|
Late-life Mortality Deceleration
In gerontology, late-life mortality deceleration is the disputed theory that hazard rate increases at a decreasing rate in late life rather than increasing exponentially as in the Gompertz law. Late-life mortality deceleration is a well-established phenomenon in insects, which often spend much of their lives in a constant hazard rate region, but it is much more controversial in mammals. Rodent studies have found varying conclusions, with some finding short-term periods of mortality deceleration in mice, others not finding such. Baboon studies show no mortality deceleration. An analogous deceleration occurs in the failure rate of manufactured products; this analogy is elaborated in the reliability theory of aging and longevity. Late-life mortality deceleration was first proposed as occurring in human aging in (which also introduced the Gompertz law), and observed as occurring in humans in , and has since become one of the pillars of the biodemography of human longevity – see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age (journal)
''GeroScience'' (formerly ''Age''; ''Journal of the American Aging Association'') is a scientific journal focused on the biology of aging and on mechanistic studies using clinically relevant models of aging and chronic age-related diseases. The journal also publishes articles on health-related aspects of human aging, including biomarkers of aging, multisystem physiology of aging and pathophysiology of age-related diseases. Topics ''GeroScience'' covers topics like chronic low-grade inflammation, cellular senescence, macromolecular damage, oxidative-nitrative stress, maladaptation to cellular and molecular stresses, impaired stem cell function and regeneration, alterations in proteostasis, epigenetic dysregulation, impaired mitochondrial function and cellular metabolism; strategies to improve cardiovascular, neurocognitive, and musculoskeletal health-span; studies using a variety of experimental approaches, including in vivo studies and investigations using isolated tissue prep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baby Boom
A baby boom is a period marked by a significant increase of births. This demography, demographic phenomenon is usually an ascribed characteristic within the population of a specific nationality, nation or culture. Baby booms are caused by various fertility factor (demography), fertility factors. The Mid-20th century baby boom, best-known baby boom occurred in the mid-twentieth century, sometimes considered to have started in the aftermath of World War II, from the late 1940s to the early 1960s. People born during this period are often called baby boomers. Africa "According to the new UNICEF report, almost 2 billion babies will be born in Africa between 2015 and 2050 and the 2 main driving forces behind this surge in births and children are continued high fertility rates and rising numbers of women able to have children of their own." By 2050, Africa is predicted to account for about 55% of all births in the world, 40% of all children under the age of five, and 37% of all children ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Function
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common S-shaped curve ( sigmoid curve) with the equation f(x) = \frac where The logistic function has domain the real numbers, the limit as x \to -\infty is 0, and the limit as x \to +\infty is L. The exponential function with negated argument (e^ ) is used to define the standard logistic function, depicted at right, where L=1, k=1, x_0=0, which has the equation f(x) = \frac and is sometimes simply called the sigmoid. It is also sometimes called the expit, being the inverse function of the logit. The logistic function finds applications in a range of fields, including biology (especially ecology), biomathematics, chemistry, demography, economics, geoscience, mathematical psychology, probability, sociology, political science, linguistics, statistics, and artificial neural networks. There are various generalizations, depending on the field. History The logistic function was introduced in a series of three papers by Pier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Theory Of Aging
The reliability theory of aging is an attempt to apply the principles of reliability theory to create a mathematical model of senescence. The theory was published in Russian by Leonid A. Gavrilov and Natalia S. Gavrilova as ''Biologiia prodolzhitelʹnosti zhizni'' in 1986, and in English translation as ''The Biology of Life Span: A Quantitative Approach'' in 1991. One of the models suggested in the book is based on an analogy with the reliability theory. The underlying hypothesis is based on the previously suggested premise that humans are born in a highly defective state. This is then made worse by environmental and mutational damage; exceptionally high redundancy due to the extremely high number of low-reliable components (e.g.., cells) allows the organism to survive for a while. The theory suggests an explanation of two aging phenomena for higher organisms: the Gompertz law of exponential increase in mortality rates with age and the "late-life mortality plateau" (mortality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difference Quotient
In single-variable calculus, the difference quotient is usually the name for the expression : \frac which when taken to the Limit of a function, limit as ''h'' approaches 0 gives the derivative of the Function (mathematics), function ''f''. The name of the expression stems from the fact that it is the quotient of the Difference (mathematics), difference of values of the function by the difference of the corresponding values of its argument (the latter is (''x'' + ''h'') - ''x'' = ''h'' in this case). The difference quotient is a measure of the average rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of the function over an Interval (mathematics), interval (in this case, an interval of length ''h''). The limit of the difference quotient (i.e., the derivative) is thus the instantaneous rate of change. By a slight change in notation (and viewpoint), for an interval [''a'', ''b''], the difference quotient : \frac is called the mean (or average) value of the derivative of ''f'' over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
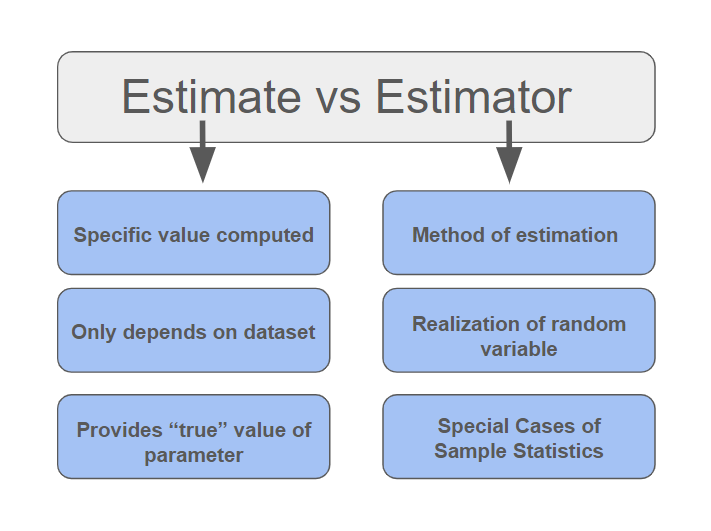
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacher Formula
Sacher is a surname. Origins can be traced back to Germany. Notable people with the surname include: *Franz Sacher, Austrian baker **Hotel Sacher, a five-star hotel in Vienna *Harry Sacher, British Zionist and lawyer *Lara Sacher, Australian actress *Paul Sacher, Swiss conductor, patron and impresario *Sarolta Zalatnay (born Charlotte Sacher, 1947), Hungarian singer See also *Leopold von Sacher-Masoch Leopold Ritter von Sacher-Masoch (; 27 January 1836 – 9 March 1895) was an Austrian nobleman, writer and journalist, who gained renown for his romantic stories of Galician life. The term ''masochism'' is derived from his name, invented by h ..., Austrian writer and journalist {{surname, Sacher German-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Master File
The Death Master File (DMF) is a computer database file made available by the United States Social Security Administration since 1980. It is known commercially as the Social Security Death Index (SSDI). The file contains information about persons who had Social Security numbers and whose deaths were reported to the Social Security Administration from 1962 to the present; or persons who died before 1962, but whose Social Security accounts were still active in 1962. , the file contained information on 111 million deaths. In 2011, some records were removed from the file. Overview The data includes: * Name (given name, surname), since 1990s the middle initial * Date of birth (year, month, day) * Date of death (year, month), since 2000 the day of month * Social Security number * Whether death has been verified or a death certificate has been observed. In 2011, the following information was removed: * Last ZIP code of the person while alive * ZIP code to which the lump sum death be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Decay
A quantity is subject to exponential decay if it decreases at a rate proportional to its current value. Symbolically, this process can be expressed by the following differential equation, where is the quantity and (lambda Lambda (; uppercase , lowercase ; , ''lám(b)da'') is the eleventh letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoen ...) is a positive rate called the exponential decay constant, disintegration constant, rate constant, or transformation constant: :\frac = -\lambda N(t). The solution to this equation (see #Solution_of_the_differential_equation, derivation below) is: :N(t) = N_0 e^, where is the quantity at time , is the initial quantity, that is, the quantity at time . Measuring rates of decay Mean lifetime If the decaying quantity, ''N''(''t''), is the number of discrete elements in a certain set (mathematics), se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerontology
Gerontology ( ) is the study of the social, culture, cultural, psychology, psychological, cognitive, and biology, biological aspects of aging. The word was coined by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov in 1903, from the Ancient Greek, Greek ('), meaning "old man", and ('), meaning "study of". The field is distinguished from geriatrics, which is the branch of medicine that specializes in the treatment of existing disease in older adults. Gerontologists include researchers and practitioners in the fields of biology, nursing, medicine, criminology, dentistry, social work, physical and occupational therapy, psychology, psychiatry, sociology, economics, political science, architecture, geography, pharmacy, public health, housing, and anthropology. The multidisciplinarity, multidisciplinary nature of gerontology means that there are a number of sub-fields which overlap with gerontology. There are policy issues, for example, involved in government planning and the operation of nursing homes, inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |