|
LAMB1
Laminin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB1'' gene. Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide variety of biological processes including cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, signaling, neurite outgrowth and metastasis. Laminins are composed of 3 non identical chains: laminin alpha, beta and gamma (formerly A, B1, and B2, respectively) and they form a cruciform structure consisting of 3 short arms, each formed by a different chain, and a long arm composed of all 3 chains. Each laminin chain is a multidomain protein encoded by a distinct gene. Several isoforms of each chain have been described. Different alpha, beta and gamma chain isomers combine to give rise to different heterotrimeric laminin isoforms, which are designated by Arabic numerals in the order of their discovery, i.e. alpha1beta1gamma1 heterotrimer is laminin 1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
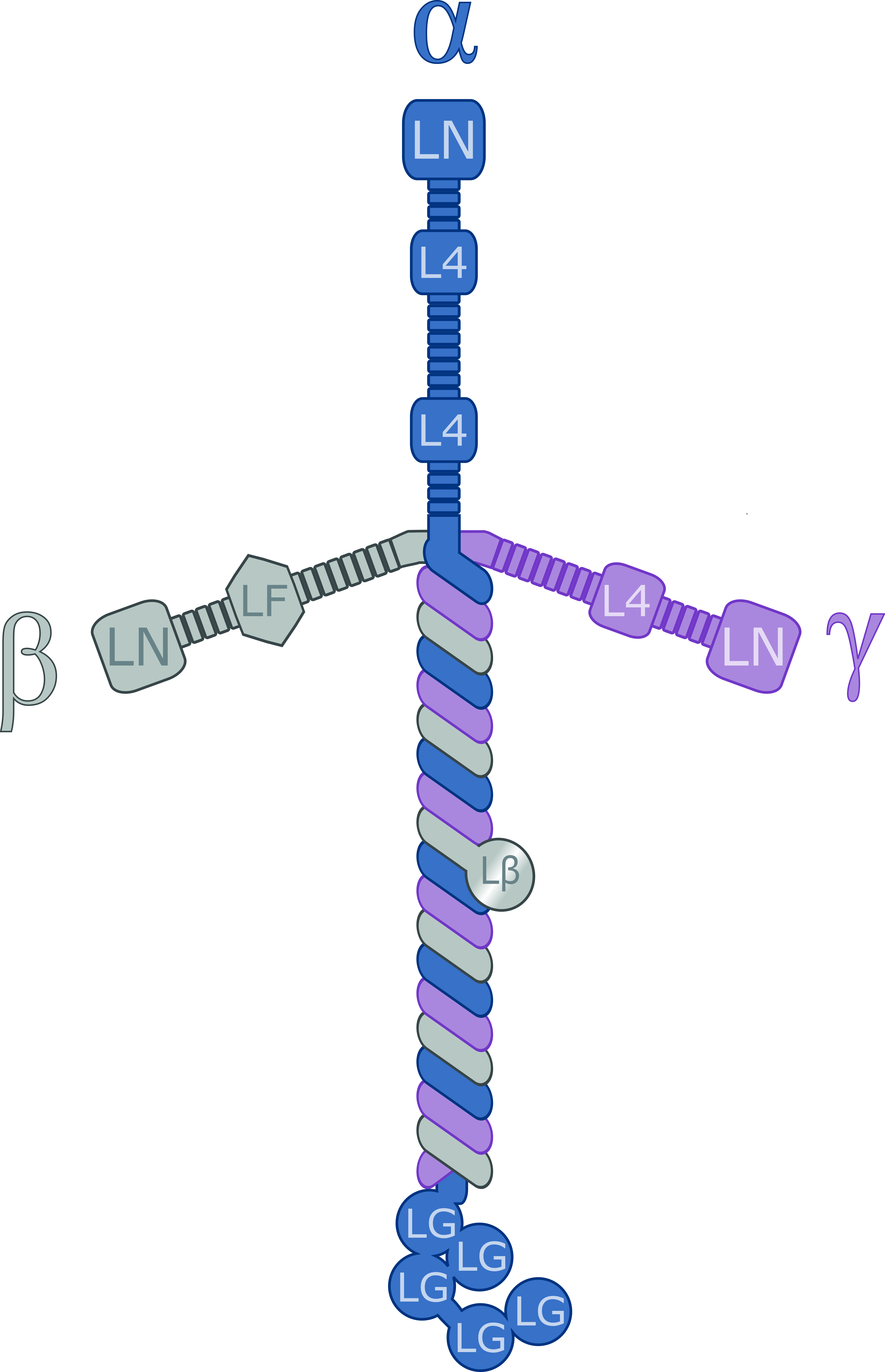
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major constituents of the basement membrane, namely the basal lamina (the protein network foundation for most cells and organs). Laminins are vital to biological activity, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa) and possess three different chains (α, β, and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition, e.g. laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect, composing a cruciform structure that is able to bind to other molecules of the extracellular matrix and cell membrane. The three short arms have an affinity for binding to other laminin molecules, conducing sheet formation. The long ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Ribosome Entry Site
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. Initiation of eukaryotic translation nearly always occurs at and is dependent on the 5' cap of mRNA molecules, where the translation initiation complex forms and ribosomes engage the mRNA. IRES elements, however, allow ribosomes to engage the mRNA and begin translation independently of the 5' cap. History IRES sequences were first discovered in 1988 in the poliovirus (PV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) RNA genomes in the laboratories of Nahum Sonenberg and Eckard Wimmer, respectively. They are described as distinct regions of RNA molecules that are able to recruit the eukaryotic ribosome to the mRNA. This process is also known as cap-independent translation. It has been shown that IRES elements have a distinct secondary or even tertiary structure, but similar structural features at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |