|
Greco-Buddhist Monasticism
The role of Greek Buddhist monks in the development of the Buddhist faith under the patronage of Emperor Ashoka around 260 BCE and subsequently during the reign of the Indo-Greek king Menander (r. 165/155–130 BCE) is described in the '' Mahavamsa'', an important non-canonical Theravada Buddhist historical text compiled in Sri Lanka in the 6th century in the Pali language. The ''Mahavamsa'' or "Great Chronicle" covers the history of Buddhism from the 6th century BCE to the 4th century CE. It was written in the 6th century by the monk Mahanama, brother of King Dhatusena of Anuradhapura, and heavily relied on the '' Dipavamsa'' or "Island Chronicle" written five centuries earlier. Background Emperor Ashoka convened the third Buddhist council around 250 BCE at Pāṭaliputra (today's Patna). It was held by the monk Moggaliputta. The Pāli Canon, which consists of the Theravada texts of reference and considered to be directly transmitted from the Buddha, was formalized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takht-I-Bahi Conjectural Restoration
Takht-i-Bahi ( Persian/ ur, , translation=throne of the water spring), is an Indo-Parthian archaeological site of an ancient Buddhist monastery in Mardan, Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. The site is considered among the most important relics of Buddhism in all of what was once Gandhara, and has been "exceptionally well-preserved." The monastery was founded in the 1st century CE,''Takht-i-Bahi'', UNESCO Office, Islamabad, Pakistan, 2002 and was in use until the 7th century. The complex is regarded by archaeologists as being particularly representative of the architecture of Buddhist monastic centers from its era. Takht-i-Bahi was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. Etymology A monastery under the domain of Purusapura which was also a center for Buddhist learning, the origin of the name Takht-i-Bahi is uncertain. Local belief postulates that site got its name from two wells on the hill, or the springs nearby. In Persian, ''Takht'' means 'top' or 'throne' while ''ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinaya Pitaka
The Vinaya (Pali & Sanskrit: विनय) is the division of the Buddhist canon ('' Tripitaka'') containing the rules and procedures that govern the Buddhist Sangha (community of like-minded ''sramanas''). Three parallel Vinaya traditions remain in use by modern ''sanghas'': the Theravada (Sri Lanka & Southeast Asia), Mulasarvastivada (Tibetan Buddhism and the Himalayan region) and Dharmaguptaka ( East Asian Buddhism). In addition to these Vinaya traditions, Vinaya texts of several extinct schools of Indian Buddhism are preserved in the Tibetan and East Asian canons, including those of the Kāśyapīya, the Mahāsāṃghika, the Mahīśāsaka, and the Sarvāstivāda The word ''Vinaya'' is derived from a Sanskrit verb that can mean to lead, take away, train, tame, or guide, or alternately to educate or teach. It is often translated as 'discipline', with ''Dhamma-vinaya'', 'doctrine and discipline', used by the Buddha to refer to his complete teachings, suggesting its integ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominalization, nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kambojas
Kamboja ( sa, कम्बोज) was a kingdom of Iron Age India that spanned parts of South and Central Asia, frequently mentioned in Sanskrit and Pali literature. Eponymous with the kingdom name, the Kambojas were an Indo-Iranian people of the Kshatriya caste inhabiting the Kamboja Mahajanapada region, forming one of the sixteen nations that made up ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE during the second urbanisation period. Earlier, during the late Vedic age, the Kambojas had emerged as an important part of the Indo Aryan Vedic people with a prominent place among the Kshatriya tribes of the Mahabharata. While historical boundaries of the Kambojas are varied, scholarly accounts altogether place the northern and western borders in present-day Tajikistan and eastern Uzbekistan, with eastern borders in present-day Jammu and Kashmir, and southern borders in present-day Iran and southern Afghanistan. Etymology The name ''Kamboja'' may derive from '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian tribe who had settled in the region before the Archaic period. Ionia proper comprised a narrow coastal strip from Phocaea in the north near the mouth of the river Hermus (now the Gediz), to Miletus in the south near the mouth of the river Maeander, and included the islands of Chios and Samos. It was bounded by Aeolia to the north, Lydia to the east and Caria to the south. The cities within the region figured large in the strife between the Persian Empire and the Greeks. Ionian cities were identified by mythic traditions of kinship and by their use of the Ionic dialect, but there was a core group of twelve Ionian cities who formed the Ionian League and had a shared sanctuary and festival at Panionion. These twelve cities were ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yona
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for " Ionians" ( grc, Ἴωνες < Ἰάoνες < *Ἰάϝoνες), who were probably the first Greeks to be known in the East. Both terms appear in ancient literature. ''Yavana'' appears, for instance, in the '''', while ''Yona'' appears in texts such as the n chronicle '' Mahavamsa''. The Yona are me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunga Empire
The Shunga Empire ( IAST: ') was an ancient Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled areas of the most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of the Maurya Empire. Its capital was Pataliputra, but later emperors such as Bhagabhadra also held court at Besnagar (modern Vidisha) in eastern Malwa. Pushyamitra ruled for 36 years and was succeeded by his son Agnimitra. There were ten Shunga rulers. However, after the death of Agnimitra, the second king of the dynasty, the empire rapidly disintegrated:K.A. Nilkantha Shastri (1970)''A Comprehensive History of India: Volume 2'' p.108: "Soon after Agnimitra there was no 'Sunga empire'." inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any Shunga hegemony.Bhandare, Shailendra. "Numismatics and History: The Maurya-Gupta Interlude in the Gangetic Plain". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. Quote: "Magadha power came to extend over the main cities and communication routes of the Ganges basin. Then, under Chandragupta Maurya (c.321–297 bce), and subsequently Ashoka his grandson, Pataliputra became the centre of the loose-knit Mauryan 'Empire' which during Ashoka's reign (c.268–232 bce) briefly had a presence throughout the main urban centres and arteries of the subcontinent, except for the extreme south." The Maurya Empire was centralized by the conquest of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, and its capital city was located at Pataliputra (modern Patna). Outside this imperial center, the empire's geographical extent was dependent on the loyalty of military commanders who controlled the armed cities sprinkling it. During ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
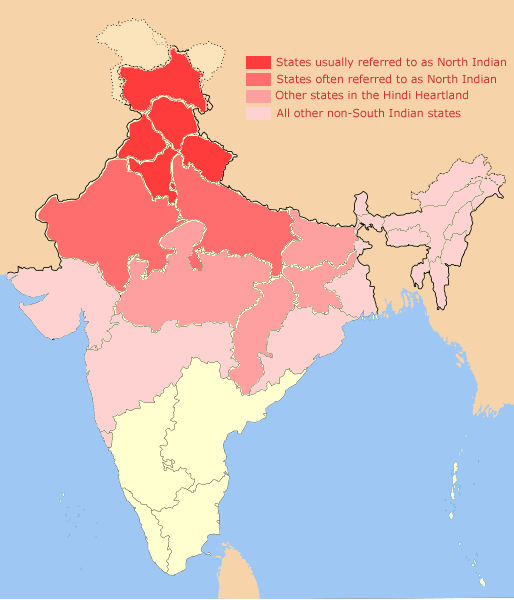
North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Indian Subcontinent from its founding in 256 BC by Diodotus I Soter to its fall BC under the reign of Heliocles I. It covered much of present-day Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan, and at its zenith, parts of Iran and Pakistan. An extension further east with military campaigns may have reached central Gansu province in China. Bactria was ruled by the Diodotid dynasty and rival Euthydemid dynasty. The capitals of Ai-Khanum and Bactra were among the largest and richest of antiquity - Bactria itself was known as the ‘''land of a thousand golden cities’''. The Indo-Greek Kingdoms, as Bactrian successor states, would last until 10 AD. History Independence and Diodotid dynasty Diodotus, the satrap of Bactria (and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |