|
Georg Nagel
Georg Nagel (born 24 August 1953 in Weingarten, Germany) is a biophysicist and professor at the Department for Neurophysiology at the University of Würzburg in Germany. His research is focused on microbial photoreceptors and the development of optogenetic tools. Scientific career Georg Nagel studied biology and biophysics at the University of Konstanz, Germany. He received his PhD from the University of Frankfurt in 1988, working at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt. As a postdoc, he worked at Yale University and Rockefeller University, US. From 1992 to 2004, he headed an independent research group in the Department of Biophysical Chemistry at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt. Since 2004, he is a professor at the University of Würzburg, Germany, first at the Department for Molecular Plant Physiology and Biophysics, since 2019 at the Department for Neurophysiology. Research Georg Nagel, together with Peter Hegemann, is credited with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prof
Jacob Lukas Anderson (born April 29, 1984), better known by his stage name Prof, is an American rapper, singer, and producer based in Minneapolis, Minnesota. He released his first full-length album, ''Project Gampo'', in 2007 and has since released six additional albums and three EPs. In 2012, ''City Pages'' named Prof on their list of Minnesota's 20 best rappers. He was formerly signed to Rhymesayers Entertainment. Early life Jacob "Jake" Anderson was born in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and grew up in the city's Powderhorn, Minneapolis, Powderhorn neighborhood. His mother, Colleen, had a rocky relationship with his father (who suffered from bipolar disorder and was physically abusive) whom she would later divorce and move away from, taking Anderson's three older sisters with her. In his teenage years, he developed a "comedic, dirty-mouthed rap persona" he named Gampo after a childhood friend. Anderson graduated from South High School (Minneapolis), Minneapolis South High School in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Gottschalk
Alexander Gottschalk is Professor of Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology at the Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany. Scientific career Alexander Gottschalk studied chemistry, biochemistry and immunology at Goethe University in Frankfurt, Philipps University in Marburg and University of Edinburgh, UK. His PhD thesis (Dr. rer. nat.) was conducted in the laboratory of Reinhard Lührmann at the University of Marburg. As a postdoctoral fellow, he worked with William R. Schafer at UC San Diego to study the nervous system of ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. In 2004, he became an independent research group leader in Frankfurt. In 2010, he was awarded a Heisenberg-Professor position and became Full Professor for Molecular Cell Biology and Neurobiochemistry in 2016. His researcgroupis located at the Buchmann Institute for Molecular Life Sciences. Research Alexander Gottschalk studies the neuronal control of behavior in the nematode ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. In 2005, he demonstrated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaw Prize
The Shaw Prize is a set of three annual awards presented by the Shaw Prize Foundation in the fields of astronomy, medicine and life sciences, and mathematical sciences. Established in 2002 in Hong Kong, by Hong Kong entertainment mogul and philanthropist Run Run Shaw (邵逸夫), the awards honour "individuals who are currently active in their respective fields and who have recently achieved distinguished and significant advances, who have made outstanding contributions in academic and scientific research or applications, or who in other domains have achieved excellence." The prize has been described as the "Nobel of the East". Award The prize consists of three awards in the fields of astronomy, life science and medicine, and mathematical sciences; it is not awarded posthumously. Nominations are submitted by invited individuals beginning each year in September. Winners are announced in the summer and receive the award at a ceremony in early autumn. Each award consists of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gero Miesenböck
Gero Andreas Miesenböck (born 15 July 1965) is an Austrian scientist. He is currently Waynflete Professor of Physiology and Director of the Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour (CNCB) at the University of Oxford and a fellow of Magdalen College, Oxford. Education and early life A native of Austria, Miesenböck was educated at the University of Innsbruck and Umeå University in Sweden. He graduated sub auspiciis praesidentis rei publicae from the University of Innsbruck Medical School. Following his Doctor of Medicine (MD) in 1993, he undertook postdoctoral training with James Rothman. Research and career Miesenböck is known as the founder of optogenetics. He was the first scientist to modify nerve cells genetically so that their electrical activity could be controlled with light. This involved inserting DNA for light-responsive opsin proteins into the cells. Miesenböck used similar genetic modifications to breed animals whose brains contained light-responsive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Boyden
Edward S. Boyden (born August 18, 1979) is an American neuroscientist and entrepreneur at MIT. He is the Y. Eva Tan Professor in Neurotechnology, and a full member of the McGovern Institute for Brain Research. He is recognized for his work on optogenetics and expansion microscopy. Boyden joined the MIT faculty in 2007, and continues to develop new optogenetic tools as well as other technologies for the manipulation and analysis of brain structure and activity. He received the 2015 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences. Early life and education Boyden was born in Plano, Texas. His mother has a masters in biochemistry and conducted nicotine research, staying home to tend to Boyden and his sister. His father was a management consultant. In childhood wanted to understand humanity, at first preferring math over science. He eventually pivoted to being interested in how our minds are capable of understanding math. As a young teenager, his thoughts resulted in what he now calls the "loop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumford Prize
Founded in 1796, the Rumford Prize, awarded by the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, is one of the oldest scientific prizes in the United States. The prize recognizes contributions by scientists to the fields of heat and light. These terms are widely interpreted; awards range from discoveries in thermodynamics to improvements in the construction of steam boilers. The award was created through the endowment of US$5,000 to the Academy by Benjamin Thompson, who held the title "Count Rumford of the United Kingdom," in 1796. The terms state that the award be given to "authors of discoverie's in any part of the Continent of America, or in any of the American islands." Although it was founded in 1796, the first prize was not given until 1839, as the academy could not find anyone who, in their judgement, deserved the award. The academy found the terms of the prize to be too restrictive, and in 1832 the Supreme Court of Massachusetts allowed the Academy to change some of the provis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Jeantet Prize For Medicine
Established in 1986, the Louis-Jeantet Prizes are funded by the Louis-Jeantet Foundation, ''Fondation Louis-Jeantet'' and awarded each year to experienced researchers who have distinguished themselves in the field of biomedical research in one of the member states of the Council of Europe. They are not intended solely as the recognition of work that has been completed, but also to encourage the continuation of innovative research projects. The prizes are awarded to fully active researchers whose scientific efforts are focused on biomedical research. When the research being recognised is close to practical applications for combating illnesses affecting humankind, one of the Louis-Jeantet Prizes converts into a Jeantet-Collen Prize for Translational Medicine, supported by generous donations from the Désiré Collen Stichting. The particular research domains in which prizes have been awarded are physiology, biophysics, structural biology, biochemistry, cellular biology, cellular an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiley Prize In Biomedical Sciences
The Wiley Prize in Biomedical Sciences is intended to recognize breakthrough research in pure or applied life science research that is distinguished by its excellence, originality and impact on our understanding of biological systems and processes. The award may recognize a specific contribution or series of contributions that demonstrate the nominee's significant leadership in the development of research concepts or their clinical application. Particular emphasis will be placed on research that champions novel approaches and challenges accepted thinking in the biomedical sciences. The Wiley Foundation, established in 2001, is the endowing body that supports the Wiley Prize in Biomedical Sciences. This international award is presented annually and consists of a $35,000 prize and a luncheon in honor of the recipient. The award is presented at a ceremony at The Rockefeller University, where the recipient delivers an honorary lecture as part of the Rockefeller University Lecture Seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
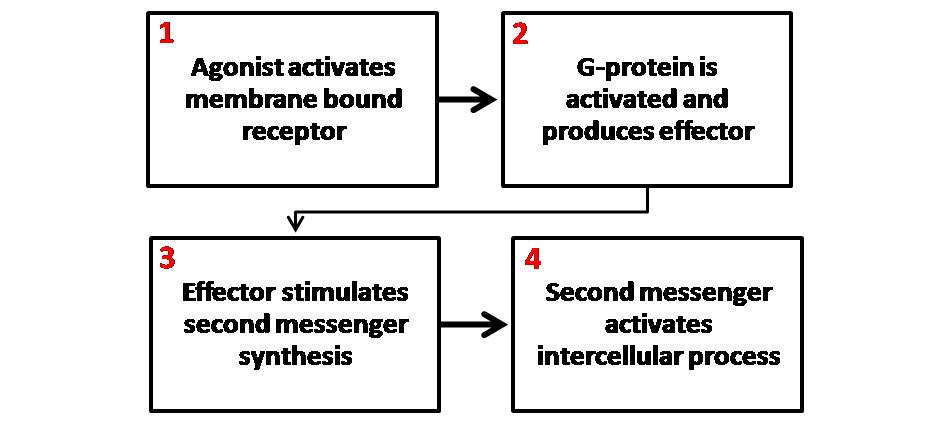
Second Messenger System
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine signaling, autocrine, juxtacrine signalling, juxtacrine, paracrine signaling, paracrine, and endocrine system, endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as Cell proliferation, proliferation, cellular differentiation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halorhodopsin
Halorhodopsin is a seven-transmembrane retinylidene protein from microbial rhodopsin family. It is a chloride-specific light-activated ion pump found in archaea known as halobacteria. It is activated by green light wavelengths of approximately 578 nm. Halorhodopsin also shares sequence similarity to channelrhodopsin, a light-gated ion channel. Halorhodopsin contains the essential light-isomerizable vitamin A derivative all-trans-retinal. Due to the dedication towards discovering the structure and function of this moleculc, halorhodopsin is one of the few membrane proteins whose crystal structure is known. Halorhodopsin uses the energy of green/yellow light to move chloride ions into the cell, overcoming the membrane potential. Beside chlorides it transports other halides and nitrates into the cell. Potassium chloride uptake by cells helps to maintain osmotic balance during cell growth. By performing the same task, light-driven anion pumps can considerably reduce the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channelrhodopsin
Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes (see optogenetics). Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism '' Chlamydomonas reinhardtii'' are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants that are sensitive to different colors of light or selective for specific ions (ACRs, KCRs) have been cloned from other species of algae and protists. History Phototaxis and photoorientation of microalgae have been studied over more than a hundred years in many laboratories worldwide. In 1980, Ken Foster developed the first consistent theory about the functionality of algal eyes. He also analyzed published a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |