|
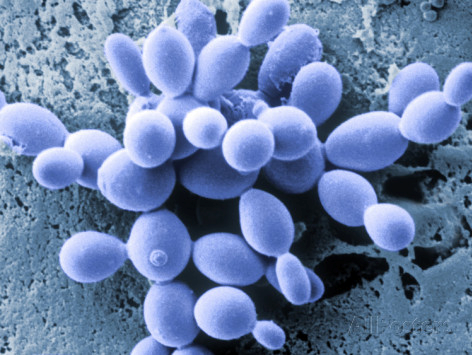
Guestia (fungus)
''Guestia'' is a genus of sac fungi in the family Xylariaceae. This is a monotypic genus, containing the single species ''Guestia gonetropospora''. The genus name of ''Guestia'' is in honour of David I. Guest (fl. 1997), an Australisian botanist (Mycology) and plant pathologist from the School of Botany in the University of Melbourne as well as at the Sydney Institute of Agriculture at the University of Sydney. The genus was circumscribed In geometry, a circumscribed circle for a set of points is a circle passing through each of them. Such a circle is said to ''circumscribe'' the points or a polygon formed from them; such a polygon is said to be ''inscribed'' in the circle. * Circum ... by Gavin J.D. Smith and Kevin D. Hyde in Fungal Diversity vol.7 on page 107 in 2001. References External linksIndex Fungorum Xylariales Monotypic Ascomycota genera {{Xylariales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus" (), a microscopic sexual reproduction, sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are Asexual reproduction, asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, yeast#Beer, brewers' and bakers' yeast, Xylaria, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (containing all of the descendants of a common ancestor). Previously placed in the Basidiomycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or Teleomorph, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycetes
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as '' Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (containing all of the descendants of a common ancestor). Previously placed in the Basidiomycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes are now identified and classified based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylariales
The Xylariales are an order (biology), order of fungi within the class (biology), class Sordariomycetes (also known as Pyrenomycetes), subdivision Pezizomycotina, division (mycology), division Ascomycota. It was the original order of the Class (taxonomy), subclass Xylariomycetidae. Xylariales was circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribed in 1932 by Swedish mycologist John Axel Nannfeldt, and Xylariomycetidae by Ove Erik Eriksson and Katarina Winka in 1997. Taxonomy Early classifications of the Xylariales varied considerably, with taxonomists recognising anywhere from three to eleven family (biology), families within the order. A milestone in understanding the order's composition came from Smith, Liew, and Hyde's 2003 molecular phylogenetics study, which established the Xylariales as a monophyletic group containing seven families: Amphisphaeriaceae, Apiosporaceae, Clypeosphaeriaceae, Diatrypaceae, Graphostromataceae, Hyponectriaceae, and Xylariaceae. During this period, fungi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylariaceae
The Xylariaceae are a family of mostly small ascomycetous fungi. It is one of the most commonly encountered groups of ascomycetes and is found throughout the temperate and tropical regions of the world. They are typically found on wood, seeds, fruits, or plant leaves, some even associated with insect nests. Most decay wood and many are plant pathogens. One example of this family is King Alfred's Cake ('' Daldinia concentrica''). Phylogenetic analyses published in 2009 suggest that there are two main lineages in this family, Hypoxyloideae and Xylarioideae. Genera This is a complete list of genera in the Xylariaceae, based on the 2007 Outline of Ascomycota. A question mark before the genus name indicates that the placement of that taxon in this family is uncertain. '' Amphirosellinia'' — '' Annulohypoxylon'' — '' Anthostomella'' — '' Appendixia'' — '' Areolospora'' — ?'' Ascotricha'' — '' Ascovirgaria'' — '' Astrocystis'' — '' Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sac Fungi
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (containing all of the descendants of a common ancestor). Previously placed in the Basidiomycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomycetes are now identified and classified based on morp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathologist
Plant pathology or phytopathology is the scientific study of plant diseases caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Plant pathology involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Plant pathogenicity Plant pathogens, organisms that cause infectious plant diseases, include fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. In most plant pathosystems, virulence depends on hydrolases and enzymes that degrade the cell wall. The vast majority of these act on pectins (for example, pectinesterase, pectate lyase, and pectinases). For microbes, the cell wall polysaccharides are both a food source and a barrier to be overcome. Many pathogens grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Melbourne
The University of Melbourne (colloquially known as Melbourne University) is a public university, public research university located in Melbourne, Australia. Founded in 1853, it is Australia's second oldest university and the oldest in the state of Victoria (Australia), Victoria. Its Parkville Campus (University of Melbourne), main campus is located in Parkville, Victoria, Parkville, an inner suburb north of Melbourne central business district, Melbourne's central business district, with several other campuses located across the state of Victoria (Australia), Victoria. Incorporated in the 19th century by the State of Victoria, colony of Victoria, the University of Melbourne is one of Australia's six sandstone universities and a member of the Group of Eight (Australian universities), Group of Eight, Universitas 21, Washington University in St. Louis, Washington University's McDonnell International Scholars Academy, and the Association of Pacific Rim Universities. Since 1872, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Sydney Institute Of Agriculture
The University of Sydney Institute of Agriculture is a constituent body of the University of Sydney, Australia Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl .... Agriculture was first taught at the University by Australia's first Professor of Agriculture, Robert Dickie Watt, in 1910. According to the University website, the faculty has over 500 members involved in teaching, research and outreach. References University of Sydney Agricultural universities and colleges in Australia {{Australia-university-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Sydney
The University of Sydney (USYD) is a public university, public research university in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in both Australia and Oceania. One of Australia's six sandstone universities, it was one of the world's first universities to admit students solely on academic merit, and opened its doors to women on the same basis as men. The university comprises eight academic faculties and university schools, through which it offers bachelor, master and doctoral degrees. Five Nobel Prize, Nobel and two Crafoord Prize, Crafoord laureates have been affiliated with the university as graduates and faculty. The university has educated 8 Prime minister of Australia, Australian prime ministers, including incumbent Anthony Albanese; 2 Governor-General of Australia, governors-general of Australia; 13 Premier of New South Wales, premiers of New South Wales; and 26 justices of the High Court of Australia, including 5 Chief Justice of Australia, chief justic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |