells are flattened, oval or round in shape. All of their cells lack cilia or centrosomes, except for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conosa
Conosa is a grouping of Amoebozoa. It is subdivided into three groups: Archamoeba, Variosea and Mycetozoa. In some classifications, the mycetozoan Myxogastria and Dictyostelia are united in Macromycetozoa (= Eumycetozoa). Conosa includes the species '' Dictyostelium discoideum,'' a social amoeba, and '' Entamoeba histolytica'', a human pathogen, among others. Conosa are morphologically defined by a conical microtubular structure, and have been found to be monophyletic. Characteristics The Conosa group was first proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 1998 as a subphylum of Amoebozoa. Cavalier-Smith originally separated this group into two infraphyla: Archamoebae and Mycetozoa. Notable characteristics of these two groups are that Mycetozoa are free living, while Archamoebae are amitochondrial. This clade is morphologically defined by their complex microtubular skeleton that forms a partial or complete cone. They have a monolayer of microtubules that surround at least some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testate Amoebae
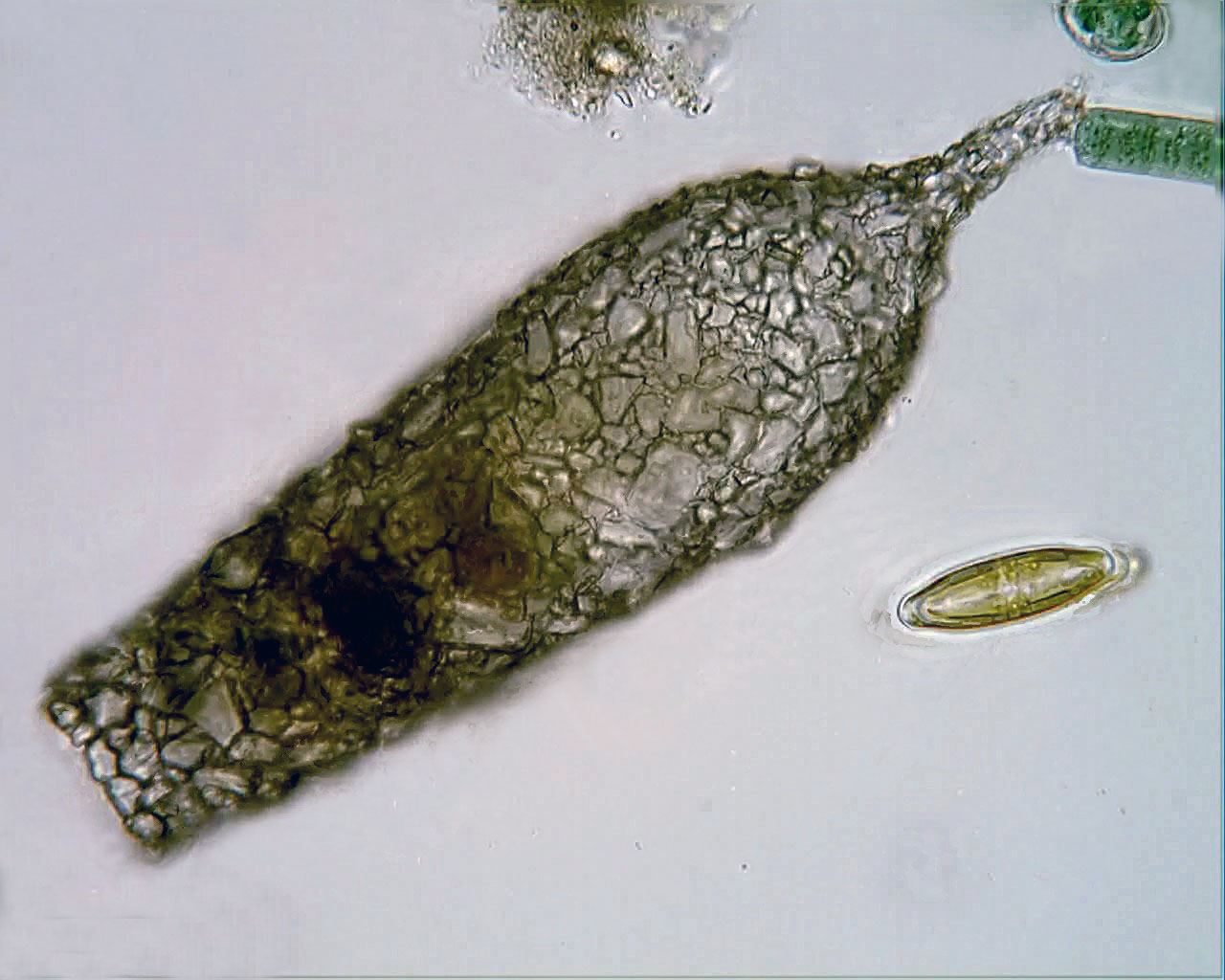
Testate amoebae (formerly thecamoebians, Testacea or Thecamoeba) are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test (biology), test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the pseudopodia emerge, that provides the amoeba with shelter from predators and environmental conditions. The test of some species is produced entirely by the amoeba and may be organic, siliceous or calcareous depending on the species (autogenic tests), whereas in other cases the test is made up of particles of sediment collected by the amoeba which are then agglutinated together by secretions from within the cell (xenogenic tests). A few taxa (Hyalospheniidae) can build either type, depending on the circumstances and availability of foreign material. The assemblage referred to as "testate amoebae" is actually composed of several, unrelated groups of organisms. However, some features they all share that have been used to g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulinea
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba'', '' Arcella'', '' Difflugia'' and '' Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists such as Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed Lobosea ''sensu stric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopodia
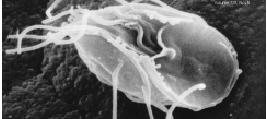
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Generally, several pseudopodia arise from the surface of the body, (''polypodial'', for example, '' Amoeba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavata
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as ''Giardia'' and '' Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now- obsolete Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged (they have a distinctive ultrastructural identity). They are considered to be a basal flagellate lineage. On the basis of phylogenomic analyses, the group was shown to contain three widely separated eukaryote groups, the discobids, metamonads, and malawimonads. A current view of the composition of the excavates is given below, indicating that the group is paraphyletic. Except for some Eugleno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic grouping (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of synapomorphies and symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term received currency during the debates of the 1960s and 1970s accompanying the rise of cladistics, having been coined by zoologist Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles), which is paraphyletic with respect to birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles and all descendants of that ancestor exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade (taxonomy)
A grade is a taxon united by a level of morphology (biology), morphological or physiological complexity. The term was coined by British biologist Julian Huxley, to contrast with clade, a strictly Phylogenetics, phylogenetic unit. Phylogenetics The concept of evolutionary grades arises in the context of phylogenetics: the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or Morphology (biology), morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. Definition of an evolutionary grade An Evolution, evolutionary grade is a group of species united by morphology (biology), morphological or physiology, physiological traits, that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba Proteus
''Amoeba proteus'' is a large species of amoeba closely related to another genus of giant amoebae, ''Chaos (genus), Chaos''. As such, the species is sometimes given the alternative scientific name ''Chaos diffluens''. This protozoan uses extensions called pseudopodia to move and to eat smaller unicellular organisms. Food is enveloped inside the cell's cytoplasm in a food vacuole, where ingested matter is slowly broken down by enzymes. ''A. proteus'' inhabits freshwater environments and feeds on protozoans, algae, rotifers, and even other smaller amoebae. They are colorless, but they may have colored inclusions derived from their food. ''A. proteus'' possesses a thick-walled cell nucleus, nucleus containing granular chromatin, and is therefore a eukaryote. Its cell membrane, membrane consists of a phospholipid bilayer similar to other eukaryotic organisms. History The first description of this amoeba is probably that of August Johann Rösel von Rosenhof who, in 1755, published dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |