|
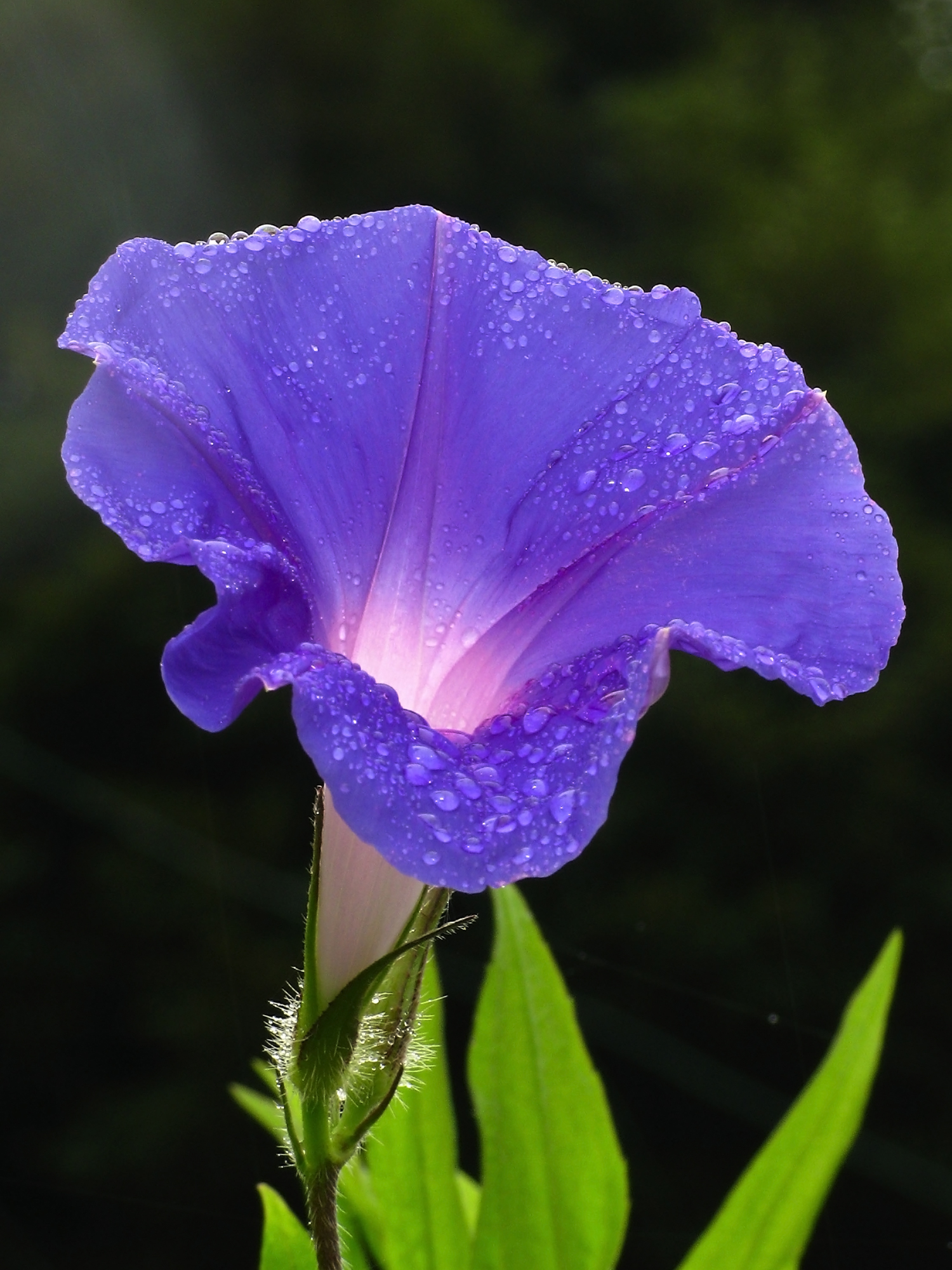
Ipomoea Purpurea
''Ipomoea purpurea'', the common morning-glory, tall morning-glory, or purple morning glory, is a species in the genus ''Ipomoea'', native to Mexico and Central America. Description Like all morning glories, the plant entwines itself around structures, growing to a height of tall. The leaves are heart-shaped and the stems are covered with brown hairs. The flowers are trumpet-shaped, predominantly blue to purple or white, and in diameter. Distribution and habitat The plant is predisposed to moist and rich soil, but can be found growing in a wide array of soil types.Richard H. Uva, Joseph C. Neal and Joseph M. Ditomaso, ''Weeds of The Northeast'', (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1997), Pp. 214-217. It is naturalized throughout warm temperate and subtropical regions of the world. Although it is often considered a noxious weed, ''I. purpurea'' is also grown for its attractive purple and white flowers, and has many cultivars. Common cultivars include ''I. purpurea'' 'Crimson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanidin
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin (glycoside version called anthocyanin#Structure, anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, Crataegus, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator. List of cyanidin derivatives * Antirrhinin (cyanidin-3-rutinoside or 3-C-R), found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3-xylosylrutinoside, found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3,4′-di-''O''-β-glucopyranoside, found in red onion * Cyanidin-4′-''O''-β-glucoside, found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicinal Plants
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including Plant defense against herbivory, defense and protection against insects, fungi, Plant disease resistance, diseases, against parasites and herbivorous mammals. The earliest historical records of herbs are found from the Sumerian civilization, where hundreds of medicinal plants including opium are listed on clay tablets, . The Ebers Papyrus from ancient Egypt, , describes over 850 plant medicines. The Greek physician Pedanius Dioscorides, Dioscorides, who worked in the Roman army, documented over 1000 recipes for medicines using over 600 medicinal plants in , ; this formed the basis of pharmacopoeias for some 1500 years. Drug research sometimes makes use of ethnobotany to search for pharmacologically active substances, and this approach has yielded hundreds of use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden Plants Of Central America
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate both natural and artificial materials. Gardens often have design features including statuary, follies, pergolas, trellises, stumperies, dry creek beds, and water features such as fountains, ponds (with or without fish), waterfalls or creeks. Some gardens are for ornamental purposes only, while others also produce food crops, sometimes in separate areas, or sometimes intermixed with the ornamental plants. Food-producing gardens are distinguished from farms by their smaller scale, more labor-intensive methods, and their purpose (enjoyment of a pastime or self-sustenance rather than producing for sale, as in a market garden). Flower gardens combine plants of different heights, colors, textures, and fragrances to create interest and delight the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundaries with the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Caribbean Sea to the southeast, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi), and is the thirteenth-largest country in the world by land area. With a population exceeding 130 million, Mexico is the tenth-most populous country in the world and is home to the largest number of native Spanish speakers. Mexico City is the capital and largest city, which ranks among the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. Human presence in Mexico dates back to at least 8,000 BC. Mesoamerica, considered a cradle of civilization, was home to numerous advanced societies, including the Olmecs, Maya, Zapotecs, Teotihuacan civilization, and Purépecha. Spanish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Central America
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring ( indigenous) native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora as in the terms ''gut flora'' or ''skin flora'' for purposes of specificity. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morning Glory
Morning glory (also written as morning-glory) is the common name for over 1,000 species of flowering plants in the family Convolvulaceae, whose taxonomy and systematics remain in flux. These species are distributed across numerous genus, genera, including: * ''Argyreia'' * ''Astripomoea'' * ''Calystegia'' * ''Convolvulus'' * ''Ipomoea'' (the largest genus) * ''Lepistemon'' * ''Merremia'' * ''Operculina'' * ''Rivea'' * ''Stictocardia'' ''Ipomoea tricolor'', commonly known simply as "morning glory", is the archetypical species for the group and is renowned for its many beautiful varieties, such as 'Heavenly Blue', 'Flying Saucers', and 'Pearly Gates'. As the name suggests, most morning glory flowers open early in the day and begin to fade by late morning, as the Corolla (botany), corolla starts to curl inward. They thrive in full sun and prefer mesic habitat, mesic soils. While many species are known for their diurnal blooming pattern, some, such as ''Ipomoea muricata'', ''Ipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loganville, Georgia
Loganville is a city in Walton and Gwinnett counties, Georgia, United States. The population was 16,516 as of 2023. Loganville is located about east of Atlanta and is part of the Atlanta metropolitan area. History An early variant name was "Buncombe". It was then renamed after James Harvie Logan, an early settler. The Georgia General Assembly incorporated Loganville as a town in 1887. Geography Loganville is in western Walton County, with the city limits extending west into southeastern Gwinnett County. U.S. Route 78 (Atlanta Highway) passes through the center of town, leading east to Monroe, the Walton County seat, and west to downtown Atlanta. Georgia State Route 20 leads northwest from Loganville to Lawrenceville, the Gwinnett County seat, and southwest to Conyers. Georgia State Route 81 leads northeast to Winder and south to Covington. According to the United States Census Bureau, Loganville has a total area of , of which is land and , or 0.60%, is water. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmercury
Methylmercury is an organometallic cation with the formula . It is the simplest organomercury compound. Methylmercury is extremely toxic, and its derivatives are the major source of organic mercury for humans. It is a bioaccumulative environmental toxicant with a 50-day half-life. Methylmercury (derived biologically from dimethylmercury) is the causative agent of the infamous Minamata disease. Methylmercury is designated as a "priority hazardous substance" according to the Directive on Environmental Quality Standards (Directive 2013/39/EU). Structure and chemistry "Methylmercury" is a shorthand for the hypothetical "methylmercury cation", sometimes written ''methylmercury(1+) cation'' or ''methylmercury(II) cation''. This functional group is composed of a methyl group Chemical bond, bonded to an atom of Mercury (element), mercury. Its chemical formula is (sometimes written as ). The Methylmercury compound has an overall charge of +1, with Hg in the +2 oxidation state. Methylmer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelargonidin
Pelargonidin is an anthocyanidin, a type of plant pigment producing a characteristic orange color used in food and industrial dyes. Natural occurrences Presence in flowers Pelargonidin can be found in red geraniums (Geraniaceae). It is the predominant pigment causing the red coloration in the spathes of ''Philodendron'' (Araceae). The orange-coloured flowers of blue pimpernel (''Anagallis monelli'', Myrsinaceae) have a higher concentration of pelargonidin pigment. Red and Pink Roses (Rosa) obtain their color from this phytochemical. Presence in food Pelargonidin can be found in berries such as ripe Raspberry, raspberries and Strawberry, strawberries, as well as Blueberry, blueberries, Blackberry, blackberries, Cranberry, cranberries but also in saskatoon berries and chokeberries. It is also found in plums and pomegranates. Pelargonidin gives red radish, radishes their color. It is present in large amounts in kidney beans. Glycosides In many plant systems, Pelargonidin c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytochemistry (journal)
''Phytochemistry'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering pure and applied plant chemistry, plant biochemistry and molecular biology. It is published by Elsevier and is an official publication for the Phytochemical Society of Europe, the Phytochemical Society of North America, and the Phytochemical Society of Asia. A sister journal ''Phytochemistry Letters'' is published since 2008. Abstracting and indexing ''Phytochemistry'' is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 4.072. References External links *{{Official website, http://www.journals.elsevier.com/phytochemistry/ Biochemistry journals Botany journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1961 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergine
Ergine, also known as lysergic acid amide (LSA or LAA) as well as LA-111, is a psychoactive compound of the ergoline and lysergamide families related to lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ergine is an ergoline alkaloid found in fungi such as '' Claviceps paspali'' (ergot) and '' Periglandula'' species such as '' Periglandula clandestina'', which are permanently connected with many morning glory vines. Ergine induces relatively mild psychedelic effects as well as pronounced sedative effects. The most common sources of ergine for use as a drug are the seeds of morning glory species including ''Ipomoea tricolor'' (tlitliltzin), '' Ipomoea corymbosa'' (ololiuhqui), and '' Argyreia nervosa'' (Hawaiian baby woodrose). Morning glory seeds have a history of entheogenic use in Mesoamerica dating back at least hundreds of years. They have also since been used by many Westerners. In addition to ergine, morning glory seeds contain other ergolines such as lysergic acid hydroxyethylamid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |