|
Giant Impact Hypothesis
The giant-impact hypothesis, sometimes called the Theia Impact, is an astrogeology hypothesis for the formation of the Moon first proposed in 1946 by Canadian geologist Reginald Daly. The hypothesis suggests that the Early Earth collided with a Mars-sized protoplanet of the same orbit approximately 4.5 billion years ago in the early Hadean eon (about 20 to 100 million years after the Solar System coalesced), and the ejecta of the impact event later accreted to form the Moon. The impactor planet is sometimes called Theia, named after the mythical Greek Titan who was the mother of Selene, the goddess of the Moon. Analysis of lunar rocks published in a 2016 report suggests that the impact might have been a direct hit, causing a fragmentation and thorough mixing of both parent bodies. The giant-impact hypothesis is currently the favored hypothesis for lunar formation among astronomers. Evidence that supports this hypothesis includes: * The Moon's orbit has a simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theia
Theia (; , also rendered Thea or Thia), also called Euryphaessa (, "wide-shining"), is one of the twelve Titans, the children of the earth goddess Gaia and the sky god Uranus in Greek mythology. She is the Greek goddess of sight and vision, and by extension the goddess who endowed gold, silver, and gems with their brilliance and intrinsic value. Her brother-consort is Hyperion, a Titan and god of the sun, and together they are the parents of Helios (the Sun), Selene (the Moon), and Eos (the Dawn). She seems to be the same figure as Aethra, who is the consort of Hyperion and mother of his children in some accounts. Like her husband, Theia features scarcely in myth, being mostly important for the children she bore, though she appears in some texts and rare traditions. Etymology The name ''Theia'' alone means simply "goddess" or "divine"; ''Theia Euryphaessa'' () brings overtones of extent (, ''eurys'', "wide", root: ) and brightness (, ''phaos'', "light", root: φαεσ-). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a Conservation law, conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be Energy transformation, converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a Classical field theory, field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Magma Ocean
The Lunar Magma Ocean (LMO) is the layer of molten rock that is theorized to have been present on the surface of the Moon. The LMO was likely present on the Moon from the time of the Moon's formation (about 4.5 or 4.4 billion years ago) to tens or hundreds of millions of years after that time. The LMO was a thermodynamic consequence of the Moon's relatively rapid formation in the aftermath of a giant impact between the proto-Earth and another planetary body. As the Moon accreted from the debris from the giant impact, gravitational potential energy was converted to thermal energy. Due to the rapid accretion of the Moon (in about a month to a year), thermal energy was trapped since it did not have sufficient time to thermally radiate away energy through the lunar surface. The subsequent thermochemical evolution of the LMO explains the Moon's largely anorthositic crust, europium anomaly, and KREEP material. The LMO was initially proposed by two groups in 1970 after they analyz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Planet
A terrestrial planet, tellurian planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate, rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Among astronomers who use the geophysical definition of a planet, two or three planetary-mass satellites – Earth's Moon, Io, and sometimes Europa – may also be considered terrestrial planets. The large rocky asteroids Pallas and Vesta are sometimes included as well, albeit rarely. The terms "terrestrial planet" and "telluric planet" are derived from Latin words for Earth (''Terra'' and ''Tellus''), as these planets are, in terms of structure, ''Earth-like''. Terrestrial planets are generally studied by geologists, astronomers, and geophysicists. Terrestrial planets have a solid planetary surface, making them substantially different from larger gaseous planets, which are composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction (geometry), direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics, Bicycles and motorcycles, flying discs, Rifling, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
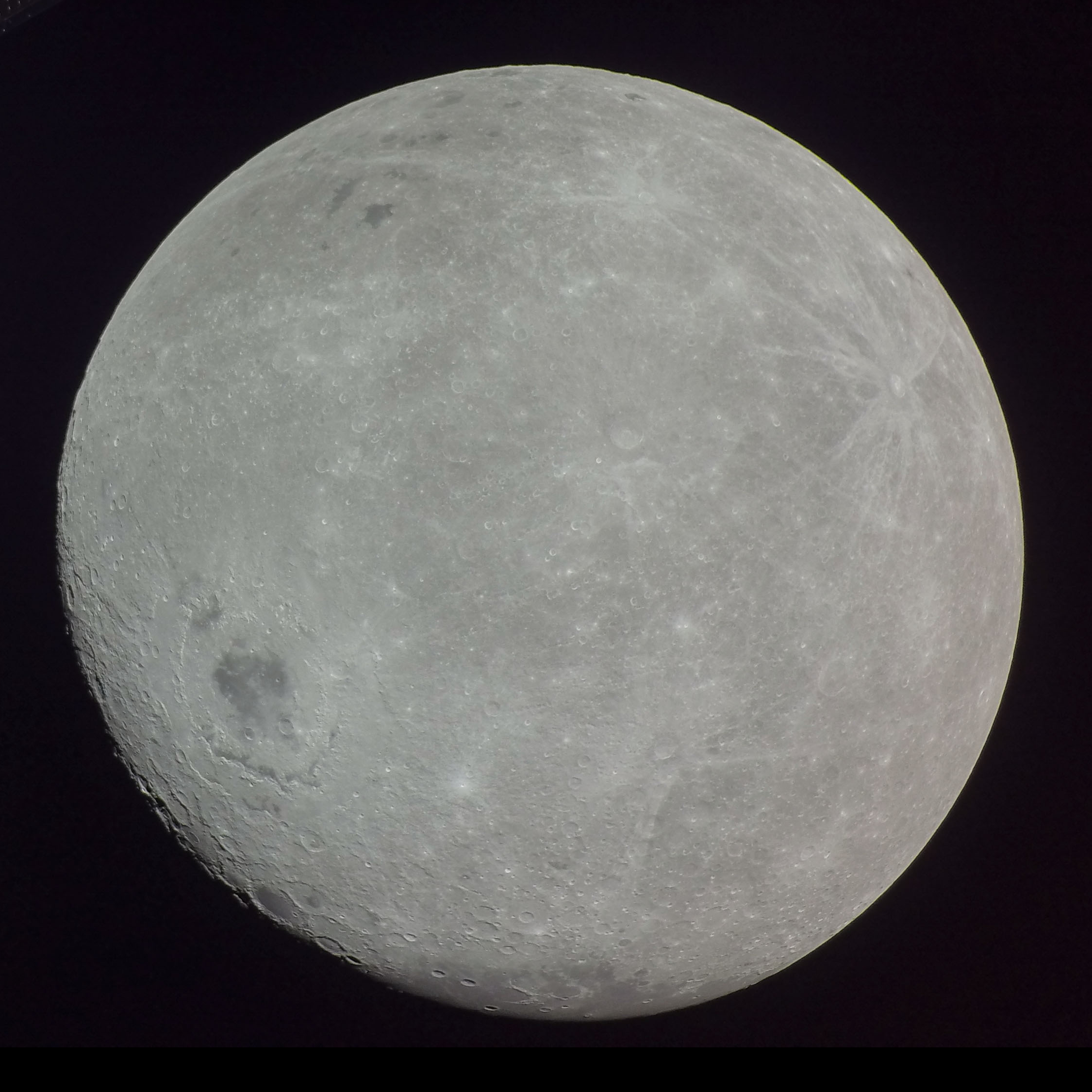
Earth–Moon System
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It orbits around Earth at an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth's diameter). The Moon rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the largest and most massive satellite in relation to its parent planet, the fifth-largest and fifth-most massive moon overall, and larger and more massive than all known dwarf planets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stable Isotope
Stable nuclides are Isotope, isotopes of a chemical element whose Nucleon, nucleons are in a configuration that does not permit them the surplus energy required to produce a radioactive emission. The Atomic nucleus, nuclei of such isotopes are not radioactive and unlike radionuclides do not spontaneously undergo radioactive decay. When these nuclides are referred to in relation to specific elements they are usually called that element's stable isotopes. The 80 elements with one or more stable isotopes comprise a total of 251 nuclides that have not been shown to decay using current equipment. Of these 80 elements, 26 have only one stable isotope and are called monoisotopic element, monoisotopic. The other 56 have more than one stable isotope. Tin has ten stable isotopes, the largest number of any element. Definition of stability, and naturally occurring nuclides Most naturally occurring nuclides are stable (about 251; see list at the end of this article), and about 35 more (tot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic Plane
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of Earth around the Sun. It was a central concept in a number of ancient sciences, providing the framework for key measurements in astronomy, astrology and calendar-making. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars – specifically the Zodiac constellations. The planets of the Solar System can also be seen along the ecliptic, because their orbital planes are very close to Earth's. The Moon's orbital plane is also similar to Earth's; the ecliptic is so named because the ancients noted that eclipses only occur when the Moon is crossing it. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Ancient scientists were able to calculate Earth's axial tilt by comparing the ecliptic plane to that of the equator. Sun's apparent motion The eclipt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Over the course of an orbital period, the obliquity usually does not change considerably, and the orientation of the axis remains the same relative to the background of stars. This causes one pole to be pointed mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in prograde motion. As viewed from the northern polar star Polaris, Earth turns counterclockwise. The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from Earth's north magnetic pole. The South Pole is the other point where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica. Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the Sun, but once every 23 hours, 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to other distant stars (#Stellar and sidereal day, see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal acceleration, tidal effects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
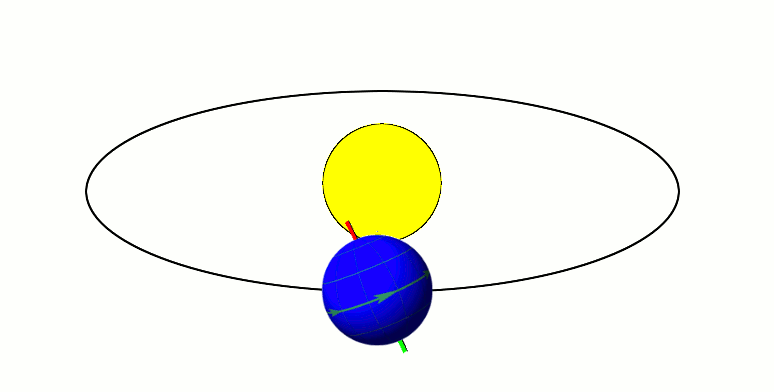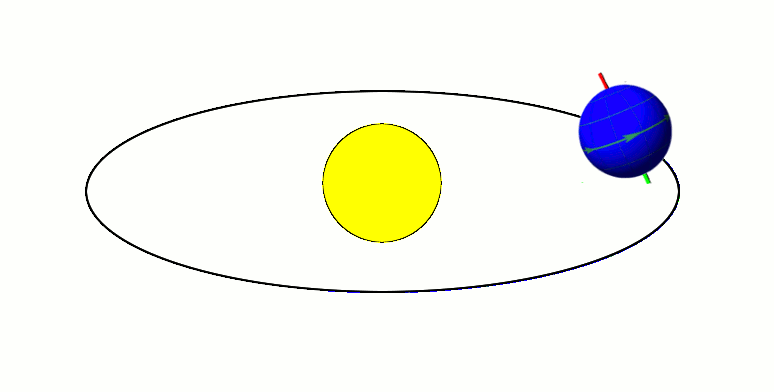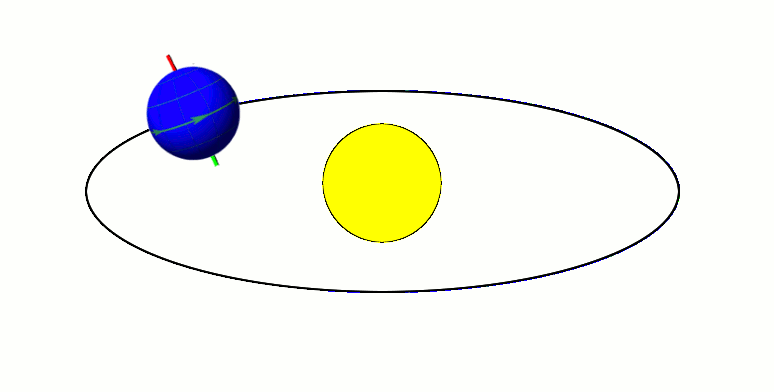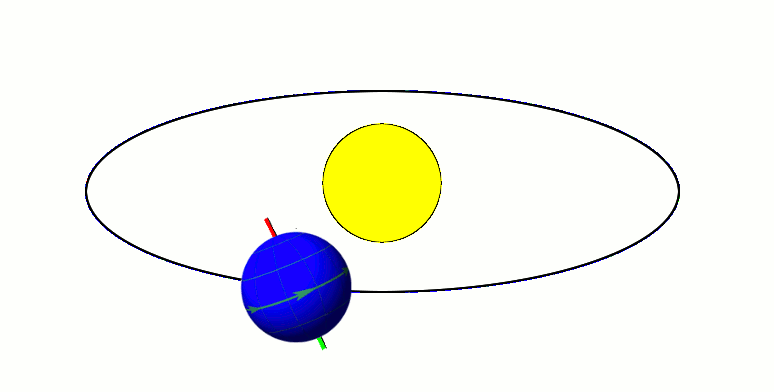
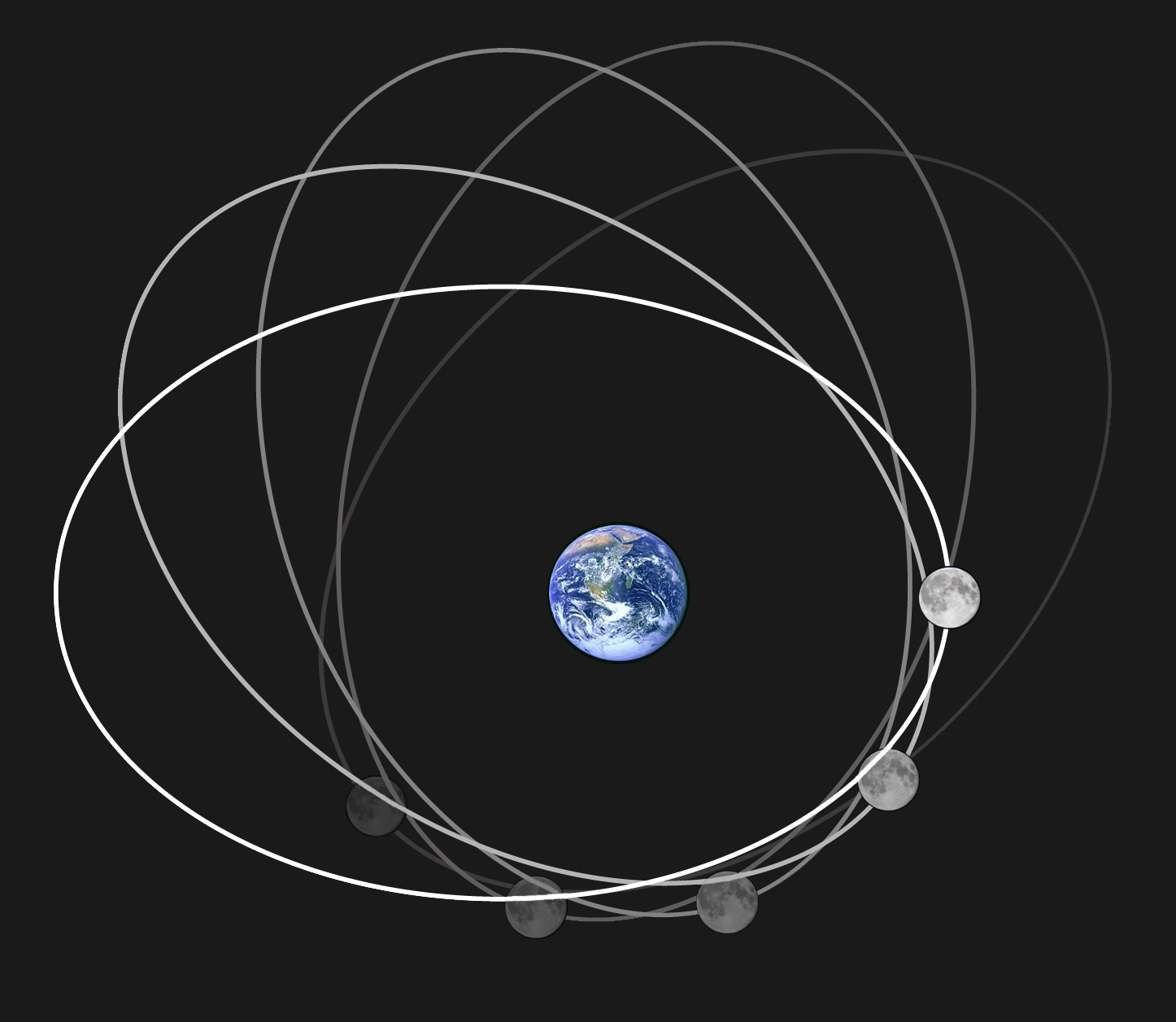
Moon's Orbit
The Moon orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the fixed stars in about 27.3 days (a tropical month and sidereal month), and one revolution relative to the Sun in about 29.5 days (a synodic month). On average, the distance to the Moon is about from Earth's centre, which corresponds to about 60 Earth radii or 1.28 light-seconds. Earth and the Moon orbit about their barycentre (common centre of mass), which lies about from Earth's centre (about 73% of its radius), forming a satellite system called the Earth–Moon system. With a mean orbital speed around the barycentre of , the Moon covers a distance of approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most regular satellites of other planets in that its orbital plane is closer to the ecliptic plane instead of its primary's (in this case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital plane is incline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |