|
Gaius Titius Antonius Peculiaris
Gaius Titius Antonius Peculiaris () was a Roman ''eques'' from Aquincum who held important offices in Pannonia. Life Peculiaris was born in the Sergia tribe, most likely in Aquincum (modern-day Budapest). His father Gaius was a member of the ''gens Antonia'', a family that—along with the ''gens Iulia''—practically controlled the tax on trade (''portorium'') in Illyricum as tenants (''conductores''). He was thus a relative of Gaius Antonius Rufus, one of the earliest who started this job. Peculiaris, through the adoption of his father, was a late member of the ''gens Titia'', an Aquileian merchant family. His father kept his original ''nomen gentilicium'' and ''cognomen''. The Titius name was common in Northern Italy and Dalmatia. The Antonius name was rare among those Pannonians who descended from the Italian Peninsula and not the eastern provinces. Not many attestations of his ''cognomen'' survive, only three from the territory of Pannonia. It means "from own property" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquincum
Aquincum (, ) was an ancient city, situated on the northeastern borders of the province of Pannonia within the Roman Empire. The ruins of the city can be found in Budapest, the capital city of Hungary. It is believed that Marcus Aurelius wrote at least part of his book ''Meditations'' at Aquincum. History Aquincum was originally settled by the Eravisci, a Celtic tribe. Aquincum served as a military base ('' castrum''), having been part of the Roman border protection system called '' limes''. Around AD 41–54, a 500-strong cavalry unit arrived, and a Roman legion of 6,000 men ( Legio II Adiutrix) was stationed there by AD 89. The city gradually grew around the fortress, and after Pannonia was reorganised by the Romans in AD 103, Aquincum became the capital city of the Roman province of Pannonia Inferior until the administrative reform of Diocletian more than a century later. Under Hadrian, the city obtained municipal status, while under Septimius Severus, Aquincum became a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bátmonostor
Bátmonostor () is a village in Bács-Kiskun county, in the Southern Great Plain region of southern Hungary. Geography It covers an area of and has a population of 1503 people (2015). Demography Residents are Magyars. There is a small community of Croats The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ... in the village. References Populated places in Bács-Kiskun County {{Bacs-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluj-Napoca
Cluj-Napoca ( ; ), or simply Cluj ( , ), is a city in northwestern Romania. It is the second-most populous city in the country and the seat of Cluj County. Geographically, it is roughly equidistant from Bucharest (), Budapest () and Belgrade (). Located in the Someșul Mic river valley, the city is considered the unofficial capital of the Historical regions of Romania, historical province of Transylvania. For some decades prior to the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, it was the official capital of the Grand Principality of Transylvania. , 286,598 inhabitants live in the city. The Cluj-Napoca metropolitan area had a population of 411,379 people, while the population of the peri-urbanisation, peri-urban area is approximately 420,000. According to a 2007 estimate, the city hosted an average population of over 20,000 students and other non-residents each year from 2004 to 2007. The city spreads out from St. Michael's Church, Cluj-Napoca, St. Michael's Church in Unirii Square, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Museum Of Transylvanian History
The National Museum of Transylvanian History (, ) is a history and archaeology museum in the city of Cluj-Napoca Cluj-Napoca ( ; ), or simply Cluj ( , ), is a city in northwestern Romania. It is the second-most populous city in the country and the seat of Cluj County. Geographically, it is roughly equidistant from Bucharest (), Budapest () and Belgrade ( ..., Romania. It features a permanent exhibition, as well as temporary exhibitions, the "Tezaur" exhibition, and Pharmacy Historical collection—this last opened in the Cluj-Napoca Hintz House, Hintz House, an historical building in the city's center. The beginnings of the museum date back to 1859 with the foundation of the Society of the Transylvanian Museum, featuring collections of antiquities and botanical, zoological and mineralogical specimens. In 1929 the collection of artefacts was transferred to the Romanian Institute of Classical Studies. After several further movements, caused by lack of space, the collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pécs
Pécs ( , ; ; Slovak language, Slovak: ''Päťkostolie''; also known by #Name, alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the fifth largest city in Hungary, on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the country's southwest, close to the border with Croatia. It is the administrative and economic centre of Baranya County, and the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Pécs. A city dating back to ancient times, settled by the Celts and the Romans, it was made an episcopal see in early medieval Hungary. It has University of Pécs, the oldest university in the country, and is one of its major cultural centers. Pécs has a rich cultural and architectural heritage stemming from 150 years of Ottoman rule, and it contains the largest number of Turkish Ottoman buildings found in any city in Central Europe. It is historically a multi-ethnic city where many cultures have interacted through 2,000 years of history. In recent times, it has been recognize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forum (Roman)
A forum (Latin: ''forum'', "public place outdoors", : ''fora''; English : either ''fora'' or ''forums'') was a public square in a municipium, or any civitas, of Ancient Rome reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, along with the buildings used for shops and the stoas used for open stalls. But such fora functioned secondarily for multiple purposes, including as social meeting places for discussion. Many fora were constructed at remote locations along a road by the magistrate responsible for the road, in which case the forum was the only settlement at the site and had its own name, such as Forum Popili or Forum Livi. Functions In addition to its standard function as a marketplace, a forum was a gathering place of great social significance, and often the scene of diverse activities, including political discussions and debates, rendezvous, meetings, et cetera. In that case, it supplemented the function of a '' conciliabulum''. Every municipality () ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymphaeum
A ''nymphaeum'' (Latin : ''nymphaea'') or ''nymphaion'' (), in ancient Greece and Rome, was a monument consecrated to the nymphs, especially those of springs. These monuments were originally natural grottoes, which tradition assigned as habitations to the local nymphs. They were sometimes so arranged as to furnish a supply of water, as at Pamphylian Side. A nymphaeum dedicated to a local water nymph, Coventina, was built along Hadrian's Wall, in the northernmost reach of the Roman Empire. Subsequently, artificial grottoes took the place of natural ones. Roman period The nymphaea of the Roman period extended the sacral use to recreational aims. They were borrowed from the constructions of the Hellenistic east. At a minimum, Roman nymphaea may be no more than a niche set into a garden wall. But many larger buildings are known. Most were rotundas, and were adorned with statues and paintings. They served the threefold purpose of sanctuaries, reservoirs and assembly-rooms. A sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munera (ancient Rome)
In ancient Rome, (Latin plural; singular ) were public works and entertainments provided for the benefit of the Roman people by individuals of high status and wealth. means "duty, obligation" (cf. English " munificence"), expressing the individual's responsibility to provide a service or contribution to his community. The word was often a synonym for gladiatorial combat, which was originally sponsored as a funeral tribute at the tomb of a deceased Roman magnate by his heir. depended on the private largesse of individuals, in contrast to , which were games, athletic contests or spectacles sponsored by the state. Types and evolution The most famous ''munera'' were the gladiatorial contests, which began as a service or gift rendered by the heirs of the deceased at funeral games. ''Munera'' could refer to the provision of such public services, or to the services themselves. In describing Rome's provision of water to the public, Frontinus describes certain lavishly decorated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
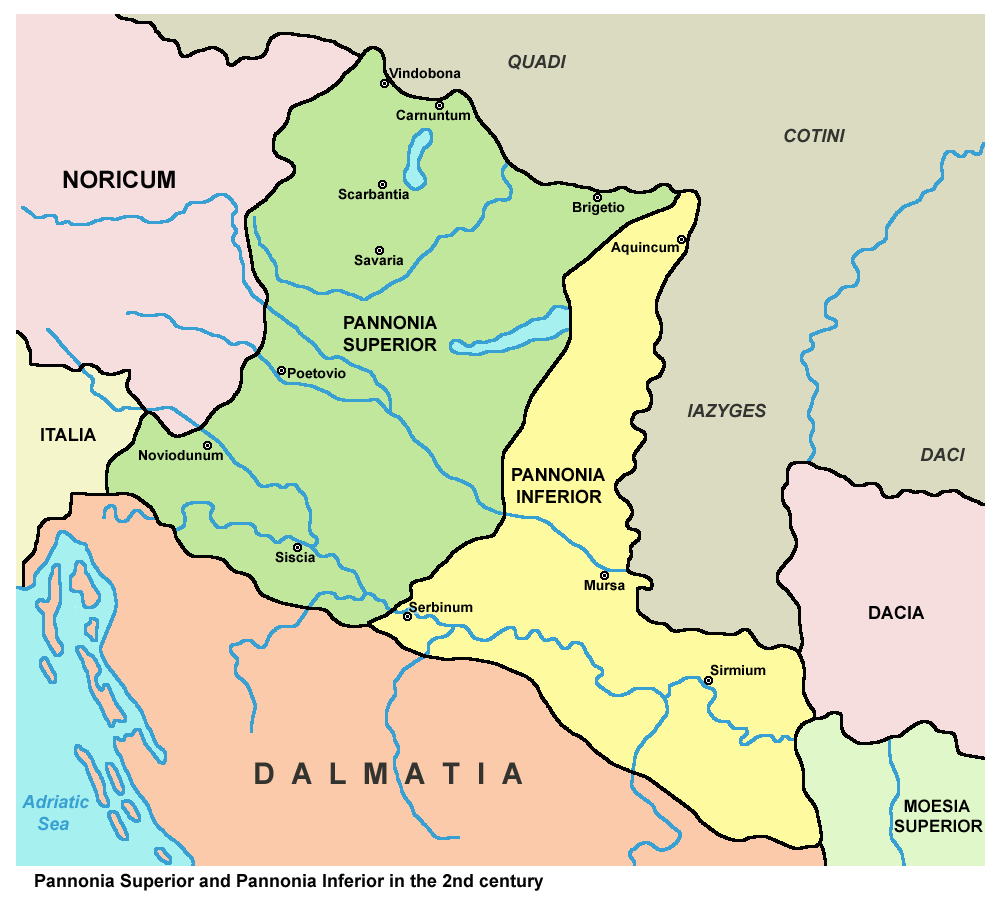
Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east. Settlements Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included: * ''Sirmium'' (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors. * '' Aquincum'' (Buda), the provincial capital. * ''Cuccium'' ( Ilok) * ''Cibalae'' (Vinkovci) * ''Mursa'' ( Osijek) * ''Certissa'' ( Đakovo) * ''Marsonia'' (Slavonski Brod) * ''Sopianae'' (Pécs) Aftermath and legacy The province was yet again split during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cursus Honorum
The , or more colloquially 'ladder of offices'; ) was the sequential order of public offices held by aspiring politicians in the Roman Republic and the early Roman Empire. It was designed for men of senatorial rank. The comprised a mixture of military and political administration posts; the ultimate prize for winning election to each "rung" in the sequence was to become one of the two consuls in a given year. These rules were altered and flagrantly ignored in the course of the last century of the Republic. For example, Gaius Marius held consulships for five years in a row between 104 and 100 BC. He was consul seven times in all, also serving in 107 and 86. Officially presented as opportunities for public service, the offices often became mere opportunities for self-aggrandizement. The constitutional reforms of Sulla between 82 and 79 BC required a ten-year interval before holding the same office again for another term. To have held each office at the youngest pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duumviri
The duumviri (Latin for 'two men'), originally duoviri and also known in English as the duumvirs, were any of various joint magistrates of ancient Rome. Such pairs of Roman magistrates were appointed at various periods of Roman history both in Rome itself and in the colonies and '' municipia''. ''Duumviri iuri'' or ''iure dicundo'' were the highest judicial magistrates in the cities of Italy and its provinces. Their chief duties were concerned with the administration of justice. The activities of these individuals are described in the local statutes such as '' Lex Julia'', '' Lex Irnitana'', '' Lex Malacitana'', ''Lex Rubria'', ''Lex Coloniae'', and ''Genetivae Iuliae''. The office was determined by election and lasted one year. The duumviri were also expected to deal with public finance of a city and with proceedings in the Ordo decurionum (town council) and to run the elections in the comitium (assembly). Combined with the aediles, they formed the ''quattuorviri'', a boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamen
A (plural ''flamines'') was a priest of the ancient Roman religion who was assigned to one of fifteen deities with official cults during the Roman Republic. The most important of these were the three (or "major priests"), who served the important Roman gods Jupiter, Mars, and Quirinus. The remaining twelve were the ("lesser priests"). Two of the served deities whose names are now unknown; among the others are deities about whom little is known other than the name. During the Imperial era, the cult of a deified emperor () also had a flamen. The fifteen Republican flamens were members of the Pontifical College, who administered state-sponsored religion. When the office of flamen was vacant, a could serve as a temporary replacement, although only the is known to have substituted for the , one of the . Etymology The etymology of remains obscure, and perhaps undecidable. Andrew Sihler ''New Comparative Grammar of Greek and Latin,'' Oxford University Press 1995 p.198:’ Tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |