|
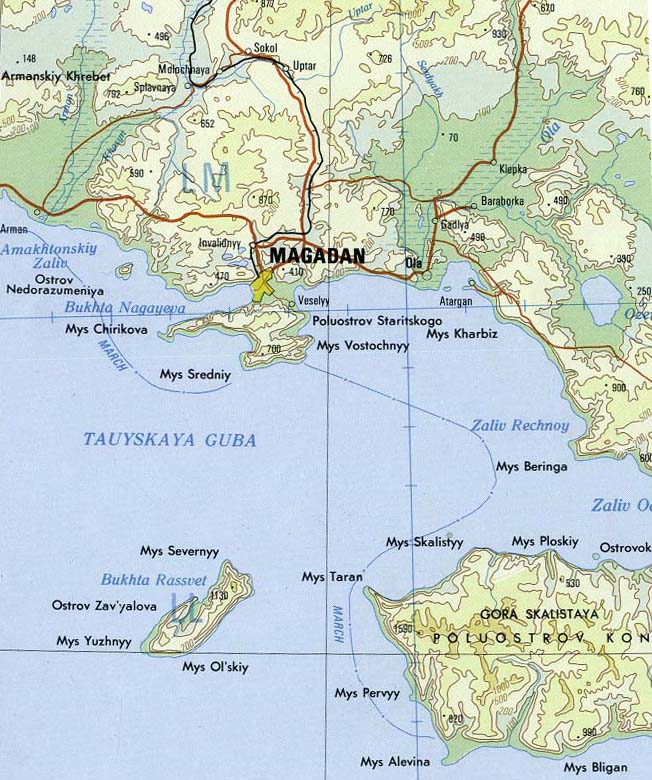
Koni Peninsula
The Koni Peninsula projects into the Sea of Okhotsk in Magadan Oblast, in the Russian Far East, and has an area of 103,434 hectares. Its north-western shores are on the Taui Bay. Its north-eastern shores are on the Odyan Bay; the latter one resolves into the ("Pusa Bay"). The Peninsula's south-eastern shore is on the . From the Zabiyaka Bay northwards the makes a notch into the isthmus between the peninsula and the mainland, into the valley of the Siglan River. The Olsky District, Ola sector of the Magadan Nature Reserve is situated on the peninsula, in its western part. Its eastern border runs from (Плоский, "Flat") in the north approximately south-eastwards along several watersheds down to the mouth of the Antara River (about 9 kilometers east of (Блиган).) The shores of the reserve are surrounded by the buffer zone, a 2-kilometer wide strip of the sea from Cape Ploskiy to two nameless streams 9km to the east of the Antara River. Like in the Reserve, any human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magadan 1978
Magadan ( rus, Магадан, p=məɡɐˈdan) is a port town and the administrative centre of Magadan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the isthmus of the Staritsky Peninsula by the Nagaev Bay; it serves as a gateway to the Kolyma region. Magadan, founded in 1929, was a major transit centre for political prisoners during the Stalin era and the administrative centre of the Dalstroy forced-labor gold-mining operation. The town later served as a port for exporting gold and other metals. Magadan plays a significant role in transportation with the Port of Magadan and Sokol Airport. The local economy relies on gold mining and fisheries, although gold production has declined. The town has various cultural institutions and religious establishments, such as the Orthodox and the Roman Catholic Church of the Nativity. The Mask of Sorrow memorial commemorates Stalin's victims. Magadan experiences a subarctic climate with prolonged and cold winters, causing the soil to remain perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of The Sea Of Okhotsk
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Ram
A ram on the bow of ''Olympias'', a modern reconstruction of an ancient Athenian trireme A naval ram is a weapon fitted to varied types of ships, dating back to antiquity. The weapon comprised an underwater prolongation of the bow of the ship to form an armoured beak, usually between in length. This would be driven into the hull of an enemy ship to puncture, sink or disable it. Antiquity It was possibly developed in late Bronze Age Egypt, but it only became widely used in later Iron Age Mediterranean galleys. The ram was a naval weapon in the Greek/ Roman antiquity and was used in such naval battles as Salamis and Actium. Naval warfare in the Mediterranean rarely used sails, and the use of rams specifically required oarsmen rather than sails in order to maneuver with accuracy and speed, and particularly to reverse the movement of a ramming ship to disentangle it from its sinking victim, lest it be pulled down when its victim sank. The Athenians were especially known fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalstroy
Dalstroy (, ), also known as Far North Construction Trust, was an organization set up in 1931 in order to manage road construction and the mining of gold in the Russian Far East, including the Magadan Region, Chukotka, parts of Yakutia and parts of present-day Kamchatka Krai. Initially it was established as ''General Directorate of Construction in the Far North'' (Главное Управление строительства Дальнего Севера) under the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Soviet Union. In 1938 it was placed under the NKVD and in 1945 it was reorganized and renamed. After the 1952 reorganization it was known as ''Main Directorate of Camps and Construction of the Far North''. Dalstroy oversaw the development and mining of the area. Over the years, Dalstroy created some 80 Gulag camps across the Kolyma region. As a result of a number of decisions, the total area covered by Dalstroy grew to three million square kilometers by 1951. The town of Magadan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
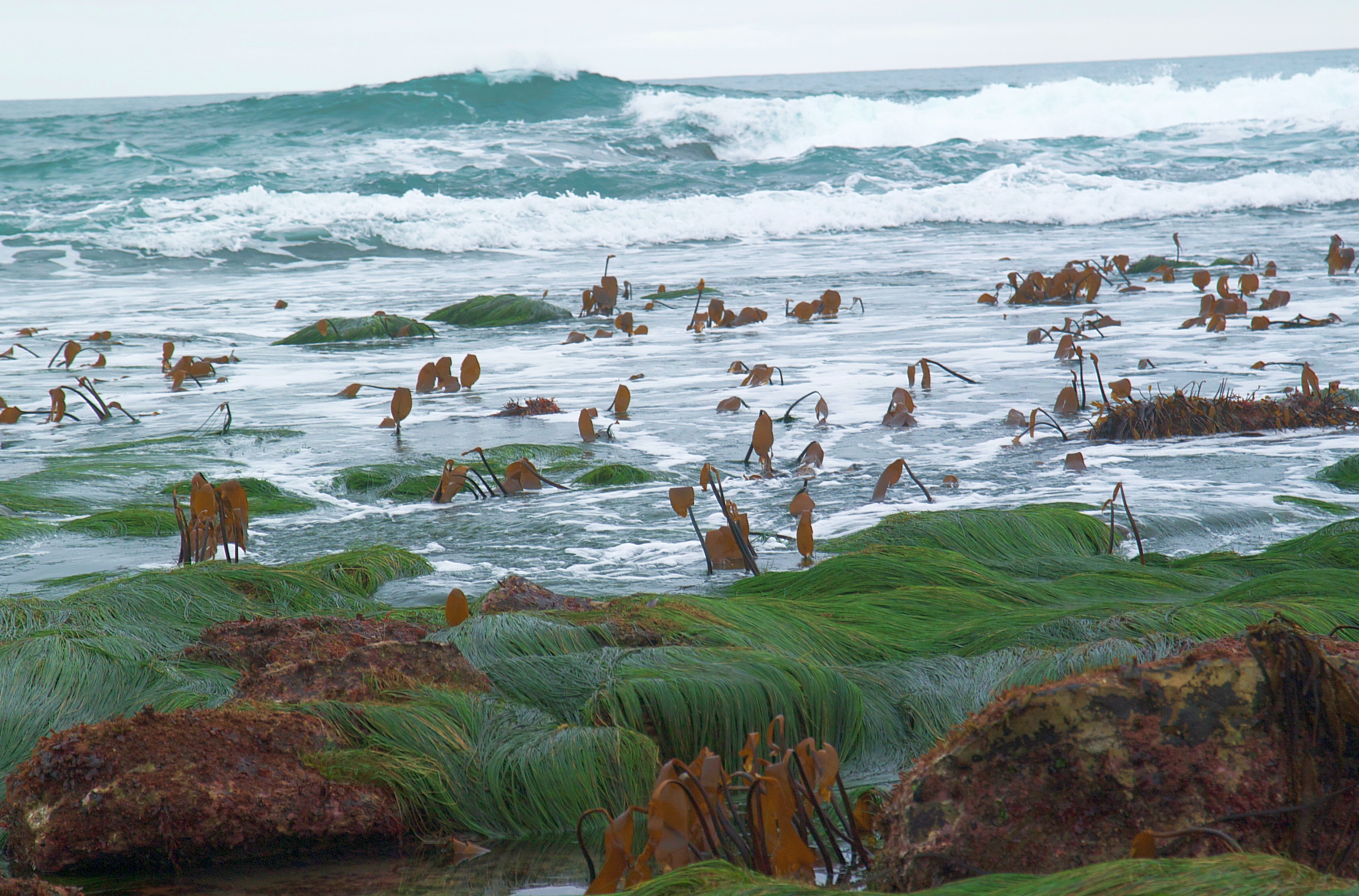
Laminaria
''Laminaria'' is a genus of brown algae, brown seaweed in the order Kelp, Laminariales (kelp), comprising 31 species native to the north Atlantic and northern Pacific Oceans. This economically important genus is characterized by long, leathery Lamina (algae), laminae and relatively large size. Some species are called Devil's apron, due to their shape, or sea colander, due to the perforations present on the Lamina (algae), lamina. Others are referred to as ''tangle''. ''Laminaria'' form a habitat for many fish and invertebrates. The life cycle of ''Laminaria'' has wikt:heteromorphic, heteromorphic alternation of generations which differs from ''Fucus''. At meiosis the male and female zoospores are produced separately, then germinate into male and female gametophytes. The female egg matures in the oogonium until the male sperm fertilizes it. Life-Cycle: The most apparent form of ''Laminaria'' is its sporophyte phase, a structure composed of the holdfast (biology), holdfast, the Sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magadan Nature Reserve
Magadan Nature Reserve () (also Magadansky) is a Russian zapovednik (strict nature reserve) located in four different sectors across the Magadan region of the Russian Far East, including the northern shore of the Sea of Okhotsk. All sites are far away from each other, have different climates, topography, flora and fauna, and no settlements or transportation routes. On the streams of the territory are some of the largest undisturbed spawning sites of the chum and coho salmon. One area, the Yam Islands, is home to colonies of sea birds, with a total of up to 6 million individuals. These include Auklets-crumbs, guillemot, spectacled guillemots, lund, and the horned puffin. The reserve is situated in the Olsky District of Magadan Oblast. Recently, the reserve has experimented with very limited cruise ship visits (under 200 passengers) to one of the islands, and plans are being studied for ways to increase educational eco-tourism in the highly inaccessible area. Topography The la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olsky District
Olsky District () is an administrativeLaw #1292-OZ and municipalLaw #511-OZ district (raion), one of the eight in Magadan Oblast, Russia. It is located in the south of the oblast, consists of two unconnected mainland parts separated by the territories of Khasynsky District and the town of oblast significance of Magadan, and also has jurisdiction over several islands. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the urban locality (an urban-type settlement) of Ola. As of the 2010 Census, the total population of the district was 10,496, with the population of Ola accounting for 59.2% of that number. Geography The Ola, the Arman (with the Khasyn) and the Yama cross the district from north to south and the Buyunda has its sources in the district. The Olsky Plateau and the Maymandzhin Range are located in the district.Google Earth Google Earth is a web mapping, web and computer program created by Google that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isthmus
An isthmus (; : isthmuses or isthmi) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus, a narrow stretch of sea between two landmasses that connects two larger bodies of water. Isthmus vs land bridge vs peninsula ''Isthmus'' and ''land bridge'' are related terms, with isthmus having a broader meaning. A land bridge is an isthmus connecting Earth's major land masses. The term ''land bridge'' is usually used in biogeology to describe land connections that used to exist between continents at various times and were important for the migration of people and various species of animals and plants, e.g. Beringia and Doggerland. An isthmus is a land connection between two bigger landmasses, while a peninsula is rather a land protrusion that is connected to a bigger landmass on one side only and surrounded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton In The Sea Of Okhotsk (9035216726) (cropped)
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pusa
''Pusa'' is a genus of the earless seals, within the family Phocidae. The three species of this genus were split from the genus '' Phoca'', and some sources still give ''Phoca'' as an acceptable synonym for ''Pusa''. The three species in this genus are found in Arctic and subarctic regions, as well as around the Caspian Sea. This includes these countries and regions: Russia, Finland, Scandinavia, Britain, Greenland, Canada, the United States, Iran, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, and Japan. Due to changing local environmental conditions, the ringed seals found in the Canadian region has varied patterns of growth. The northern Canadian ringed seals grow slowly to a larger size, while the southern seals grow quickly to a smaller size. Only the Caspian seal species of ''Pusa'' is endangered, while two subspecies of the ringed seal are vulnerable and endangered, Ladoga seal and Saimaa ringed seal The Saimaa ringed seal (''Pusa hispida saimensis'', Finnish: ''saimaannorppa'') is a sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odyan Bay
Odyan Bay (Russian: Залив Одян, trans.: ''Zaliv Odyan'') is a small bay on the north coast of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is in the eastern corner of Taui Bay and washes the Koni Peninsula on the south. The bay is entered between Cape Beringa to the northeast and Cape Skalisty to the southwest. It is 19.3 km (about 12 mi) wide. The high entrance points of the bay merge to form a low, sandy shore at its head. Sea ice Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less density, dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans. Much of the world' ... remains in the bay longer than in other parts of Taui Bay. It is sheltered from all but west winds. Umara Island lies just off its south shore.National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. (2014). ''Sailing Directions (Enroute): East Coast of Russia''. U.S. Government, Springfield, Virginia. References Bays of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |