|
Internal Ribosome Entry Site
An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. Initiation of eukaryotic translation nearly always occurs at and is dependent on the 5' cap of mRNA molecules, where the translation initiation complex forms and ribosomes engage the mRNA. IRES elements, however, allow ribosomes to engage the mRNA and begin translation independently of the 5' cap. History IRES sequences were first discovered in 1988 in the poliovirus (PV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) RNA genomes in the laboratories of Nahum Sonenberg and Eckard Wimmer, respectively. They are described as distinct regions of RNA molecules that are able to recruit the eukaryotic ribosome to the mRNA. This process is also known as cap-independent translation. It has been shown that IRES elements have a distinct secondary or even tertiary structure, but similar structural features at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (genetics)
In biology, translation is the process in living cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in the addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The polypeptide can also start folding during protein synthesis. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survival
Survival or survivorship, the act of surviving, is the propensity of something to continue existing, particularly when this is done despite conditions that might kill or destroy it. The concept can be applied to humans and other living things (or, hypothetically, any sentient being), to a physical object, and to abstract things such as beliefs or ideas. Living things generally have a self-preservation instinct to survive, while objects intended for use in harsh conditions are designed for survivability. Meaning The word, "survival", derives from the Late Latin '' supervivere'', literally meaning "to outlive". Most commonly, "the term 'survival' means physical survival — that is, a struggle to avoid physical extermination". For example, Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection incorporates the concept of the survival of the fittest in the struggle for existence. Darwin defines the biological concept of fitness as reproductive success, so in Darwinian terms the phrase i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF5
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EIF5'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... EIF5 is a GTPase-activating protein. References External links Cap-dependent translation initiationfrom Nature Reviews Microbiology. A good image and overview of the function of initiation factors PDBe-KBprovides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 (EIF5) Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-14-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF3
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3) is a multiprotein complex that functions during the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation. It is essential for most forms of Eukaryotic translation#Cap-dependent initiation, cap-dependent and Eukaryotic translation#cap-independent, cap-independent translation initiation. In humans, eIF3 consists of 13 nonidentical subunits (eIF3a-m) with a combined molecular weight of ~800 kDa, making it the largest Eukaryotic initiation factor, translation initiation factor. The eIF3 complex is broadly conserved across eukaryotes, but the conservation of individual subunits varies across organisms. For instance, while most mammalian eIF3 complexes are composed of 13 subunits, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, budding yeast's eIF3 has only six subunits (eIF3a, b, c, g, i, j). Function eIF3 stimulates nearly all steps of translation initiation. eIF3 also appears to participate in other phases of translation, such as recycling, where it promotes the splitting of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF2
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (eIF2) is a eukaryotic initiation factor. It is required for most forms of eukaryotic translation initiation. eIF2 mediates the binding of tRNAiMet to the ribosome in a GTP-dependent manner. eIF2 is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha (also called subunit 1, EIF2S1), a beta (subunit 2, EIF2S2), and a gamma (subunit 3, EIF2S3) subunit. Once the initiation phase has completed, eIF2 is released from the ribosome bound to GDP as an inactive binary complex. To participate in another round of translation initiation, this GDP must be exchanged for GTP. Function eIF2 is an essential factor for protein synthesis that forms a ternary complex (TC) with GTP and the initiator Met- tRNAiMet. After its formation, the TC binds the 40S ribosomal subunit to form the 43S preinitiation complex (43S PIC). 43S PIC assembly is believed to be stimulated by the initiation factors eIF1, eIF1A, and the eIF3 complex according to ''in vitro'' experiments. The 43 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (genetics)
In biology, translation is the process in living cells in which proteins are produced using RNA molecules as templates. The generated protein is a sequence of amino acids. This sequence is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA. The nucleotides are considered three at a time. Each such triple results in the addition of one specific amino acid to the protein being generated. The matching from nucleotide triple to amino acid is called the genetic code. The translation is performed by a large complex of functional RNA and proteins called ribosomes. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The polypeptide can also start folding during protein synthesis. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
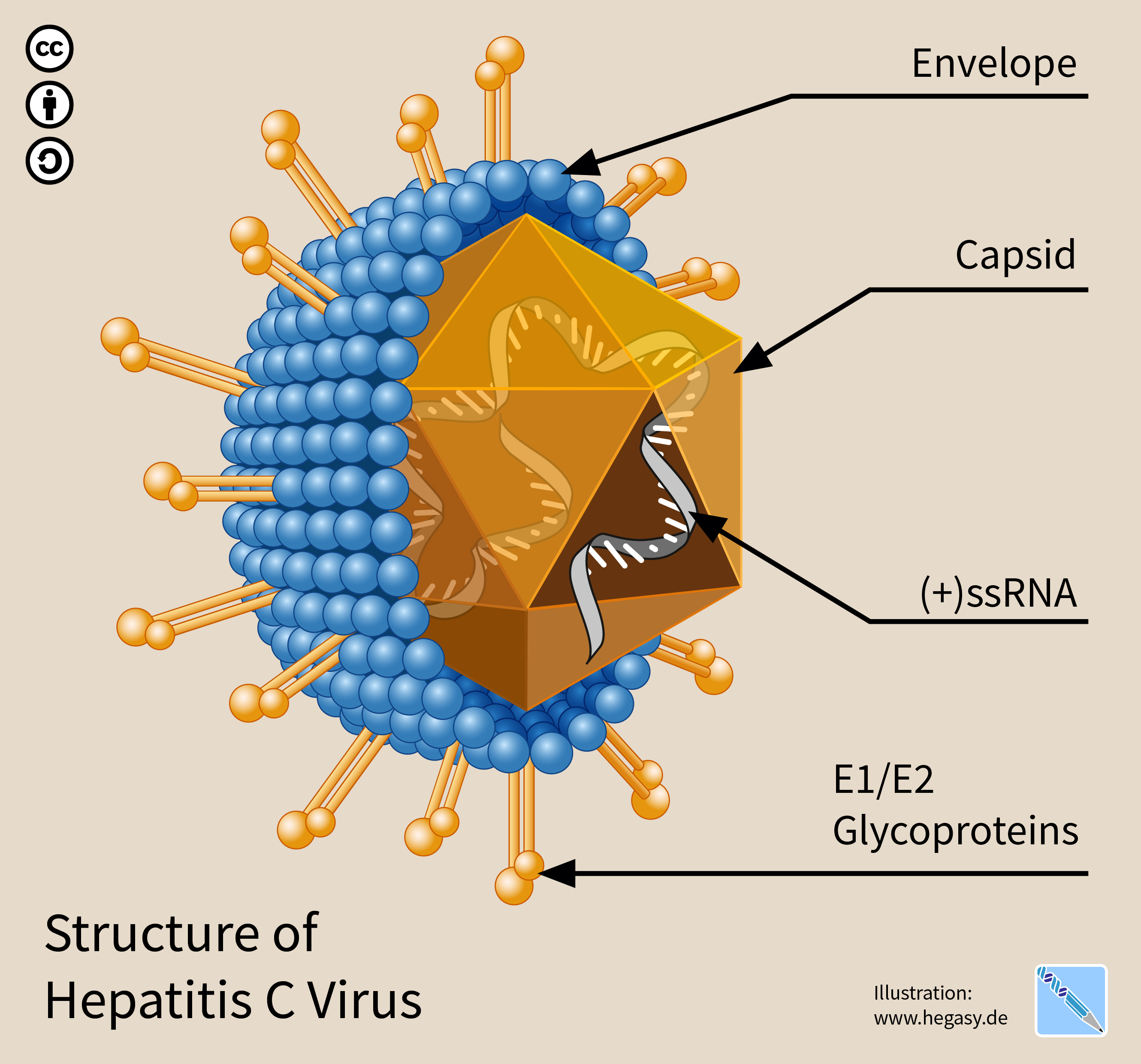
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death
Programmed cell death (PCD) sometimes referred to as cell, or cellular suicide is the death of a cell (biology), cell as a result of events inside of a cell, such as apoptosis or autophagy. PCD is carried out in a biological process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's biological life cycle, lifecycle. For example, the Limb development, differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits are separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and animal tissue development. Apoptosis and autophagy are both forms of programmed cell death. Necrosis is the death of a cell caused by external factors such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. Necrosis was long seen as a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury, but in the 2000s, a form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, was recognized as an alternative f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Mitosis is preceded by the S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is followed by telophase and cytokinesis, which divide the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane of one cell into two new cell (biology), cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic phase (M phase) of a cell cycle—the cell division, division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eukaryotes, polyadenylation is part of the process that produces mature mRNA for translation. In many bacteria, the poly(A) tail promotes degradation of the mRNA. It, therefore, forms part of the larger process of gene expression. The process of polyadenylation begins as the transcription of a gene terminates. The 3′-most segment of the newly made pre-mRNA is first cleaved off by a set of proteins; these proteins then synthesize the poly(A) tail at the RNA's 3′ end. In some genes these proteins add a poly(A) tail at one of several possible sites. Therefore, polyadenylation can produce more than one transcript from a single gene (alternative polyadenylation), similar to alternative splicing. The poly(A) tail is important for the nuclea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic Small Ribosomal Subunit (40S)
The eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit (40S) is the smaller subunit of the 80S, eukaryotic 80S ribosomes, with the other major component being the eukaryotic large ribosomal subunit (60S), large ribosomal subunit (60S). The "40S" and "60S" names originate from the convention that ribosomal particles are denoted according to their sedimentation coefficients in Svedberg, Svedberg units. It is structurally and functionally related to the 30S, 30S subunit of 70S, 70S prokaryotic ribosomes. However, the 40S subunit is much larger than the prokaryotic 30S subunit and contains many additional protein segments, as well as rRNA expansion segments. Function The 40S subunit contains the decoding center which monitors the complementarity of tRNA and mRNA in protein translation. It is the largest component of several translation initiation complexes, including the 43S and 48S preinitiation complexes (PICs), being bound by several eukaryotic initiation factors, including eIF1, eIF1AX, eIF1A, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4F
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF4F) is a heterotrimeric protein complex that binds the 5' cap of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) to promote eukaryotic translation initiation. The eIF4F complex is composed of three non-identical subunits: the DEAD-box RNA helicase eIF4A, the cap-binding protein eIF4E, and the large "scaffold" protein eIF4G. The mammalian eIF4F complex was first described in 1983, and has been a major area of study into the molecular mechanisms of cap-dependent translation initiation ever since. Function eIF4F is important for recruiting the small ribosomal subunit (40S) to the 5' cap of mRNAs during cap-dependent translation initiation. Components of the complex are also involved in cap-independent translation initiation; for instance, certain viral proteases cleave eIF4G to remove the eIF4E-binding region, thus inhibiting cap-dependent translation. Structure Structures of eIF4F components have been solved individually and as partial complexes by a variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |