|
Linear Biochemical Pathway
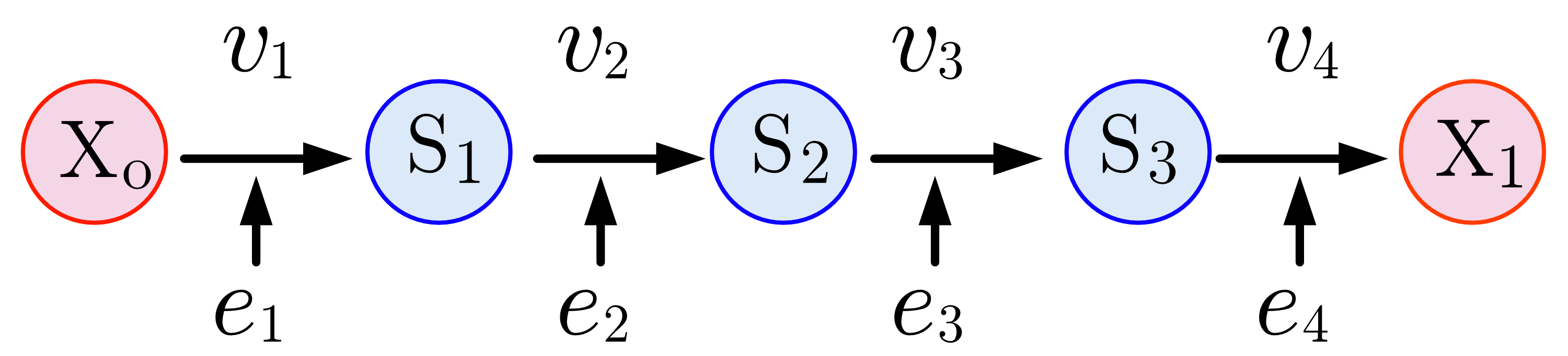
A linear biochemical pathway is a chain of Enzyme catalysis, enzyme-catalyzed reaction steps where the product of one reaction becomes the Substrate (chemistry), substrate for the next Chemical reaction, reaction. The molecules progress through the pathway sequentially from the starting substrate to the final product. Each step in the pathway is usually facilitated by a different specific enzyme that Catalysis, catalyzes the chemical transformation. An example includes DNA replication, which connects the starting substrate and the end product in a straightforward sequence. Biological cells consume Nutrient, nutrients to sustain life. These nutrients are broken down to smaller molecules. Some of the molecules are used in the cells for various biological functions, and others are reassembled into more complex structures required for life. The breakdown and reassembly of nutrients is called metabolism. An individual cell contains thousands of different kinds of small molecules, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Catalysis
Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a process by an "enzyme", a biological molecule. Most enzymes are proteins, and most such processes are chemical reactions. Within the enzyme, generally catalysis occurs at a localized site, called the active site. Most enzymes are made predominantly of proteins, either a single protein chain or many such chains in a multi-subunit complex. Enzymes often also incorporate non-protein components, such as metal ions or specialized organic molecules known as cofactor (e.g. adenosine triphosphate). Many cofactors are vitamins, and their role as vitamins is directly linked to their use in the catalysis of biological process within metabolism. Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital since many but not all metabolically essential reactions have very low rates when uncatalysed. One driver of protein evolution is the optimization of such catalytic activities, although only the most crucial enzymes operate near catalytic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |