|
Internal Coordinate Mechanics
Internal Coordinate Mechanics (ICM) is a software program and algorithm to predict low-energy conformations of molecules by sampling the space of internal coordinates (bond lengths, bond angles and dihedral angles) defining molecular geometry. In ICM each molecule is constructed as a tree from an entry atom where each next atom is built iteratively from the preceding three atoms via three internal variables. The rings kept rigid or imposed via additional restraints. ICM is used for modelling peptides and interactions with substrates and coenzymes. Software ICM also is a programming environment for various tasks in computational chemistry and computational structural biology, sequence analysis and rational drug design. The original goal was to develop algorithms for energy optimization of several biopolymers with respect to an arbitrary subset of internal coordinates such as bond lengths, bond angles torsion angles and phase angles. The efficient and general global optimization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Length
In molecular geometry, bond length or bond distance is defined as the average distance between Atomic nucleus, nuclei of two chemical bond, bonded atoms in a molecule. It is a Transferability (chemistry), transferable property of a bond between atoms of fixed types, relatively independent of the rest of the molecule. Explanation Bond length is related to bond order: when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond is shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy: all other factors being equal, a stronger bond will be shorter. In a bond between two identical atoms, half the bond distance is equal to the covalent radius. Bond lengths are measured in the solid phase by means of X-ray diffraction, or approximated in the gas phase by microwave spectroscopy. A bond between a given pair of atoms may vary between different molecules. For example, the carbon to hydrogen bonds in methane are different from those in methyl chlori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom. Molecular geometry influences several properties of a substance including its reactivity, polarity, phase of matter, color, magnetism and biological activity. The angles between bonds that an atom forms depend only weakly on the rest of a molecule, i.e. they can be understood as approximately local and hence transferable properties. Determination The molecular geometry can be determined by various spectroscopic methods and diffraction methods. IR, microwave and Raman spectroscopy can give information about the molecule geometry from the details of the vibrational and rotational absorbance detected by these techniques. X-ray crystallography, neutron diffraction and electron diffraction can g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. A human hair is about a million carbon atoms wide. Atoms are smaller than the shortest wavelength of visible light, which means humans cannot see atoms with conventional microscopes. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is not possible due to quantum mechanics, quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. Protons hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (biochemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or Metal ions in aqueous solution, metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalysis, catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in Biochemistry, biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from Ligand (biochemistry), ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be classified into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called Enzyme#Coenzymes, coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a "prosthetic group", which consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulations to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry incorporated into computer programs to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. The importance of this subject stems from the fact that, with the exception of some relatively recent findings related to the hydrogen molecular ion (dihydrogen cation), achieving an accurate quantum mechanical depiction of chemical systems analytically, or in a closed form, is not feasible. The complexity inherent in the many-body problem exacerbates the challenge of providing detailed descriptions of quantum mechanical systems. While computational results normally complement information obtained by chemical experiments, it can occasionally predict unobserved chemical phenomena. Overview Computational chemistry differs from theoretical chemistry, which involves a mathematical description of chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Biology
Structural biology deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every level of organization. Early structural biologists throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries were primarily only able to study structures to the limit of the naked eye's visual acuity and through magnifying glasses and light microscopes. In the 20th century, a variety of experimental techniques were developed to examine the 3D structures of biological molecules. The most prominent techniques are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and Electron microscope, electron microscopy. Through the discovery of X-ray, X-rays and its applications to protein crystals, structural biology was revolutionized, as now scientists could obtain the three-dimensional structures of biological molecules in atomic detail. Likewise, Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy allowed information about protein structure and dynamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Analysis
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. It can be performed on the entire genome, transcriptome or proteome of an organism, and can also involve only selected segments or regions, like tandem repeats and transposable elements. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological databases, and others. Since the development of methods of high-throughput production of gene and protein sequences, the rate of addition of new sequences to the databases increased very rapidly. Such a collection of sequences does not, by itself, increase the scientist's understanding of the biology of organisms. However, comparing these new sequences to those with known functions is a key way of understanding the biology of an organism from which the new sequence comes. Thus, sequence analysis can be used to assign fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
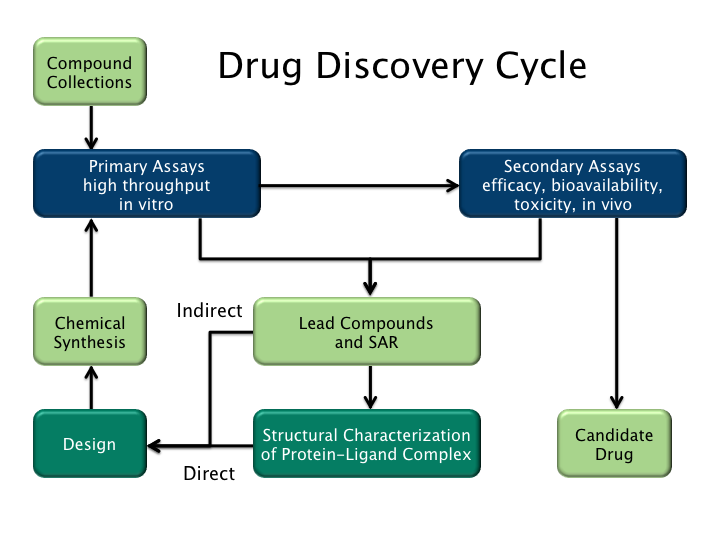
Drug Design
Drug design, often referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the invention, inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic compound, organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic effect, therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and electric charge, charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on molecular modelling, computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is sometimes referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, classified according to the monomers used and the structure of the biopolymer formed: polynucleotides, polypeptides, and polysaccharides. The Polynucleotides, RNA and DNA, are long polymers of nucleotides. Polypeptides include proteins and shorter polymers of amino acids; some major examples include collagen, actin, and fibrin. Polysaccharides are linear or branched chains of sugar carbohydrates; examples include starch, cellulose, and alginate. Other examples of biopolymers include natural rubbers (polymers of isoprene), suberin and lignin (complex polyphenolic polymers), cutin and cutan (complex polymers of long-chain fatty acids), melanin, and polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs). In addition to their many essential roles in living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |