|
FGI-106
FGI-106 is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed as a potential treatment for enveloped RNA viruses, in particular viral hemorrhagic fevers from the bunyavirus, flavivirus and filovirus families. It acts as an inhibitor which blocks viral entry into host cells. In animal tests FGI-106 shows both prophylactic and curative action against a range of deadly viruses for which few existing treatments are available, including the bunyaviruses hantavirus, Rift Valley fever virus and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, the flavivirus dengue virus, and the filoviruses Ebola virus and Marburg virus. See also * Brincidofovir * BCX4430 * Favipiravir * FGI-103 * FGI-104 * LJ-001 * TKM-Ebola * ZMapp References Anti–RNA virus drugs Antiviral drugs Ebola Experimental antiviral drugs Nitrogen heterocycles Heterocyclic compounds with 4 rings Dimethylamino compounds {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCX4430
Galidesivir (BCX4430, immucillin-A) is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog (a type of nucleoside analog). It was developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals with funding from NIAID, originally intended as a treatment for hepatitis C, but subsequently developed as a potential treatment for deadly filovirus infections such as Ebola virus disease and Marburg virus disease, as well as Zika virus. Currently, galidesivir is under phase 1 human trial in Brazil for coronavirus. It also shows broad-spectrum antiviral effectiveness against a range of other RNA virus families, including bunyaviruses, arenaviruses, paramyxoviruses, coronaviruses, flaviviruses, and phleboviruses. Galidesivir has been demonstrated to protect against both Ebola and Marburg viruses in both rodents and monkeys, even when administered up to 48 hours after infection, and development for use in humans was then being fast-tracked due to concerns about the lack of treatment options for the 2013-2016 Ebola virus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LJ-001
LJ-001 is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed as a potential treatment for enveloped viruses. It acts as an inhibitor which blocks viral entry into host cells at a step after virus binding but before virus–cell fusion, and also irreversibly inactivates the virions themselves by generating reactive singlet oxygen molecules which damage the viral membrane. In cell culture tests ''in vitro'', LJ-001 was able to block and disable a wide range of different viruses, including influenza A, filoviruses, poxviruses, arenaviruses, bunyaviruses, paramyxoviruses, flaviviruses, and HIV. Unfortunately LJ-001 itself was unsuitable for further development, as it has poor physiological stability and requires light for its antiviral mechanism to operate. However the discovery of this novel mechanism for blocking virus entry and disabling the virion particles has led to LJ-001 being used as a lead compound to develop a novel family of more effective antiviral drugs with improved properties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FGI-104
FGI-104 is the name of an experimental broad-spectrum antiviral drug, with activity against a range of viruses including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, Ebola virus, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. Mechanism The drug acts by inhibiting the protein TSG101, which transports newly manufactured virions to the exterior of an infected cell, thus breaking the replication cycle of the virus. In pre-clinical studies, FGI-104 has been shown to protect mice from Ebola virus disease Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infe .... See also * FGI-103 * FGI-106 * LJ-001 References Antiviral drugs Ebola Quinolines Chloroarenes Phenols Phenol ethers Diethylamino compounds Primary alcohols {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FGI-103
FGI-103 is an antiviral drug developed as a potential treatment for the filoviruses Ebola virus and Marburg virus Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the '' Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus '' Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhag .... In tests on mice FGI-103 was effective against both Ebola and Marburg viruses when administered up to 48 hours after infection. The mechanism of action of FGI-103 has however not yet been established, as it was found not to be acting by any of the known mechanisms used by similar antiviral drugs. See also * FGI-104 * FGI-106 * LJ-001 References Antiviral drugs Ebola Experimental antiviral drugs Benzimidazoles Benzofurans {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Favipiravir
Favipiravir, sold under the brand name Avigan among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat influenza in Japan. It is also being studied to treat a number of other viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Like the experimental antiviral drugs T-1105 and T-1106, it is a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative. It is being developed and manufactured by Toyama Chemical (a subsidiary of Fujifilm) and was approved for medical use in Japan in 2014. In 2016, Fujifilm licensed it to Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical Co. It became a generic drug in 2019. Medical use Favipiravir has been approved to treat influenza in Japan. It is, however, only indicated for novel influenza (strains that cause more severe disease) rather than seasonal influenza. As of 2020, the probability of resistance developing appears low. Side effects There is evidence that use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Teratogenic and embryotoxic effects were shown on four animal species. In one case report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Heterocycles
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal in 1790 when it was found that nitrogen was present in nitric acid and nitrates. Antoine Lavoisier suggested instead the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Antiviral Drugs
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
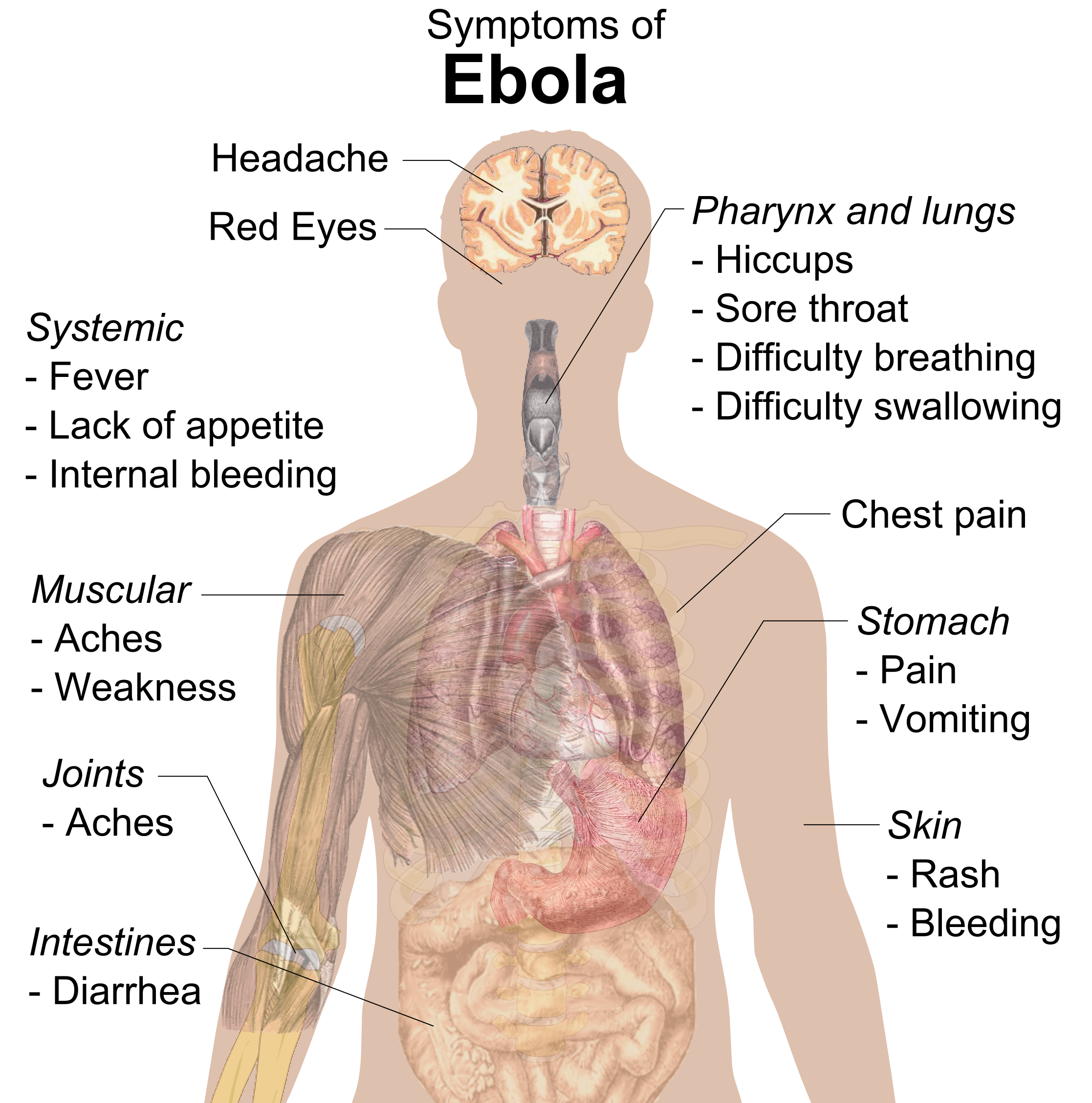
Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after infection. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. It kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between 6 and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start.Ebola in Uganda: An Ebola vaccine was approved by the US FDA in December 2019. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, herpes viruses, the hepatitis B and C viruses, and influenza A and B viruses. Viruses use the host's cells to replicate and this makes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZMapp
ZMapp is an experimental biopharmaceutical medication comprising three chimeric monoclonal antibodies under development as a treatment for Ebola virus disease. Two of the three components were originally developed at the Public Health Agency of Canada's National Microbiology Laboratory (NML), and the third at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases; the cocktail was optimized by Gary Kobinger, a research scientist at the NML and underwent further development under license by Mapp Biopharmaceutical. ZMapp was first used on humans during the Western African Ebola virus epidemic, having only been previously tested on animals and not yet subjected to a randomized controlled trial. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) ran a clinical trial starting in January 2015 with subjects from Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Liberia aiming to enroll 200 people, but the epidemic waned and the trial closed early, leaving it too statistically underpowered to give a meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TKM-Ebola
TKM-Ebola was an experimental antiviral drug for Ebola disease that was developed by Arbutus Biopharma (formerly Tekmira Pharmaceuticals Corp.) in Vancouver, Canada. The drug candidate was formerly known as Ebola-SNALP. TKM-Ebola is a combination of small interfering RNAs targeting three of the seven proteins in Ebola virus: Zaire Ebola L polymerase, Zaire Ebola membrane-associated protein (VP24), and Zaire Ebola polymerase complex protein (VP35).David Kroll for Forbes. 7 August 201FDA Moves On Tekmira's Ebola Drug While Sarepta's Sits Unused/ref> By down-regulating these three proteins, TKM-Ebola inhibits virus replication and eliminates the infection. The drug was effective in rhesus monkeys infected with Ebola. After the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014, the new variant responsible for it was isolated from several Ebola virus families and the specific genomic sequence was determined. The company re-designed TKM-Ebola and renamed it as "TKM-Ebola-Guinea". In January 2014, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |