|
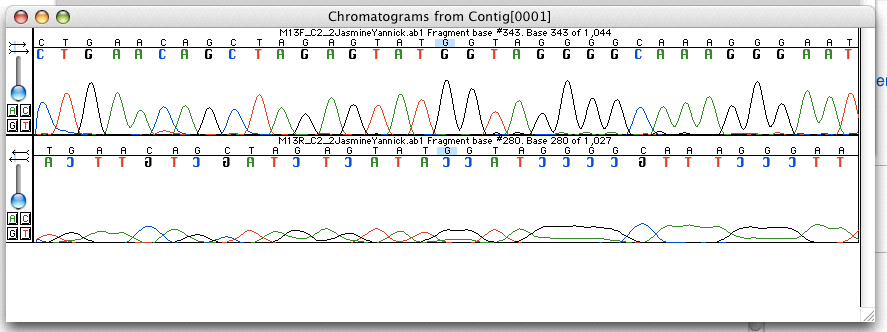
Electropherogram
An electropherogram (also called electrophoretogram, sequencing chromatogram, EPG, and e-gram) is a record or chart produced when electrophoresis is used in an analytical technique, primarily in the fields of forensic biology, molecular biology, and biochemistry. The method plots data points that represent a specific time and fluorescence intensity at various wavelengths of light to represent a DNA profile.. In the field of genetics, an electropherogram is a plot of DNA fragment sizes, typically used for genotyping such as DNA sequencing. The data is plotted with time, shown via base pairs (bps), on the x-axis and fluorescence intensity on the y-axis. Such plots are often achieved using an instrument such as an automated DNA sequencer paired with capillary electrophoresis (CE). Such electropherograms may be used to determine DNA sequence genotypes, or genotypes that are based on the length of specific DNA fragments or number of short tandem repeats (STR) at a specific locus b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Profiling
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting and genetic fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is called DNA barcoding. DNA profiling is a forensic technique in criminal investigations, comparing criminal suspects' profiles to DNA evidence so as to assess the likelihood of their involvement in the crime. It is also used in paternity testing, to establish immigration eligibility, and in genealogical and medical research. DNA profiling has also been used in the study of animal and plant populations in the fields of zoology, botany, and agriculture. Background Starting in the mid 1970s, scientific advances allowed the use of DNA as a material for the identification of an individual. The first patent covering the direct use of DNA variation for forensicsUS5593832A was filed by Jeffrey Glassberg in 1983, based upon work he had done while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Biology
Forensic biology is the application of biological principles and techniques in the investigation of criminal and civil cases. Forensic biology is primarily concerned with analyzing biological and serological evidence in order to obtain a DNA profile, which aids law enforcement in the identification of potential suspects or unidentified remains. This field encompasses various sub-branches, including forensic anthropology, forensic entomology, forensic odontology, forensic pathology, and forensic toxicology. History The first recorded use of forensic procedures dates back to the 7th century when the concept of using fingerprints as a means of identification was first established. By the end of the 7th century, forensic procedures were being used to determine the guilt of criminals. An early pioneer in criminal identification through biology was Alphonse Bertillon, also known as the "father of criminal identification". In 1879, he introduced a scientific approach to personal ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis Of Nucleic Acids
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids is an analytical technique to separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules are placed on a gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids (which are negatively charged due to their sugar-phosphate backbone) to migrate toward the positively charged anode. The molecules separate as they travel through the gel based on the each molecule's size and shape. Longer molecules move more slowly because the gel resists their movement more forcefully than it resists shorter molecules. After some time, the electricity is turned off and the positions of the different molecules are analyzed. The nucleic acid to be separated can be prepared in several ways before separation by electrophoresis. In the case of large DNA molecules, the DNA is frequently cut into smaller fragments using a DNA restriction endonuclease (or restriction enzyme). In other instances, such as PCR amplified samples, enzymes present in the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatogram
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be ''preparative'' or ''analytical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Paternity Testing
DNA paternity testing uses DNA profiling, DNA profiles to determine whether an individual is the biology, biological parent of another individual. Paternity testing can be essential when the rights and duties of the father are in issue, and a child's Father, paternity is in doubt. Tests can also determine the likelihood of someone being a biological grandparent. Though genetics, genetic testing is the most reliable standard, older methods also exist, including blood type, ABO blood group typing, analysis of various other proteins and enzymes, or using human leukocyte antigen antigens. The current paternity testing techniques are polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP). Paternity testing can now also be performed while the woman is still pregnant from a blood draw. DNA testing is currently the most advanced and accurate technology to determine parentage. In a DNA paternity test, the result (called the 'probability of parentage) is 0% whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Genealogy
Genetic genealogy is the use of genealogical DNA tests, i.e., DNA profiling and DNA testing, in combination with traditional genealogical methods, to infer genetic relationships between individuals. This application of genetics came to be used by family historians in the 21st century, as DNA tests became affordable. The tests have been promoted by amateur groups, such as Surname DNA project, surname study groups or regional genealogical groups, as well as research projects such as the Genographic Project. about 30 million people had been tested. As the field developed, the aims of practitioners broadened, with many seeking knowledge of their ancestry beyond the recent centuries, for which traditional pedigrees can be constructed. History The investigation of surnames in genetics Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics and features. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance. Biometric identifiers are the distinctive, measurable characteristics used to label and describe individuals. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological characteristics which are related to the shape of the body. Examples include, but are not limited to fingerprint, palm veins, face recognition, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris recognition, retina, odor/scent, voice, shape of ears and gait. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of behavior of a person, including but not limited to mouse movement, typing rhythm, gait, signature, voice, and behavioral profiling. Some researchers have coined the term behaviometrics (behavioral biom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Genetics
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can either be inserted randomly or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be ''preparative'' or ''analytical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, speciation, and population stratification, population structure. Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics. Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, laboratory, and field work. Population genetic models are used both for statistical inference from DNA sequence data and for proof/disproof of concept. What sets population genetics apart from newer, more phenotypic approaches to modelling evolution, such as evolutionary game theory and evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogical DNA Test
A genealogical DNA test is a DNA-based Genetic testing, genetic test used in genetic genealogy that looks at specific locations of a person's genome in order to find or verify ancestral genealogical relationships, or (with lower reliability) to estimate the ethnicity, ethnic mixture of an individual. Since different testing companies use different ethnic reference groups and different matching algorithms, ethnicity estimates for an individual vary between tests, sometimes dramatically. Three principal types of genealogical DNA tests are available, with each looking at a different part of the genome and being useful for different types of genealogical research: Genealogical DNA test#Autosomal DNA (atDNA) testing, autosomal (atDNA), Genealogical DNA test#Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) testing, mitochondrial (mtDNA), and Genealogical DNA test#Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) testing, Y-chromosome (Y-DNA). Autosomal tests may result in a large number of DNA matches to both males and females who have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |