|
ITRS 2.0
The International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) is a set of documents that was coordinated and organized by Semiconductor Research Corporation and produced by a group of experts in the semiconductor industry. These experts were representative of the sponsoring organisations, including the Semiconductor Industry Associations of Taiwan, South Korea, the United States, Europe, Japan, and China. As of 2017, ITRS is no longer being updated. Its successor is the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems. The documents carried disclaimer: "The ITRS is devised and intended for technology assessment only and is without regard to any commercial considerations pertaining to individual products or equipment". The documents represent best opinion on the directions of research and time-lines up to about 15 years into the future for the following areas of technology: History Constructing an integrated circuit, or any semiconductor device, requires a series of operations� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Research Corporation
Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC), commonly known as SRC, is a high-technology research consortium active in the semiconductor industry. It is a leading semiconductor research consortium. Todd Younkin is the incumbent president and chief executive officer of the company. The consortium comprises more than twenty-five companies and government agencies with more than a hundred universities under contract performing research. History SRC was founded in 1982 by Semiconductor Industry Association as a consortium to fund research and development by semiconductor companies. In the past, it has funded university research projects in hardware and software co-design, new architectures, circuit design, transistors, memories, interconnects, and materials and has sponsored over 15,000 Bachelors, Masters, and Ph.D. students. Research SRC has funded research in areas such as automotive, advanced memory technologies, logic and processing, advanced packaging, edge intelligence, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISTE Ltd
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memristors
A memristor (; a portmanteau of ''memory resistor'') is a non-linear terminal (electronics), two-terminal electronic component, electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. It was described and named in 1971 by Leon Chua, completing a theoretical quartet of fundamental electrical components which also comprises the resistor, capacitor and inductor. Chua and Kang later generalized the concept to memristive systems. Such a system comprises a circuit, of multiple conventional components, which mimics key properties of the ideal memristor component and is also commonly referred to as a memristor. Several such memristor system technologies have been developed, notably ReRAM. The identification of memristive properties in electronic devices has attracted controversy. Experimentally, the ideal memristor has yet to be demonstrated. As a fundamental electrical component Chua in his 1971 paper identified a theoretical symmetry between the non-linear resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spintronics
Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices. The field of spintronics concerns spin-charge coupling in metallic systems; the analogous effects in insulators fall into the field of multiferroics. Spintronics fundamentally differs from traditional electronics in that, in addition to charge state, electron spins are used as a further degree of freedom, with implications in the efficiency of data storage and transfer. Spintronic systems are most often realised in dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) and Heusler alloys and are of particular interest in the field of quantum computing and neuromorphic computing, upon which leads to integrated research requirements around Hyperdimensional Computation. History Spintronics emerged from discoveries in the 1980s concerning spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss ", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type semiconductor, p-type and n-type semiconductor, n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including Nonvolatile BIOS memory, CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data conversion, data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1948, Bardeen and Brattain patented an insulated-gate transistor (IGFET) with an inversion layer. Bardeen's concept forms the basis of CMOS technology today. The CMOS process was presented by Fairchild Semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
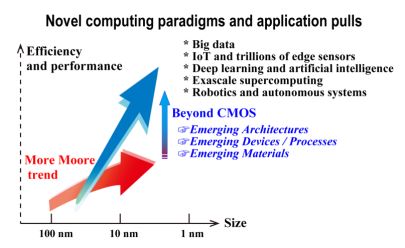
Beyond CMOS
Beyond CMOS refers to the possible future digital logic technologies beyond the scaling limits of CMOS technology. which limits device density and speeds due to heating effects. ''Beyond CMOS'' is the name of one of the 7 focus groups in ITRS 2.0 (2013) and in its successor, the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems. CPUs using CMOS were released from 1986 (e.g. 12 MHz Intel 80386). As CMOS transistor dimensions were shrunk the clock speeds also increased. Since about 2004 CMOS CPU clock speeds have leveled off at about 3.5 GHz. CMOS devices sizes continue to shrink – see Intel's process–architecture–optimization model (and older tick–tock model) and ITRS: * 22 nanometer Ivy Bridge in 2012 * first 14 nanometer processors shipped in Q4 2014. * In May 2015, Samsung Electronics showed a 300 mm wafer of 10 nanometer FinFET chips. It is not yet clear if CMOS transistors will still work below 3 nm. See 3 nanometer. Comparisons of techno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its storage, using for example, the pumped-storage method. Consumable electricity is not freely available in nature, so it must be "produced", transforming other forms of energy to electricity. Production is carried out in power stations, also called "power plants". Electricity is most often generated at a power plant by electromechanical generators, primarily driven by heat engines fueled by combustion or nuclear fission, but also by other means such as the kinetic energy of flowing water and wind. Other energy sources include solar photovoltaics and geothermal power. There are exotic and speculative methods to recover energy, such as proposed fusion reactor designs which aim to directly extract energy from intense magnetic fields generated by fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEMS
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of the large surface area to volume ratio of MEMS, forces produced by ambient electromagnetism (e.g., electrostatic charges and magnetic moments), and fluid dynamics (e.g., surface tension and viscosity) are more important design considerations than with larger scale mechanical devices. MEMS technology is distinguished from molecular nanotechnolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Technologies
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information (''telecommunication'') between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth, or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio ''wireless technology'' include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Integration
System integration is defined in engineering as the process of bringing together the component sub-systems into one system (an aggregation of subsystems cooperating so that the system is able to deliver the overarching functionality) and ensuring that the subsystems function together as a system, and in information technology as the process of linking together different computing systems and software applications physically or functionally, to act as a coordinated whole. The system integrator integrates discrete systems utilizing a variety of techniques such as computer networking, enterprise application integration, business process management or manual programming. System integration involves integrating existing, often disparate systems in such a way "that focuses on increasing value to the customer" (e.g., improved product quality and performance) while at the same time providing value to the company (e.g., reducing operational costs and improving response time). In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Rebooting Computing
The Task Force on Rebooting Computing (TFRC), housed within IEEE Computer Society, is the new home for the IEEE Rebooting Computing Initiative. Founded in 2013 by the IEEE Future Directions Committee, Rebooting Computing has provided an international, interdisciplinary environment where experts from a wide variety of computer-related fields can come together to explore novel approaches to future computing. IEEE Rebooting Computing began as a global initiative launched by IEEE that proposes to rethink the concept of computing through a holistic look at all aspects of computing, from the device itself to the user interface. As part of its work, IEEE Rebooting Computing provides access to various resources like conferences and educational events, feature and scholarly articles, reports, and videos. History IEEE Future Directions Committee established an "IEEE Rebooting Computing" working group in late 2012 with the broad vision of "rebooting" the entire field of computer technolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship. It is an experience-curve law, a type of law quantifying efficiency gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel and former CEO of the latter, who in 1965 noted that the number of components per integrated circuit had been exponential growth, doubling every year, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. Moore's empirical evidence did not directly imply that the historical trend would continue, nevertheless, his prediction has held si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |