|
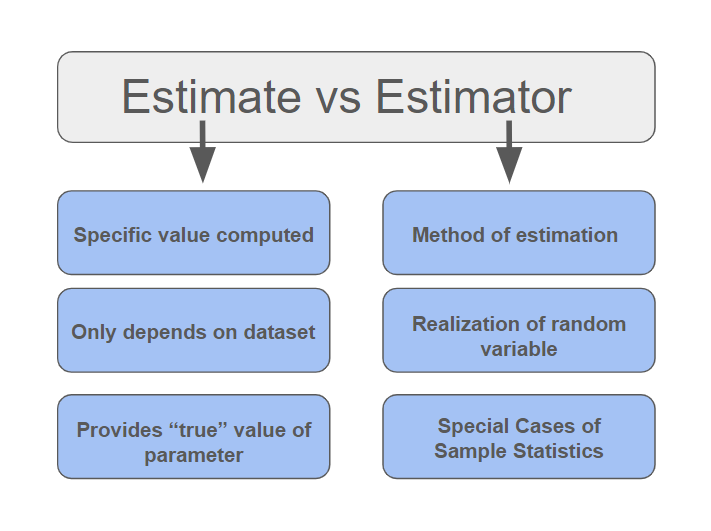
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Square Error
In statistics, the mean squared error (MSE) or mean squared deviation (MSD) of an estimator (of a procedure for estimating an unobserved quantity) measures the average of the squares of the errors—that is, the average squared difference between the estimated values and the true value. MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss. The fact that MSE is almost always strictly positive (and not zero) is because of randomness or because the estimator does not account for information that could produce a more accurate estimate. In machine learning, specifically empirical risk minimization, MSE may refer to the ''empirical'' risk (the average loss on an observed data set), as an estimate of the true MSE (the true risk: the average loss on the actual population distribution). The MSE is a measure of the quality of an estimator. As it is derived from the square of Euclidean distance, it is always a positive value that decreases as the error app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estimation Theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of Statistical parameter, parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their value affects the distribution of the measured data. An ''estimator'' attempts to approximate the unknown parameters using the measurements. In estimation theory, two approaches are generally considered: * The probabilistic approach (described in this article) assumes that the measured data is random with probability distribution dependent on the parameters of interest * The set estimation, set-membership approach assumes that the measured data vector belongs to a set which depends on the parameter vector. Examples For example, it is desired to estimate the proportion of a population of voters who will vote for a particular candidate. That proportion is the parameter sought; the estimate is based on a small random sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unbiasedness
In statistics, the bias of an estimator (or bias function) is the difference between this estimator's expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called ''unbiased''. In statistics, "bias" is an property of an estimator. Bias is a distinct concept from consistency: consistent estimators converge in probability to the true value of the parameter, but may be biased or unbiased (see bias versus consistency for more). All else being equal, an unbiased estimator is preferable to a biased estimator, although in practice, biased estimators (with generally small bias) are frequently used. When a biased estimator is used, bounds of the bias are calculated. A biased estimator may be used for various reasons: because an unbiased estimator does not exist without further assumptions about a population; because an estimator is difficult to compute (as in unbiased estimation of standard deviation); because a biased estima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Function
In mathematical optimization and decision theory, a loss function or cost function (sometimes also called an error function) is a function that maps an event or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "cost" associated with the event. An optimization problem seeks to minimize a loss function. An objective function is either a loss function or its opposite (in specific domains, variously called a reward function, a profit function, a utility function, a fitness function, etc.), in which case it is to be maximized. The loss function could include terms from several levels of the hierarchy. In statistics, typically a loss function is used for parameter estimation, and the event in question is some function of the difference between estimated and true values for an instance of data. The concept, as old as Pierre-Simon Laplace, Laplace, was reintroduced in statistics by Abraham Wald in the middle of the 20th century. In the context of economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consistent Estimator
In statistics, a consistent estimator or asymptotically consistent estimator is an estimator—a rule for computing estimates of a parameter ''θ''0—having the property that as the number of data points used increases indefinitely, the resulting sequence of estimates converges in probability to ''θ''0. This means that the distributions of the estimates become more and more concentrated near the true value of the parameter being estimated, so that the probability of the estimator being arbitrarily close to ''θ''0 converges to one. In practice one constructs an estimator as a function of an available sample of size ''n'', and then imagines being able to keep collecting data and expanding the sample ''ad infinitum''. In this way one would obtain a sequence of estimates indexed by ''n'', and consistency is a property of what occurs as the sample size “grows to infinity”. If the sequence of estimates can be mathematically shown to converge in probability to the true value '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Parameter
In statistics, as opposed to its general use in mathematics, a parameter is any quantity of a statistical population that summarizes or describes an aspect of the population, such as a mean or a standard deviation. If a population exactly follows a known and defined distribution, for example the normal distribution, then a small set of parameters can be measured which provide a comprehensive description of the population and can be considered to define a probability distribution for the purposes of extracting samples from this population. A "parameter" is to a population as a "statistic" is to a sample; that is to say, a parameter describes the true value calculated from the full population (such as the population mean), whereas a statistic is an estimated measurement of the parameter based on a sample (such as the sample mean, which is the mean of gathered data per sampling, called sample). Thus a "statistical parameter" can be more specifically referred to as a population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of Sample (statistics), sample data (and similar data from a larger Statistical population, population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, the Data generating process, data-generating process. When referring specifically to probability, probabilities, the corresponding term is probabilistic model. All Statistical hypothesis testing, statistical hypothesis tests and all Estimator, statistical estimators are derived via statistical models. More generally, statistical models are part of the foundation of statistical inference. A statistical model is usually specified as a mathematical relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables. As such, a statistical model is "a formal representation of a theory" (Herman J. Adèr, Herman Adèr quoting Kenneth A. Bollen, Kenneth Bollen). Introduction Informally, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Estimator
In statistics, point estimation involves the use of sample data to calculate a single value (known as a point estimate since it identifies a point in some parameter space) which is to serve as a "best guess" or "best estimate" of an unknown population parameter (for example, the population mean). More formally, it is the application of a point estimator to the data to obtain a point estimate. Point estimation can be contrasted with interval estimation: such interval estimates are typically either confidence intervals, in the case of frequentist inference, or credible intervals, in the case of Bayesian inference. More generally, a point estimator can be contrasted with a set estimator. Examples are given by confidence sets or credible sets. A point estimator can also be contrasted with a distribution estimator. Examples are given by confidence distributions, randomized estimators, and Bayesian posteriors. Properties of point estimates Biasedness “Bias” is defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a Mathematics, mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on randomness, random events. The term 'random variable' in its mathematical definition refers to neither randomness nor variability but instead is a mathematical function (mathematics), function in which * the Domain of a function, domain is the set of possible Outcome (probability), outcomes in a sample space (e.g. the set \ which are the possible upper sides of a flipped coin heads H or tails T as the result from tossing a coin); and * the Range of a function, range is a measurable space (e.g. corresponding to the domain above, the range might be the set \ if say heads H mapped to -1 and T mapped to 1). Typically, the range of a random variable is a subset of the Real number, real numbers. Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parameter Space
The parameter space is the space of all possible parameter values that define a particular mathematical model. It is also sometimes called weight space, and is often a subset of finite-dimensional Euclidean space. In statistics, parameter spaces are particularly useful for describing parametric families of probability distributions. They also form the background for parameter estimation. In the case of extremum estimators for parametric models, a certain objective function is maximized or minimized over the parameter space. Theorems of existence and consistency of such estimators require some assumptions about the topology of the parameter space. For instance, compactness of the parameter space, together with continuity of the objective function, suffices for the existence of an extremum estimator. Sometimes, parameters are analyzed to view how they affect their statistical model. In that context, they can be viewed as inputs of a function, in which case the technical term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |