Rumford Prize on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Founded in 1796, the Rumford Prize, awarded by the
Founded in 1796, the Rumford Prize, awarded by the







 Source
Source
American Academy of Arts and Sciences: Past Prizes
 Founded in 1796, the Rumford Prize, awarded by the
Founded in 1796, the Rumford Prize, awarded by the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (The Academy) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other ...
, is one of the oldest scientific prizes in the United States. The prize recognizes contributions by scientists to the fields of heat and light. These terms are widely interpreted; awards range from discoveries in thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
to improvements in the construction of steam boiler
file:Dampfkessel für eine Stationärdampfmaschine im Textilmuseum Bocholt.jpg, An industrial boiler, originally used for supplying steam to a stationary steam engine
A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat ...
s.
The award was created through the endowment of US$
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
5,000 to the Academy by Benjamin Thompson
Colonel (United Kingdom), Colonel Sir Benjamin Thompson, Count Rumford, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (26 March 175321 August 1814), was an American-born British military officer, scientist and inventor. Born in Woburn, Massachusetts, he sup ...
, who held the title "Count Rumford of the United Kingdom," in 1796. The terms state that the award be given to "authors of discoverie's in any part of the Continent of America, or in any of the American islands." Although it was founded in 1796, the first prize was not given until 1839, as the academy could not find anyone who, in their judgement, deserved the award. The academy found the terms of the prize to be too restrictive, and in 1832 the Supreme Court of Massachusetts allowed the Academy to change some of the provisions; mainly, the award was to be given annually instead of biennially, and the Academy was allowed to award the prize as it saw fit, whereas before it had to give it yearly. The first award was given to Robert Hare, for his invention of the oxy-hydrogen blowpipe, in 1839. Twenty-three years elapsed before the award was given a second time, to John Ericsson
John Ericsson (born Johan Ericsson; July 31, 1803 – March 8, 1889) was a Swedish-American engineer and inventor. He was active in England and the United States.
Ericsson collaborated on the design of the railroad steam locomotive Novelty (lo ...
.
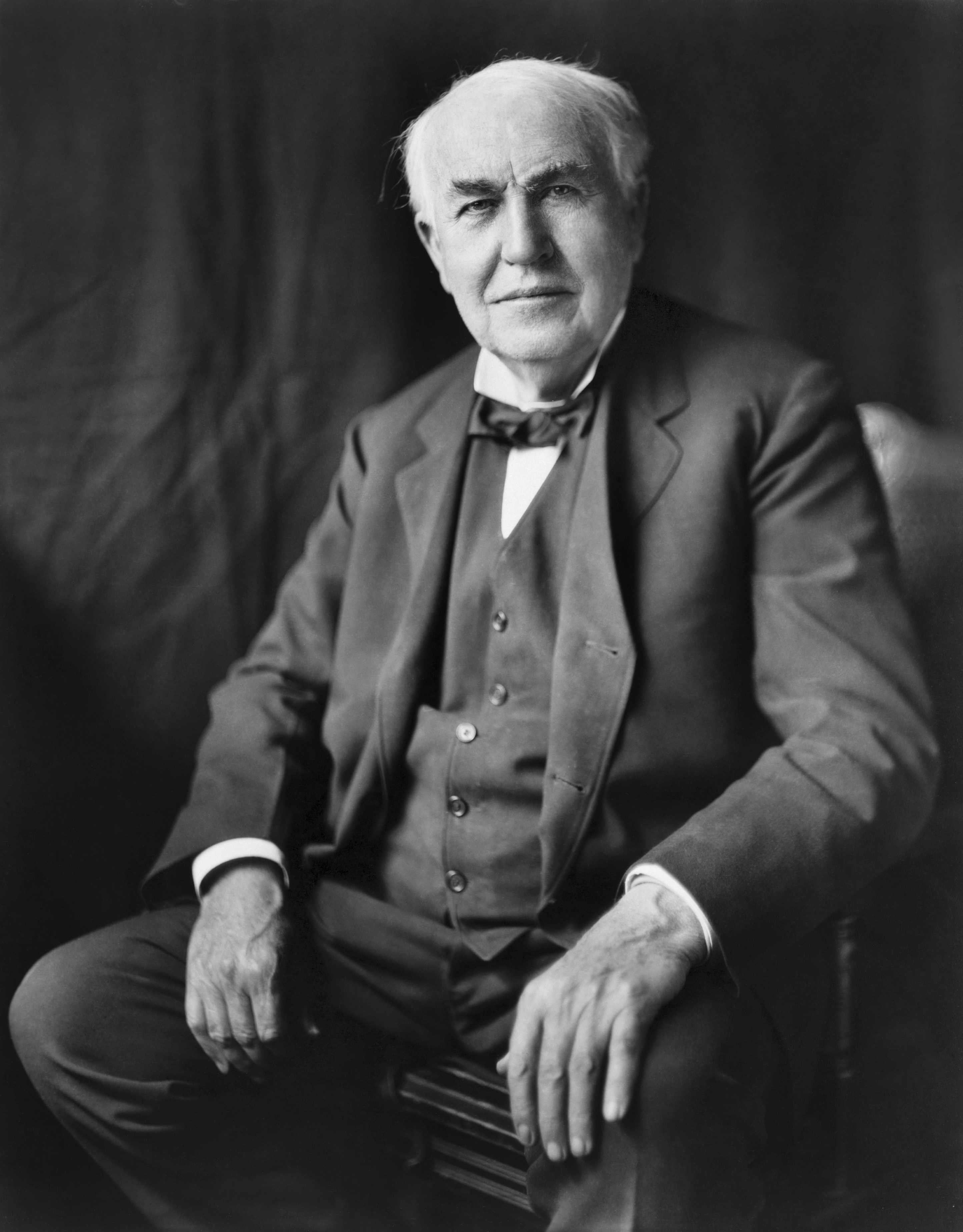
The prize is awarded whenever the academy recognizes a significant achievement in either of the two fields. Awardees receive a gold-and-silver medal. Previous prizewinners include Thomas Alva Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions ...
, for his investigations in electric lighting; Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi (; 29 September 1901 – 28 November 1954) was an Italian and naturalized American physicist, renowned for being the creator of the world's first artificial nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1, and a member of the Manhattan Project ...
, for his studies of radiation theory and nuclear energy
Nuclear energy may refer to:
*Nuclear power, the use of sustained nuclear fission or nuclear fusion to generate heat and electricity
*Nuclear binding energy, the energy needed to fuse or split a nucleus of an atom
*Nuclear potential energy, the pot ...
; and Charles H. Townes, for his development of the laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
. One man, Samuel Pierpont Langley, has won both the Rumford Prize and the related Rumford Medal (the European equivalent of the Rumford Prize), both in 1886. The most recent award was given in 2021 to Charles L. Bennett for his contributions to cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
. The prize has been given to researchers outside of the United States only twice—once to John Stanley Plaskett, from British Columbia, and once to a group of Canadian scientists "for their work in the field of long-baseline interferometry."
List of recipients








 Source
SourceAmerican Academy of Arts and Sciences: Past Prizes
See also
*List of physics awards
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but ...
References and notes
{{featured list Physics awards 1796 establishments in the United States Awards of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences