|
Haplogroup F-M89 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup F, also known as F-M89 and previously as Haplogroup FT, is a very common Y-chromosome haplogroup. The clade and its subclades constitute over 95% of paternal lineages outside of Africa. The vast majority of individual males with F-M89 fall into its direct descendant Haplogroup GHIJK (F1329/M3658/PF2622/YSC0001299).ISOGG, 2015, ''Y-DNA Haplogroup F and its Subclades - 2015'' (8 September 2015). In addition to GHIJK, haplogroup F has three other immediate descendant subclades: F1 (P91/P104), F2 (M427/M428), and F3 (M481). These three, with F* (M89*), constitute the F(xGHIJK). They are primarily found throughout South Asia, Southeast Asia and parts of Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula and the South Caucasus. The region is separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. West Asia contains the majority of the similarly defined Middle East. The ''Middle East'' is a political term invented by Western geographers that has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup J (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J,ISOGG] ''Y-DNA Haplogroup J and its Subclades - 2016'' (2 February 2016). is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in the Caucasus or Iran.' The clade spread from there during the Neolithic, primarily into North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago, Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia, South Asia, and Southeast Asia. Haplogroup J-M304 is divided into two main subclades (branches), Haplogroup J-M267, J-M267 and Haplogroup J-M172, J-M172. Origins Haplogroup J-M304 is believed to have split from the haplogroup I-M170 roughly 43,000 years ago in Western Asia, as both lineages are haplogroup IJ subclades. Haplogroup IJ and haplogroup K derive from haplogroup IJK, and only at this level of classification does haplogroup IJK join with Haplogroup G-M201 and Haplogroup H (Y-DNA), Haplogroup H as immediate descendants of Haplogroup F-M89. J-M304 (Transcaucasian origin) is defined by the M3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen, as well as southern Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula was also considered a part of Arabia. The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the north-east, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Arab world and globally due to its vast reserves of petroleum, oil and natural gas. Before the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a Guanine, G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an Adenine, A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the Factor H, CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
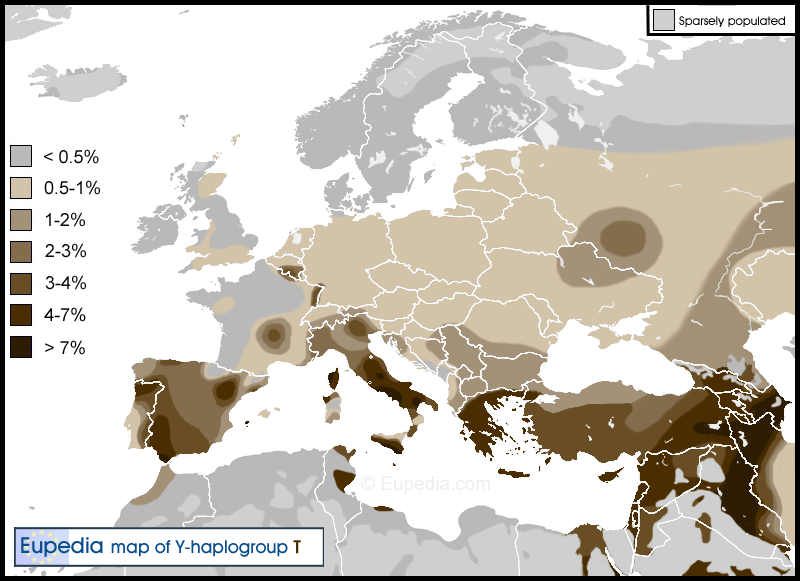
Haplogroup T (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup T-M184, also known as Haplogroup T, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. The unique-event polymorphism that defines this clade is the single-nucleotide polymorphism known as ''M184''. T-M184 is unusual in that it is both geographically widespread and relatively rare. T1 (T-L206) – the numerically dominant primary branch of T-M184 – appears to have originated in Western Asia, and spread from there into East Africa, South Asia, Europe, Egypt and adjoining regions. T1* may have expanded with the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B culture (PPNB) which originated in West Asia. Subclades of T-M70 appear to have been present in Europe since the Neolithic with Neolithic Farmers from Western Asia. The moderately high frequency (~18%) of T1b* chromosomes in the Lemba of southern Africa supports the hypothesis of a West Asian origin for their paternal line. Structure ;Subclade structure of Haplogroup T (M184). *T1 (L206) **T1a (M70/Page46/PF5662) ***T1a1 (L162/Page21, L454 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup L (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup L-M20 is a human Y-DNA haplogroup, which is defined by SNPs M11, M20, M61 and M185. As a secondary descendant of haplogroup K and a primary branch of haplogroup LT, haplogroup L currently has the alternative phylogenetic name of K1a, and is a sibling of haplogroup T (a.k.a. K1b). The presence of L-M20 has been observed at varying levels throughout South Asia, peaking in populations native to the southern Pakistani province of Balochistan (28%), Northern Afghanistan (25%), and Southern India (19%). The clade also occurs in Tajikistan and Anatolia, as well as at lower frequencies in Iran. It has also been present for millennia at very low levels in the Caucasus, Europe and Central Asia. The subclade L2 (L-L595) has been found in Europe and Western Asia, but is extremely rare. Phylogenetic tree There are several confirmed and proposed phylogenetic trees available for haplogroup L-M20. The scientifically accepted one is the Y-Chromosome Consortium (YCC) one publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup S (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup S also known as S-B254 is a human human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, Y-DNA haplogroup, defined by the Single-nucleotide polymorphism, SNPs B254 and Z33355.International Society of Genetic Genealogy (ISOGG; 2017), ''Y-DNA Haplogroup Tree 2015'' (24 March 2017). Until 2016, it was known as Haplogroup S1. S-M254 is the most common haplogroup among males in the New Guinea Highlands, Papua New Guinea Highlands. It is also relatively common in some parts of Oceania, Wallacea and among indigenous Australians. In a major correction to the phylogenetic tree during 2016, Haplogroup S-M230 was "demoted" from the position of basal (phylogenetics), basal clade S*, becoming S1a1b, while S-B254 was "promoted" in its place to the level of S*. It has two primary sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
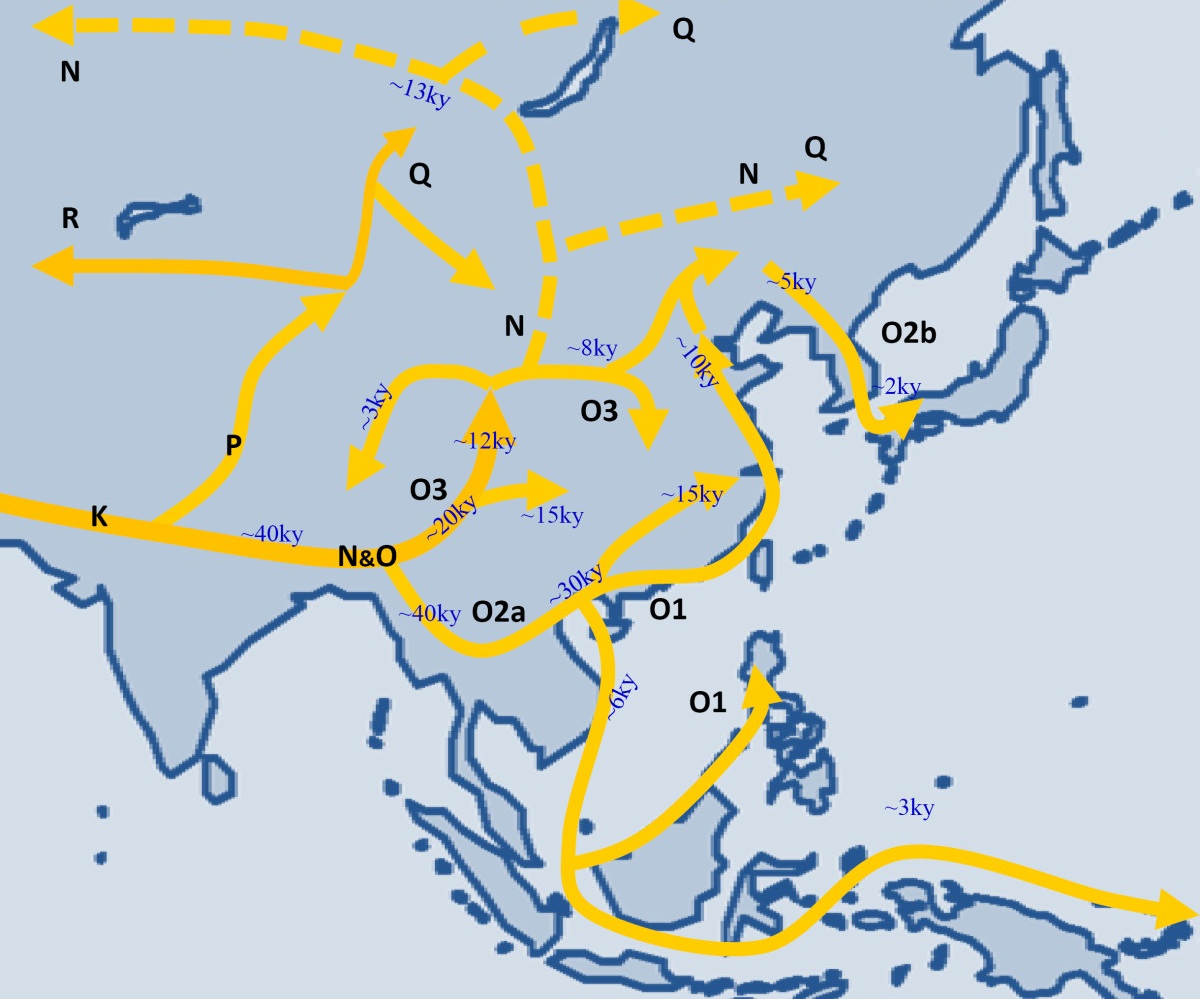
Haplogroup R (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R, or R-M207, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is both numerous and widespread among modern populations. Some descendant subclades have been found since pre-history in Europe, Central Asia and South Asia. Others have long been present, at lower levels, in parts of West Asia and Africa. Some authorities have also suggested, more controversially, that R-M207 has long been present among Native Americans in North America – a theory that has not yet been widely accepted. According to geneticist Spencer Wells, haplogroup K originated in the Middle East or Central Asia. "Given the widespread distribution of K, it probably arose somewhere in the Middle East or Central Asia, perhaps in the region of Iran or Pakistan." However, Karafet et al. (2014) proposed that "rapid diversification ... of K-M526", also known as K2, likely occurred in Southeast Asia (near Indonesia) and later expanded to mainland Asia, although they could not rule out that it might have arisen in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup Q or Q-M242 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It has two primary subclades: Q1/Q-L472 (also known as Q-MEH2) and Q2/Q-L275). These include numerous subclades that have been sampled and identified in males among modern populations. Q is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among Native Americans, Swati tribe and several peoples of Central Asia and Northern Siberia. Defining mutations The polymorphism M242, is a C→T transition residing in intron 1 (IVS-866) of the DBY gene and was discovered by Mark Seielstad et al. in 2003. The technical details of M242 are: :Nucleotide change: C to T :Position (base pair): 180 :Total size (base pairs): 366 :Forward 5′→ 3′: :Reverse 5′→ 3′: Other defining SNPs unique to Q-M242 include: FGC1752, F2603/M1020, L232/S432, M1115, Y2000/FGC1757, FGC6793, Y1984/FGC1753, Y1987/FGC1754/F6492, FGC7650(H), E337/L808/CTS3727/M1105, M1047(H), M1074, M1154, M1166, Y1972/FGC4603/F7839(H), Y2002/FGC1756/F6477(H), CTS7532/M1133, F30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup P (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup P also known as P-F5850 or K2b2 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup in human genetics. P-F5850 is a branch of K2b (previously Haplogroup MPS; P331), which is a branch of Haplogroup K2 (K-M526). The haplogroup K2b splits into K2b1 (haplogroup MS*) and K2b2 (haplogroup P-F580, Y-DNA P*). Basal P* (P-PF5850*) is found in Southeast Asia. The primary branches (clades) of P-F580 are P-P295 (P1a, formerly P*) which is found among South and Southeast Asians as well as Oceanians, P-FT292000 (P1b, formerly P3) with unknown distribution, and P-M45 (P1c, formerly P1) commonly found among Siberians and Central Asians. P-M45 (P1c) is, in turn, the parent node of Haplogroup Q (Q-M242) and Haplogroup R (R-M207). The major subclades of Haplogroups P-M45, Q and R now include most males among Europeans, Native Americans, South Asians, North Africans, and Central Asians. Origin and dispersal Karafet et al. 2015 suggests an origin and dispersal of haplogroup P and its ancestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup O (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup O, also known as O-M175, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is primarily found among populations in Southeast Asia and East Asia. It also is found in various percentages of populations of the Russian Far East, South Asia, Central Asia, Caucasus, Crimea, Ukraine, Iran, Oceania, Madagascar and the Comoros. Haplogroup O is a primary descendant of haplogroup NO-M214. The O-M175 haplogroup is very common amongst males from East and Southeast Asia. It has two primary branches: O1 (O-F265) and O2 (O-M122). O1 is found at high frequencies amongst males native to Southeast Asia, Taiwan, the Japanese Archipelago, the Korean Peninsula, Madagascar and some populations in southern China and Austroasiatic speakers of India. O2 is found at high levels amongst Han Chinese, Tibeto-Burman populations (including many of those in Yunnan, Tibet, Burma, Northeast India, and Nepal), Manchu, Mongols (especially those who are citizens of the PRC), Koreans, Vietnamese, Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |