|
Elliptic Cone
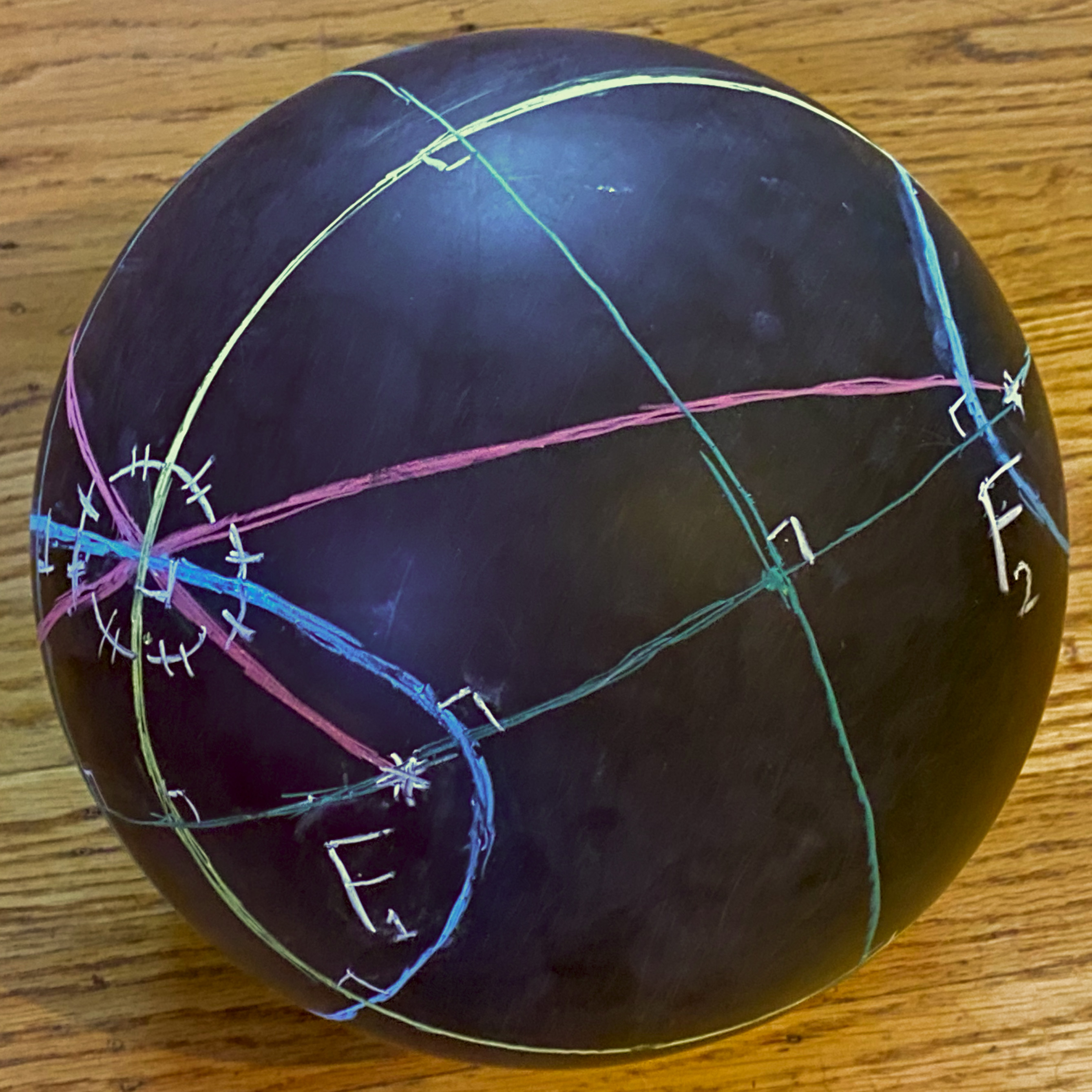
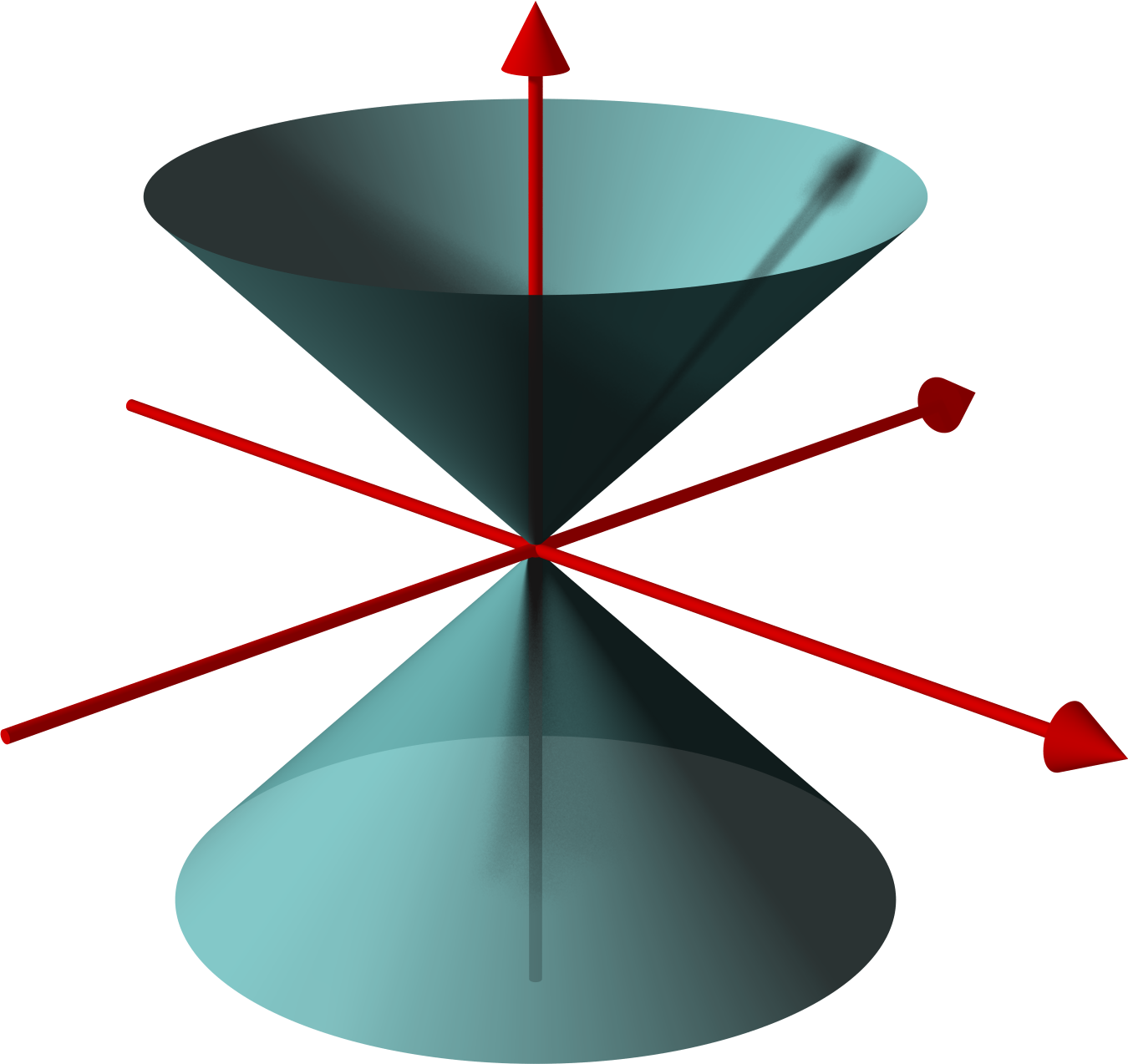
An elliptical cone is a cone with an elliptical base. It is a generalization of the '' circular cone'' and a special case of the '' generalized cone''. The term might refer to the solid figure bounded by the base or only to the lateral conic surface, a quadric called ''conical quadric'' or ''quadratic cone''. In a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, an elliptic cone is the locus of an equation of the form: \frac + \frac = z^2 . It is an affine image of the unit right circular cone with equation x^2+y^2=z^2\ . From the fact that the affine image of a conic section is a conic section of the same type (ellipse, parabola, etc.), any plane section of an elliptic cone is a conic section (see Circular section#Elliptic cone). The intersection curve of an elliptic cone with a concentric sphere is a ''spherical conic In mathematics, a spherical conic or sphero-conic is a curve on the sphere, the intersection of the sphere with a concentric elliptic cone. It is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptical Cone Quadric
Elliptical may mean: * having the shape of an ellipse, or more broadly, any oval shape ** in botany, having an elliptic leaf shape ** of aircraft wings, having an elliptical planform * characterised by ellipsis (the omission of words), or by concision In common usage and linguistics, concision (also called conciseness, succinctness, terseness, brevity, or laconicism) is a communication principle of eliminating redundancy (linguistics), redundancy,UNT Writing Lab. "Concision, Clarity, and Cohes ... more broadly * elliptical trainer, an exercise machine See also * Ellipse (other) * Ellipsis (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison-Wesley
Addison–Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson plc, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison–Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison–Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison–Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include '' The Art of Computer Programming'', '' The C++ Programming Language'', '' The Mythical Man-Month'', and '' Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison–Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison–Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Conic
In mathematics, a spherical conic or sphero-conic is a curve on the sphere, the intersection of the sphere with a concentric elliptic cone. It is the spherical analog of a conic section (ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola) in the plane, and as in the planar case, a spherical conic can be defined as the locus (mathematics), locus of points the sum or difference of whose great-circle distances to two focus (geometry), foci is constant. By taking the antipodal point to one focus, every spherical ellipse is also a spherical hyperbola, and vice versa. As a space curve, a spherical conic is a quartic function, quartic, though its orthogonal projections in three Principal axis theorem, principal axes are planar conics. Like planar conics, spherical conics also satisfy a "reflection property": the great-circle arcs from the two foci to any point on the conic have the tangent and normal to the conic at that point as their angle bisectors. Many theorems about conics in the plane extend to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Section
In geometry, a circular section is a circle on a quadric surface (such as an ellipsoid or hyperboloid). It is a special plane (geometry), plane section of the quadric, as this circle is the intersection with the quadric of the plane containing the circle. Any plane section of a sphere is a circular section, if it contains at least 2 points. Any surface of revolution, quadric of revolution contains circles as sections with planes that are orthogonal to its axis; it does not contain any other circles, if it is not a sphere. More hidden are circles on other quadrics, such as tri-axial ellipsoids, elliptic cylinders, etc. Nevertheless, it is true that: *Any quadric surface which contains ellipses contains circles, too. Equivalently, all quadric surfaces contain circles except parabolic and hyperbolic cylinders and hyperbolic paraboloids. If a quadric contains a circle, then every intersection of the quadric with a plane parallel to this circle is also a circle, provided it contains at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane Section
In geometry and science, a cross section is the non-empty intersection (set theory), intersection of a solid body in three-dimensional space with a Plane (geometry), plane, or the analog in higher-dimensional spaces. Cutting an object into slices creates many parallel cross-sections. The boundary of a cross-section in three-dimensional space that is parallel to two of the Cartesian coordinate system, axes, that is, parallel to the plane determined by these axes, is sometimes referred to as a contour line; for example, if a plane cuts through mountains of a raised-relief map parallel to the ground, the result is a contour line in two-dimensional space showing points on the surface of the mountains of equal elevation. In technical drawing a cross-section, being a Planar projection, projection of an object onto a plane that intersects it, is a common tool used to depict the internal arrangement of a 3-dimensional object in two dimensions. It is traditionally crosshatched with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabola
In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is Reflection symmetry, mirror-symmetrical and is approximately U-shaped. It fits several superficially different Mathematics, mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. One description of a parabola involves a Point (geometry), point (the Focus (geometry), focus) and a Line (geometry), line (the Directrix (conic section), directrix). The focus does not lie on the directrix. The parabola is the locus (mathematics), locus of points in that plane that are equidistant from the directrix and the focus. Another description of a parabola is as a conic section, created from the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane (geometry), plane Parallel (geometry), parallel to another plane that is tangential to the conical surface. The graph of a function, graph of a quadratic function y=ax^2+bx+ c (with a\neq 0 ) is a parabola with its axis parallel to the -axis. Conversely, every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conic Section
A conic section, conic or a quadratic curve is a curve obtained from a cone's surface intersecting a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though it was sometimes considered a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a '' focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curve of degree 2; that is, as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Circular Cone
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the ''apex'' or '' vertex''. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lines, it extends infinitely far. In the case of lines, the cone extends infinitely far in both directions from the apex, in which case it is sometimes called a ''double cone''. Each of the two halves of a double cone split at the apex is called a ''nappe''. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is an open surface, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Map
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, '' affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a function which maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lying on a straight line. If is the point set of an affine space, then every affine transformation on can be re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (mathematics)
In geometry, a locus (plural: ''loci'') (Latin word for "place", "location") is a set (mathematics), set of all Point (geometry), points (commonly, a line (geometry), line, a line segment, a curve (mathematics), curve or a Surface (topology), surface), whose location satisfies or is determined by one or more specified conditions.. The set of the points that satisfy some property is often called the ''locus of a point'' satisfying this property. The use of the singular in this formulation is a witness that, until the end of the 19th century, mathematicians did not consider infinite sets. Instead of viewing lines and curves as sets of points, they viewed them as places where a point may be ''located'' or may move. History and philosophy Until the beginning of the 20th century, a geometrical shape (for example a curve) was not considered as an infinite set of points; rather, it was considered as an entity on which a point may be located or on which it moves. Thus a circle (mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone
In geometry, a cone is a three-dimensional figure that tapers smoothly from a flat base (typically a circle) to a point not contained in the base, called the '' apex'' or '' vertex''. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lines, it extends infinitely far. In the case of lines, the cone extends infinitely far in both directions from the apex, in which case it is sometimes called a ''double cone''. Each of the two halves of a double cone split at the apex is called a ''nappe''. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is an open surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane (geometry), plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point (geometry), point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the positive and negative numbers, signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called ''coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the ''Origin (mathematics), origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes direction (geometry), directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |