|
Ekembo
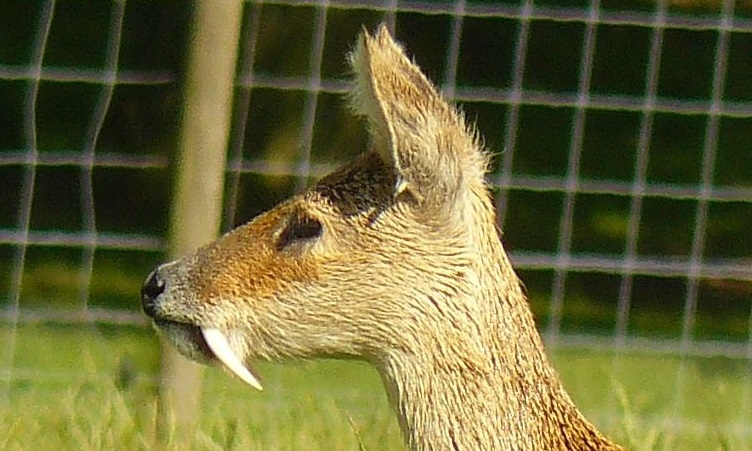
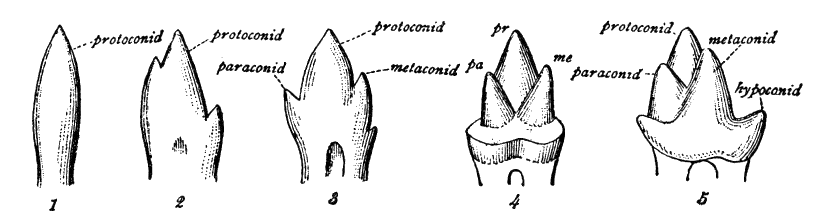
''Ekembo'' is an early ape (hominoid) genus found in 17- to 20-million-year-old sediments from the Miocene epoch. Specimens have been found at sites around the ancient Kisingiri volcano in Kenya on Rusinga Island and Mfangano Island in Lake Victoria. The name ''Ekembo'' is Suba for "ape" or "monkey". To account for substantial morphological variation in the genus ''Proconsul'', two species, ''P. nyanzae'' and ''P. heseloni'', were placed in the new genus ''Ekembo''. ''Ekembo'' is one of the earliest ape (Hominoids), after having diverged from the old world monkeys. The Dendropithecidae appear to be sister to ''Ekembo''. ''Ekembo'' was found to be paraphyletic with respect to ''Proconsul'' and the more advanced Hominoidea. Description ''Ekembo'' is distinguished from other early Miocene catarrhines on the basis of dental and mandibular morphology. The molars of ''Ekembo'' are more rounded or bunodont than those of ''Proconsul'' and the canine teeth taper to a point while those o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekembo Nyanzae
''Ekembo nyanzae'', originally classed as a species of ''Proconsul'', is a species of fossil primate first discovered by Louis Leakey on Rusinga Island in 1942, which he published in ''Nature'' in 1943. It is also known by the name ''Dryopithecus africanus''. A joint publication of Wilfrid Le Gros Clark and Louis Leakey in 1951, "The Miocene Hominoidea of East Africa", first defines ''Proconsul nyanzae''. In 1965 Simons and Pilbeam replaced ''Proconsul'' with ''Dryopithecus'', using the same species names. In 1967, Louis defined '' Kenyapithecus africanus'' on seven fossils from Rusinga Island. He saw it as an ancestor of ''wickeri'' and also of man, with a date of 20 mya in the middle Miocene. Another fossil found by the VanCouverings on Rusinga in 1967 seemed to confirm ''africanus''. In 1969 Simons and Pilbeam moved ''Kenyapithecus africanus'' into ''Dryopithecus nyanzae''. By 1978 the genus had recovered from the Dryopithecine event and was back to ''Proconsul''. In that yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proconsul (mammal)
''Proconsul'' is an extinct genus of primates that existed from 21 to 17 million years ago during the Miocene epoch. Fossil remains are present in Eastern Africa, including Kenya and Uganda. Four species have been classified to date: Proconsul africanus, ''P. africanus'', ''P. gitongai'', ''Proconsul major, P. major'' and ''P. meswae''. The four species differ mainly in body size. Environmental reconstructions for the Early Miocene ''Proconsul'' sites are still tentative and range from forested environments to more open, arid grasslands. The gibbon and great apes, including humans, are held in evolutionary biology to share a common ancestral lineage, which may have included ''Proconsul''. Its name, meaning "before Consul" (Consul being a certain chimpanzee that, at the time of the genus's discovery, was on display in London), implies that it is ancestral to the Common chimpanzee, chimpanzee. It might also be ancestral to the rest of the apes. Description The genus had a mixture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Primates Of Africa
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the connections between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Primate Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, dioecious species, which consist of most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, color, markings, or behavioral or cognitive traits. Male-male reproductive competition has evolved a diverse array of sexually dimorphic traits. Aggressive utility traits such as "battle" teeth and blunt heads reinforced as battering rams are used as weapons in aggressive interactions between rivals. Passive displays such as ornamental feathering or song-calling have also evolved mainly through sexual selection. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', when both biological sexes are phenotype, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canine Tooth
In mammalian oral anatomy, the canine teeth, also called cuspids, dogteeth, eye teeth, vampire teeth, or fangs, are the relatively long, pointed teeth. In the context of the upper jaw, they are also known as '' fangs''. They can appear more flattened, however, causing them to resemble incisors and leading them to be called ''incisiform''. They developed and are used primarily for firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally as weapons. They are often the largest teeth in a mammal's mouth. Individuals of most species that develop them normally have four, two in the upper jaw and two in the lower, separated within each jaw by incisors; humans and dogs are examples. In most species, canines are the anterior-most teeth in the maxillary bone. The four canines in humans are the two upper maxillary canines and the two lower mandibular canines. They are specially prominent in dogs (Canidae), hence the name. Details There are generally four canine teeth: two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendropithecidae
The family Dendropithecidae is an extinct family of catarrhine apes. They date from the Early Miocene, around 20-12 million years ago. Fossils of the two ''Dendropithecus'' species, ''Dendropithecus macinnesi'' and ''Dendropithecus ugandensis'', have been found in East Africa, including several partial skeletons of ''Dendropithecus macinnesi'' on Rusinga Island in Lake Victoria. Other species are ''Simiolus andrewsi'', ''Simiolus cheptumoae'', ''Simiolus enjiessi''. ''Micropithecus clarki'' and ''Micropithecus leakeyorum'' may not be part Dendropithecidae, and may be sister to the crown Catarrhini (or, depending on the definition, the apes and the Cercopithecidae Old World monkeys are primates in the family (biology), family Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genus, genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons (genus ''Papio''), red colo ... may have emerged in the Dendropithecidae). The later Nyanzapithecin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |