|
Living Stump
A living stump is created when a live tree is cut, burned, eaten, or infected, causing its cambium to die above the root system. Living stumps are generally characterized as having a thin outer layer of living cells that surround a hollow central cavity. Living stumps can survive for several years by * using excess carbon reserves, * transfer of nutrients from the roots of neighbouring trees, often aided by mycorrhiza or * root grafting to the root system of living trees. Root grafting allows for carbon transfer from living trees to living stumps resulting in incremental cambium growth in the stump. Stumps can grow a callus tissue over its cross section which prolongs longevity of the stump by protecting it from infection and insect damage. A living stump which is capable of producing sprouts or cuttings is known as a stool, and is used in the coppicing method of woodland management.Crist, John B.; Mattson, James A.; Winsauer, Sharon A. 1983. Effect of severing method and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Stump - Geograph
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated Plant stem, stem, or trunk (botany), trunk, usually supporting Branch, branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only Bark (botany), woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller Arecaceae, palms, Cyatheales, tree ferns, Musa (genus), bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a Monophyletic group, monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that Convergent evolution, have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are around three trillion mature trees in the world currently. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
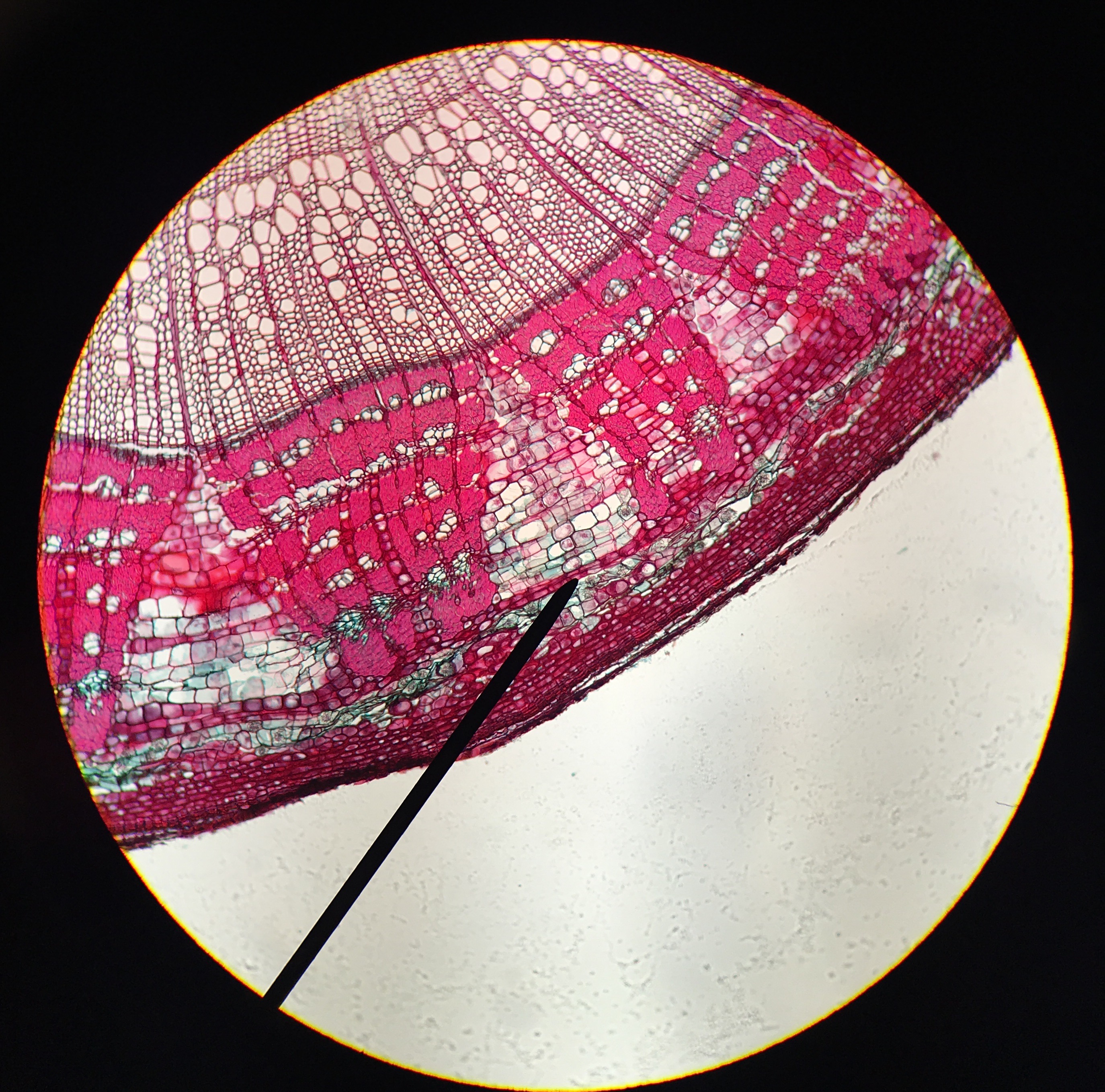
Cambium
A cambium (: cambiums or cambia), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycorrhiza
A mycorrhiza (; , mycorrhiza, or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plant's rhizosphere, the plant root system and its surroundings. Mycorrhizae play important roles in plant nutrition, soil biology, and soil chemistry. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus colonizes the host plant's root tissues, either intracellularly as in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, or extracellularly as in ectomycorrhizal fungi. The association is normally mutualistic. In particular species, or in particular circumstances, mycorrhizae may have a parasitic association with host plants. Definition A mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between a green plant and a fungus. The plant makes organic molecules by photosynthesis and supplies them to the fungus in the form of sugars or lipids, while the fungus supplies the plant with water and mineral nutrients, such as phosphorus, taken from the soil. Myco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutting (plant)
A plant cutting is a piece of a plant that is used in horticulture for vegetative reproduction, vegetative (asexual) plant propagation, propagation. A piece of the Plant stem, stem or root of the source plant is placed in a suitable medium such as moist soil. If the conditions are suitable, the plant piece will begin to grow as a new plant independent of the Mother plant, parent, a process known as striking. A stem cutting produces new roots, and a root cutting produces new stems. Some plants can be grown from leaf pieces, called leaf cuttings, which produce both stems and roots. The scions used in grafting are also called cuttings. Propagating plants from cuttings is an ancient form of cloning. There are several advantages of cuttings, mainly that the produced offspring are practically clones of their parent plants. If a plant has favorable traits, it can continue to pass down its advantageous genetic information to its offspring. This is especially economically advantageous as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppicing
Coppicing is the traditional method in woodland management of cutting down a tree to a tree stump, stump, which in many species encourages new Shoot (botany), shoots to grow from the stump or roots, thus ultimately regrowing the tree. A forest or grove that has been subject to coppicing is called a copse or coppice, in which young tree stems are repeatedly cut down to near ground level. The resulting living stumps are called Living stump, stools. New growth emerges, and after a number of years, the coppiced trees are harvested, and the cycle begins anew. Pollarding is a similar process carried out at a higher level on the tree in order to prevent grazing animals from eating new shoots. ''Daisugi'' (台杉, where ''sugi'' refers to Japanese cedar) is a similar Japanese technique. Many silviculture practices involve cutting and regrowth; coppicing has been of significance in many parts of lowland temperate Europe. The widespread and long-term practice of coppicing as a landscape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland Management
Forest management is a branch of forestry concerned with overall administrative, legal, economic, and social aspects, as well as scientific and technical aspects, such as silviculture, forest protection, and forest regulation. This includes management for timber, aesthetics, recreation, urban values, water, wildlife, inland and nearshore fisheries, wood products, plant genetic resources, and other forest resource values. Management objectives can be for conservation, utilisation, or a mixture of the two. Techniques include timber extraction, planting and replanting of different species, building and maintenance of roads and pathways through forests, and preventing fire. Many tools like remote sensing, GIS and photogrammetry modelling have been developed to improve forest inventory and management planning. Scientific research plays a crucial role in helping forest management. For example, climate modeling, biodiversity research, carbon sequestration research, GIS applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Strobus
''Pinus strobus'', commonly called the eastern white pine, northern white pine, white pine, Weymouth pine (British), and soft pine is a large pine native to eastern North America. It occurs from Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, Canada, west through the Great Lakes region to southeastern Manitoba and Minnesota, United States, and south along the Appalachian Mountains and upper Piedmont (United States), Piedmont to northernmost Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and very rare in some of the higher elevations in northeastern Alabama. It is considered rare in Indiana. The Haudenosaunee maintain the tree as the central symbol of their multinational confederation, calling it the "Tree of Peace", where the Seneca use the name ''o’sóä’'' and the Mohawk people, Kanienʼkehá:ka call it ''onerahtase'ko:wa''. Within the Wabanaki Confederacy, the Mi'kmaq use the term ''guow'' to name the tree, both the Maliseet, Wolastoqewiyik and Passamaquoddy, Peskotomuhkatiyik call it ''kuw'' or ''ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Chestnut
The American chestnut (''Castanea dentata'') is a large, fast-growing deciduous tree of the Fagaceae, beech family native to eastern North America. As is true of all species in the genus ''Chestnut, Castanea'', the American chestnut produces Bur, burred fruit with edible nuts. The American chestnut was once common in its Appalachian Mountains, Appalachian Mountain range and was a Dominance (ecology), dominant species in the oak-chestnut forest region of its central and southern range. During the early to mid-20th century, American chestnut trees were devastated by chestnut blight, a fungal disease that came from Castanea crenata, Japanese chestnut trees that were introduced into North America from Japan. It is estimated that the blight killed between three and four billion American chestnut trees in the first half of the 20th century, beginning in 1904.Griffin, Gary"Recent advances in research and management of chestnut blight on American chestnut" Phytopathology (journal), Phyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsuga
''Tsuga'' (, from Japanese (), the name of '' Tsuga sieboldii'') is a genus of conifers in the subfamily Abietoideae of Pinaceae, the pine family. The English-language common name "hemlock" arose from a perceived similarity in the smell of its crushed foliage to that of the unrelated plant hemlock. Unlike the latter, ''Tsuga'' species are not poisonous. The genus comprises eight to ten species (depending on the authority), with four species occurring in North America and four to six in eastern Asia. Description They are medium-sized to large evergreen trees, ranging from tall, with a conical to irregular crown, the latter occurring especially in some of the Asian species. The leading shoots generally droop. The bark is scaly and commonly deeply furrowed, with the colour ranging from grey to brown. The branches stem horizontally from the trunk and are usually arranged in flattened sprays that bend downward towards their tips. Short spur shoots, which are present in many gy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas-fir
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is the tallest tree in the Pinaceae family. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''menziesii''), Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''glauca'') and Mexican Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''lindleyana''). Despite its common names, it is not a true fir (genus '' Abies''), spruce (genus '' Picea''), or pine (genus ''Pinus''). It is also not a hemlock; the genus name ''Pseudotsuga'' means "false hemlock". Description Douglas-firs are medium-sized to extremely large evergreen trees, tall (although only coast Douglas-firs reach heights near 100 m) and commonly reach in diameter, although trees with diameters of almost exist. The largest coast Douglas-firs regularly live over 500 years, with the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedrus
''Cedrus'', with the common English name cedar, is a genus of coniferous trees in the plant family Pinaceae (subfamily Abietoideae). They are native to the mountains of the western Himalayas and the Mediterranean region, occurring at altitudes of in the Himalayas and in the Mediterranean.Farjon, A. (1990). ''Pinaceae: Drawings and Descriptions of the Genera''. Koeltz Scientific Books. . Description ''Cedrus'' trees can grow up to 30–40 m (occasionally 60 m) tall with spicy-resinous scented wood, thick ridged or square-cracked bark, and broad, level branches. The shoots are dimorphic and are made up of long shoots, which form the framework of the branches, and short shoots, which carry most of the leaves. The leaves are evergreen and needle-like, 8–60 mm long, arranged in an open spiral phyllotaxis on long shoots, and in dense spiral clusters of 15–45 together on short shoots; they vary from bright grass-green to dark green to strongly glaucous pale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |