|
Eavor Technologies
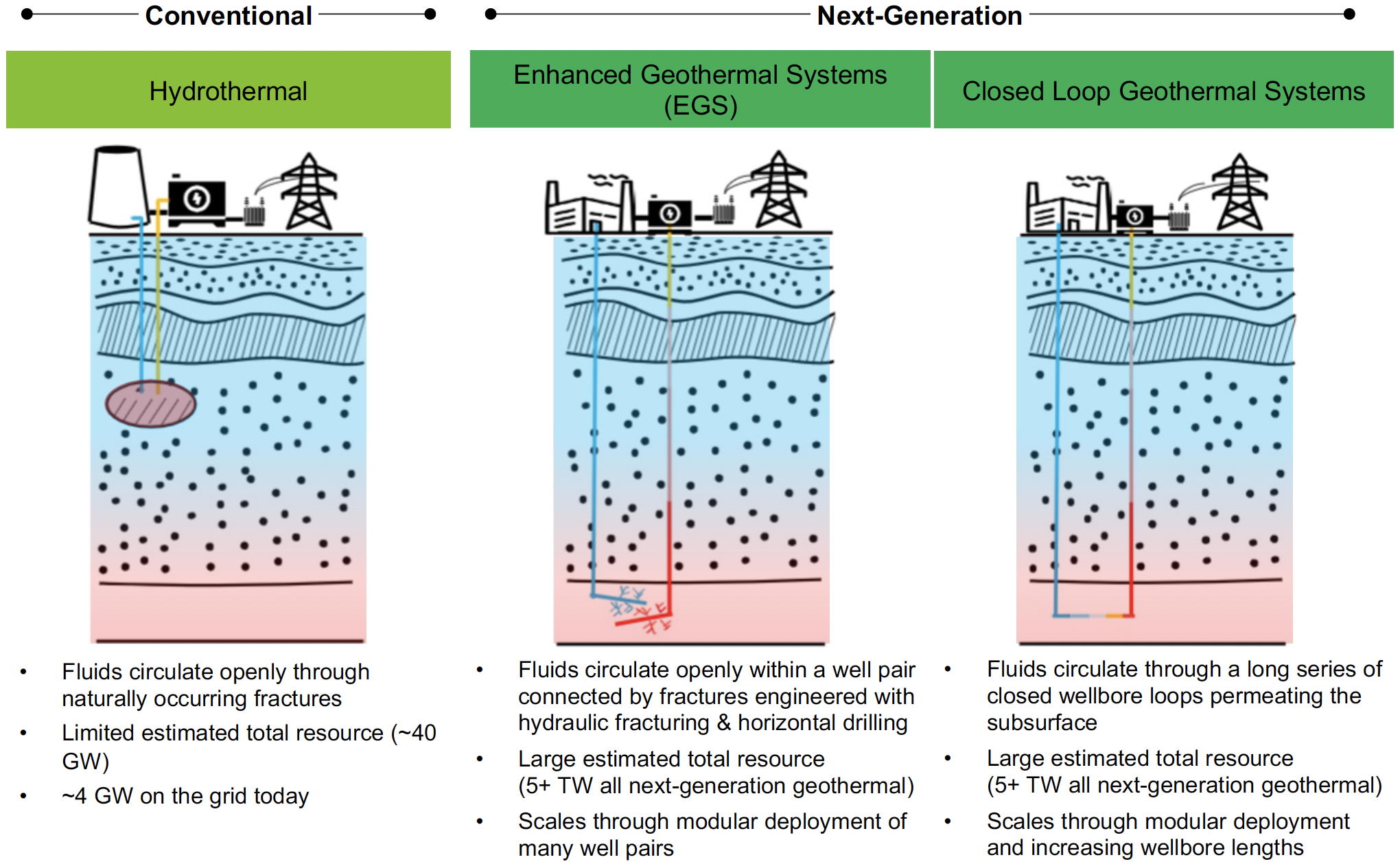
Eavor Technologies Inc. ( ) is a global geothermal technology company headquartered in Calgary, Alberta. The firm was founded in 2017 with the goal of producing a scalable form of baseload energy. The main difference between traditional geothermal and Eavor-Loop™ is scalability. Traditional geothermal energy systems rely on specific geological conditions, such as the presence of naturally occurring hot underground aquifers, to extract heat for energy generation. These conditions are relatively rare, limiting the global applicability of traditional geothermal technology. The Eavor-Loop™, in contrast, is an Advanced Geothermal System (AGS), or a closed-loop system, designed to operate independently of such geological constraints, offering the potential for broader scalability in diverse locations. A report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) describes these advancements as innovative next-generation geothermal technologies due to their reservoir-independent approach. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for millennia. Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since Roman times. Geothermal power (generation of electricity from geothermal energy), has been used since the 20th century. Unlike wind and solar energy, geothermal plants produce power at a constant rate, without regard to weather conditions. Geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs. Most extraction occurs in areas near tectonic plate boundaries. The cost of generating geothermal power decreased by 25% during the 1980s and 1990s. Technological advances continued to reduce costs and thereby expand the amount of viable resources. In 2021, the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calgary Alberta
Calgary () is a major city in the Canadian province of Alberta. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806 making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Calgary is at the confluence of the Bow River and the Elbow River in the southwest of the province, in the transitional area between the Rocky Mountain Foothills and the Canadian Prairies, about east of the front ranges of the Canadian Rockies, roughly south of the provincial capital of Edmonton and approximately north of the Canada–United States border. The city anchors the south end of the Statistics Canada-defined urban area, the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor. Calgary's economy includes activity in many sectors: energy; financial services; film and television; transportation and logistics; technology; manufacturing; aerospace; health and wellness; retail; and tourism. The Calgary Metropolitan Region is home to Canada's second-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system. In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that a company can increase sales given increased resources. For example, a package delivery system is scalable because more packages can be delivered by adding more delivery vehicles. However, if all packages had to first pass through a single warehouse for sorting, the system would not be as scalable, because one warehouse can handle only a limited number of packages. In computing, scalability is a characteristic of computers, networks, algorithms, networking protocols, programs and applications. An example is a search engine, which must support increasing numbers of users, and the number of topics it indexes. Webscale is a computer architectural approach that brings the capabilities of large-scale cloud computing companies into enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Load
The base load (also baseload) is the minimum level of demand on an electrical grid over a span of time, for example, one week. This demand can be met by unvarying power plants or dispatchable generation, depending on which approach has the best mix of cost, availability and reliability in any particular market. The remainder of demand, varying throughout a day, is met by intermittent sources together with dispatchable generation (such as load following power plants, peaking power plants, which can be turned up or down quickly) or energy storage. Power plants that do not change their power output quickly, such as some large coal or nuclear plants, are generally called baseload power plants.Donald G. Fink, H. Wayne Beatty (ed), ''Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers'', Eleventh Edition, Mc-Graw Hill, 1978 , pp. 12-16 through 12-18 In the 20th century most or all of base load demand was met with baseload power plants, whereas new capacity based around renewables often employs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed-loop Geothermal
Closed-loop geothermal systems (also known as “advanced geothermal systems” or “AGS”) are a type of engineered geothermal energy system containing subsurface working fluid that is heated in a hot rock reservoir without direct contact with rock pores and fractures.: Instead, the subsurface working fluid stays inside a closed loop of deeply buried pipes that conduct Earth’s heat. Closed-loop geothermal systems are one of the prominent categories of next-generation geothermal systems in development today. Like all geothermal systems, closed-loop geothermal systems provide renewable energy, and primarily operate as baseload resources that produce energy at a constant rate. Unlike conventional geothermal energy plants, closed-loop geothermal plants can be placed anywhere in the world, depending only on the depth of the hot rock resource. Closed-loop geothermal projects are under development in the United States, Canada, Japan, and Germany. Technology Closed-loop geotherma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. The 31 member countries and 13 association countries of the IEA represent 75% of global energy demand. The IEA was set up under the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis to respond to physical disruptions in global oil supplies, provide data and statistics about the global Petroleum industry, oil market and Energy industry, energy sector, promote energy savings and conservation, and establish international technical collaboration. Since its founding, the IEA has also coordinated use of the oil reserves that its members are required to hold. By regularly underestimating the role of renewable energies and overestimating the growth of nuclear energy, the IEA promotes the nuclear industry. In subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhanced Geothermal System
An enhanced geothermal system (EGS) generates geothermal electricity without natural convective hydrothermal resources. Traditionally, geothermal power systems operated only where naturally occurring heat, water, and rock permeability are sufficient to allow energy extraction. However, most geothermal energy within reach of conventional techniques is in dry and impermeable rock. EGS technologies expand the availability of geothermal resources through stimulation methods, such as 'hydraulic stimulation'. Overview In many rock formations natural cracks and pores do not allow water to flow at economic rates. Permeability can be enhanced by hydro-shearing, pumping high-pressure water down an injection well into naturally-fractured rock. The injection increases the fluid pressure in the rock, triggering shear events that expand pre-existing cracks and enhance the site's permeability. As long as the injection pressure is maintained, high permeability is not required, nor are hydrau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conduction
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy until an object has the same kinetic energy throughout. Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by , is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature. Essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat. Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient (i.e. from a hotter body to a colder body). For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosiphon
A thermosiphon (or thermosyphon) is a device that employs a method of passive heat transfer, heat exchange based on natural convection, which circulates a fluid without the necessity of a mechanical pump. Thermosiphoning is used for circulation of liquids and volatile gases in heating and cooling applications such as heat pumps, water heaters, boilers and furnaces. Thermosiphoning also occurs across air temperature gradients such as those occurring in a wood-fire chimney or solar chimney. This circulation can either be open-loop, as when the substance in a holding tank is passed in one direction via a heated transfer tube mounted at the bottom of the tank to a distribution point — even one mounted above the originating tank — or it can be a vertical closed-loop circuit with return to the original container. Its purpose is to simplify the transfer of liquid or gas while avoiding the cost and complexity of a conventional pump. Simple thermosiphon Natural convection of the liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom Hole Assembly
A bottom hole assembly (BHA) is a component of a drilling rig. It is the lowest part of the drill string, extending from the bit to the drill pipe. The assembly can consist of drill collars, subs such as stabilisers, reamers, shocks, hole-openers, and the bit sub and bit. The BHA design is based upon the requirements of having enough weight transfer to the bit (WOB) to be able to drill and achieve a sufficient Rate of Penetration (ROP), giving the Driller or Directional Driller directional control to drill as per the planned trajectory and to also include whatever Logging While Drilling (LWD) / Measurement While Drilling (MWD) tools for formation evaluation. As such BHA design can vary greatly from simple vertical wells with little or no LWD requirements to complex directional wells which must run multi-combo LWD suites. Prior to running a BHA most oilfield service providers have software to model the BHA behaviour such as the maximum WOB achievable, the directional tendencies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracking
Fracking (also known as hydraulic fracturing, fracing, hydrofracturing, or hydrofracking) is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of formations in bedrock by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of "fracking fluid" (primarily water, containing sand or other proppants suspended with the aid of thickening agents) into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formations through which natural gas, petroleum, and brine will flow more freely. When the hydraulic pressure is removed from the well, small grains of hydraulic fracturing proppants (either sand or aluminium oxide) hold the fractures open. Fracking, using either hydraulic pressure or acid, is the most common method for well stimulation. Well stimulation techniques help create pathways for oil, gas or water to flow more easily, ultimately increasing the overall production of the well. Both methods of fracking are classed as ''unconventional'', because they aim t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Energy Technology Companies
A renewable resource (also known as a flow resource) is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of time in a human time scale. It is also known as non conventional energy resources. When the recovery rate of resources is unlikely to ever exceed a human time scale, these are called perpetual resources. Renewable resources are a part of Earth's natural environment and the largest components of its ecosphere. A positive life-cycle assessment is a key indicator of a resource's sustainability. Definitions of renewable resources may also include agricultural production, as in agricultural products and to an extent water resources.What are "Renewable Resources" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |