|
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic predisposition refers to a genetic characteristic which influences the possible phenotypic development of an individual organism within a species or population under the influence of environmental conditions. The term genetic susceptibility is often used synonymously with genetic predisposition and is further defined as the inherited risk for specific conditions, based on genetic variants. While environmental factors can influence disease onset, genetic predisposition plays a role in inherited risk of conditions, such as various cancers. At the molecular level, genetic predisposition often involves specific gene mutation, regulatory pathways, or epigenetic modifications that alter cellular processes, increasing disease risk. How to predict genetic predisposition There are several approaches commonly used in the field of genetics to predict a genetic predisposition toward a disease. * Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): studies that identify genetic variants link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other irregular combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chromos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenomatous Polyposis Coli
Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) also known as deleted in polyposis 2.5 (DP2.5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APC'' gene. The APC protein is a Down-regulation, negative regulator that controls beta-catenin concentrations and interacts with E-cadherin, which are involved in cell adhesion. Mutations in the ''APC'' gene may result in colorectal cancer and desmoid tumors. ''APC'' is classified as a tumor suppressor gene. Tumor suppressor genes prevent the uncontrolled growth of cells that may result in cancerous tumors. The protein made by the ''APC'' gene plays a critical role in several cellular processes that determine whether a cell may develop into a tumor. The APC protein helps control how often a cell divides, how it attaches to other cells within a tissue, how the cell polarizes and the morphogenesis of the 3D structures, or whether a cell moves within or away from tissue. This protein also helps ensure that the chromosome number in cells produced through c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant inherited condition in which numerous adenomatous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when they are left untreated. Three variants are known to exist, FAP and attenuated FAP (originally called hereditary flat adenoma syndrome) are caused by ''APC'' gene defects on chromosome 5 while autosomal recessive FAP (or MUTYH-associated polyposis) is caused by defects in the '' MUTYH'' gene on chromosome 1. Of the three, FAP itself is the most severe and most common; although for all three, the resulting colonic polyps and cancers are initially confined to the colon wall. Detection and removal before metastasis outside the colon can greatly reduce and in many cases eliminate the spread of cancer. The root cause of FAP is understood to be a genetic mutation—a change in the body's tumour suppressor genes that prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSH6
MSH6 or mutS homolog 6 is a gene that codes for DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 in the budding yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. It is the homologue of the human "G/T binding protein," (GTBP) also called p160 or hMSH6 (human MSH6). The MSH6 protein is a member of the Mutator S (MutS) family of proteins that are involved in DNA damage repair. Defects in hMSH6 are associated with atypical hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer not fulfilling the Amsterdam criteria for HNPCC. hMSH6 mutations have also been linked to endometrial cancer and the development of endometrial carcinomas. Discovery MSH6 was first identified in the budding yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' because of its homology to MSH2. The identification of the human GTBP gene and subsequent amino acid sequence availability showed that yeast MSH6 and human GTBP were more related to each other than any other MutS homolog, with a 26.6% amino acid identity. Thus, GTBP took on the name human MSH6, or hMSH6. Structure In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSH2
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 also known as MutS homolog 2 or MSH2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSH2'' gene, which is located on chromosome 2. MSH2 is a tumor suppressor gene and more specifically a caretaker gene that codes for a DNA mismatch repair (MMR) protein, MSH2, which forms a heterodimer with MSH6 to make the human MutSα mismatch repair complex. It also dimerizes with MSH3 to form the MutSβ DNA repair complex. MSH2 is involved in many different forms of DNA repair, including transcription-coupled repair, homologous recombination, and base excision repair. Mutations in the MSH2 gene are associated with microsatellite instability and some cancers, especially with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). At least 114 disease-causing mutations in this gene have been discovered. Clinical significance Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), sometimes referred to as Lynch syndrome, is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLH1
DNA mismatch repair protein Mlh1 or MutL protein homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MLH1'' gene located on chromosome 3. The gene is commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Orthologs of human MLH1 have also been studied in other organisms including mouse and the budding yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. Function Variants in this gene can cause hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (Lynch syndrome). It is a human homolog of the ''E. coli'' DNA mismatch repair gene, mutL, which mediates protein-protein interactions during mismatch recognition, strand discrimination, and strand removal. Defects in MLH1 are associated with the microsatellite instability observed in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described, but their full-length natures have not been determined. Role in DNA mismatch repair MLH1 protein is one component of a system of seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) is a hereditary predisposition to colon cancer. HNPCC includes (and was once synonymous with) Lynch syndrome, an autosomal dominant genetic condition that is associated with a high risk of colon cancer, endometrial cancer (second most common), ovary, stomach, small intestine, hepatobiliary tract, upper urinary tract, brain, and skin. The increased risk for these cancers is due to inherited genetic mutations that impair DNA mismatch repair. It is a type of cancer syndrome. Other HNPCC conditions include Lynch-like syndrome, polymerase proofreading-associated polyposis and familial colorectal cancer type X. Signs and symptoms Risk of cancer ''Lifetime risk and mean age at diagnosis for Lynch syndrome–associated cancers'' In addition to the types of cancer found in the chart above, it is understood that Lynch syndrome also contributes to an increased risk of small bowel cancer, pancreatic cancer, ureter/renal pelvis cancer, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the Colon (anatomy), colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include Lower gastrointestinal bleeding, blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, abdominal pain and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to lifestyle factors and genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol (drug), alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a adenoma, benign tumor, often in the form of a colorectal poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
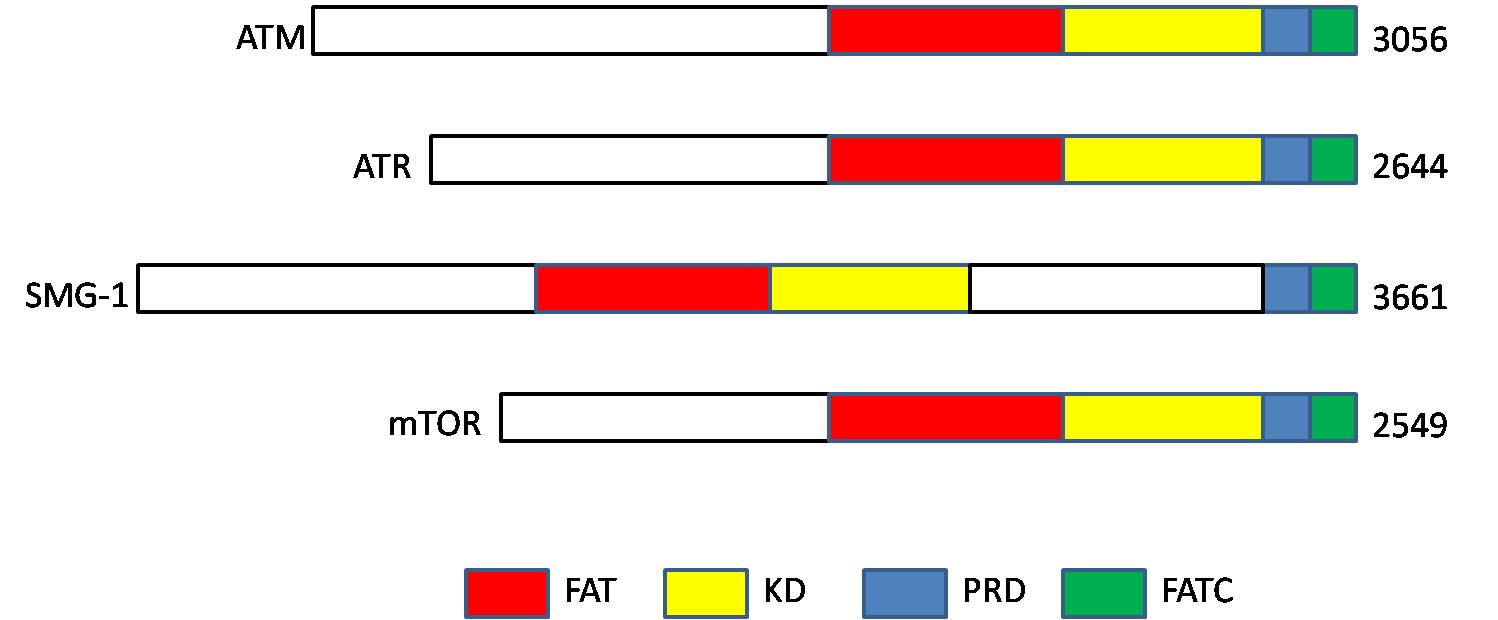
ATM Serine/threonine Kinase
ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks (canonical pathway), oxidative stress, topoisomerase cleavage complexes, splicing intermediates, R-loops and in some cases by single-strand DNA breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors. In 1995, the gene was discovered by Yosef Shiloh who named its product ATM since he found that its mutations are responsible for the disorder ataxia–telangiectasia. In 1998, the Shiloh and Kastan laboratories independently showed that ATM is a protein kinase whose activity is enhanced by DNA damage. Throughout the cell cycle DNA is monitored for damage. Damages result from errors during replication, by-products of met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHEK2
CHEK2 (Checkpoint kinase 2) is a tumor suppressor gene that encodes the protein CHK2, a serine-threonine kinase. CHK2 is involved in DNA repair, cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Mutations to the CHEK2 gene have been linked to a wide range of cancers. Gene location The CHEK2 gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 22 at position 12.1. Its location on chromosome 22 stretches from base pair 28,687,742 to base pair 28,741,904. Protein structure The CHEK2 protein encoded by the CHEK2 gene is a serine threonine kinase. The protein consists of 543 amino acids and the following domains: * N-terminal SQ/TQ cluster domain (SCD) * Central forkhead-associated (FHA) domain * C-terminal serine/threonine kinase domain (KD) The SCD domain contains multiple SQ/TQ motifs that serve as sites for phosphorylation in response to DNA damage. The most notable and frequently phosphorylated site being Thr68. CHK2 appears as a monomer in its inactive state. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA2
''BRCA2'' and BRCA2 () are human genes and their protein products, respectively. The official symbol (BRCA2, italic for the gene, nonitalic for the protein) and the official name (originally breast cancer 2; currently BRCA2, DNA repair associated) are gene nomenclature, maintained by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee. One alternative symbol, FANCD1, recognizes its association with the FANC proteins, FANC protein complex. Orthologs, styled ''Brca2'' and Brca2, are common in other vertebrate species. May 2021 ''BRCA2'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (specifically, a caretaker gene), found in all humans; its protein, also called by the synonym breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein, is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA2'' and ''BRCA1'' are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosome, chromosomal damage with an important role in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |