Closed-loop Geothermal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Closed-loop geothermal systems (also known as “advanced geothermal systems” or “AGS”) are a type of engineered 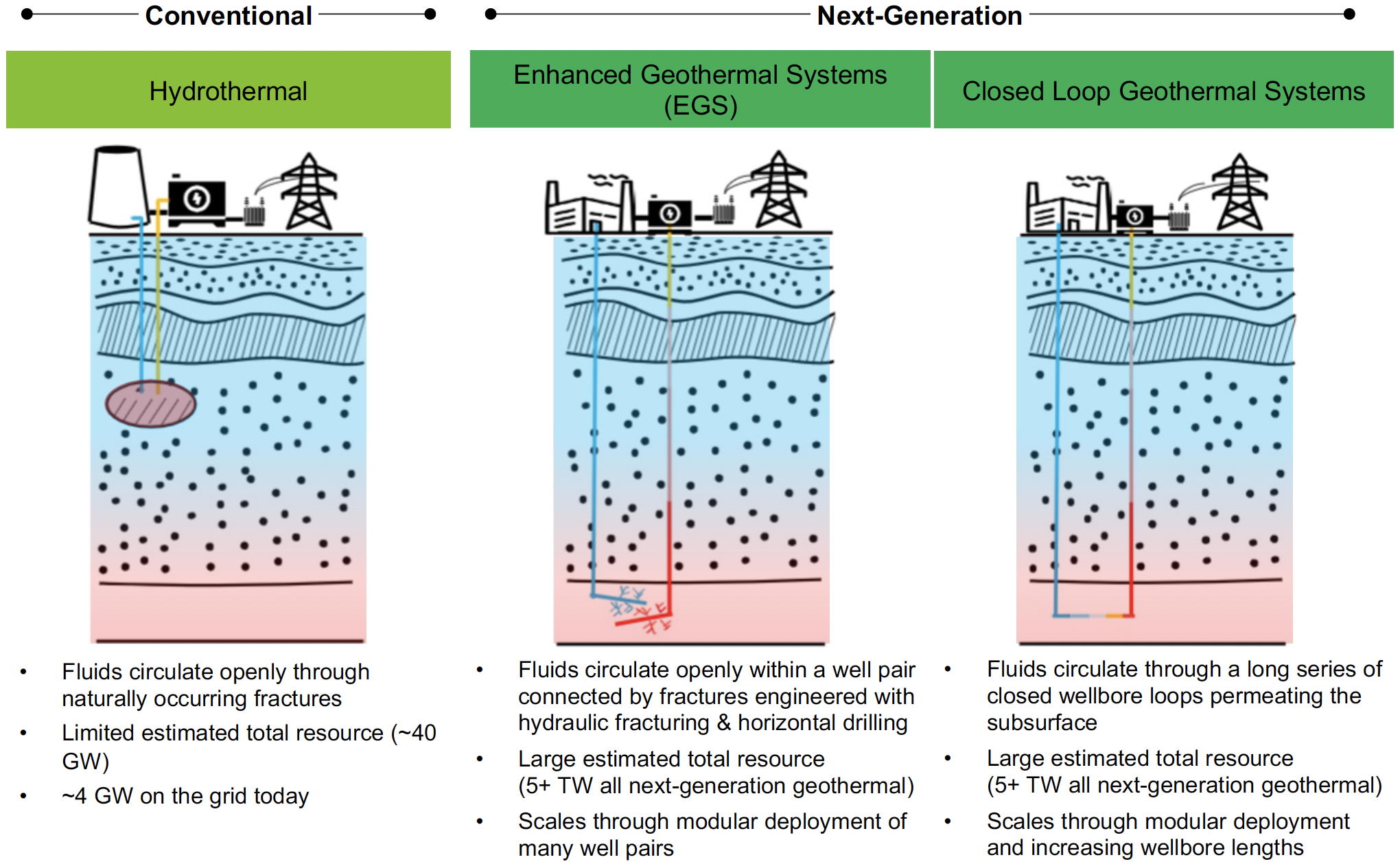 Like all geothermal systems, closed-loop geothermal systems provide
Like all geothermal systems, closed-loop geothermal systems provide
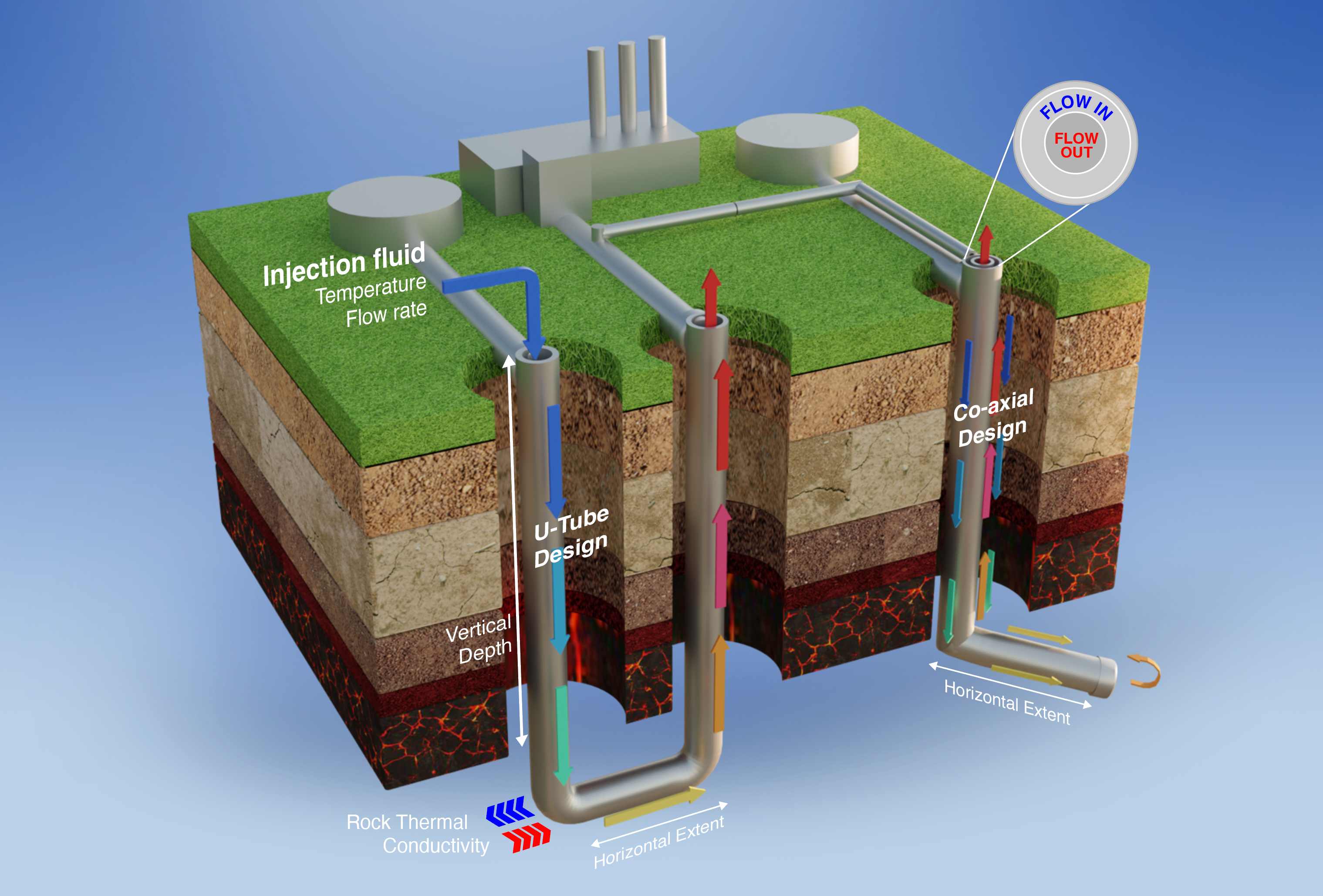 Closed-loop geothermal companies use a wide variety of engineered systems to produce geothermal energy. These systems primarily vary based on the length and geometry of the closed-loop wells placed subsurface, but can also vary in the materials used in well construction and the working fluid used.
Two commons designs of closed-loop geothermal systems are the U-tube and the tube-in-tube:
* U-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, cool water is pumped down one deep vertical pipe, which then extends horizontally for a certain distance at a depth where the rock is hot and then comes up in a different location. The horizontal section may be composed of one or multiple lateral (horizontal) well sections.
* Tube-in-a-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, the cool water is pumped down along the outer layer of a pipe to a certain depth, at which point the pipe may extend an additional horizontal distance at that depth. When the hot water hits the end of the pipe it is pushed into the inner pipe, through which the hot water returns to the surface. Also called a coaxial or pipe-in-pipe system.
Closed-loop geothermal companies use a wide variety of engineered systems to produce geothermal energy. These systems primarily vary based on the length and geometry of the closed-loop wells placed subsurface, but can also vary in the materials used in well construction and the working fluid used.
Two commons designs of closed-loop geothermal systems are the U-tube and the tube-in-tube:
* U-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, cool water is pumped down one deep vertical pipe, which then extends horizontally for a certain distance at a depth where the rock is hot and then comes up in a different location. The horizontal section may be composed of one or multiple lateral (horizontal) well sections.
* Tube-in-a-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, the cool water is pumped down along the outer layer of a pipe to a certain depth, at which point the pipe may extend an additional horizontal distance at that depth. When the hot water hits the end of the pipe it is pushed into the inner pipe, through which the hot water returns to the surface. Also called a coaxial or pipe-in-pipe system.
 Multiple deep hot dry rock wells have been drilled around the world, including the US, Japan, Australia, France, and the UK. Whereas hydrothermal energy production can exploit already present hot fluids, HDR recovers heat from dry rock via the circulation of an artificially introduced working fluid. Ongoing efforts are underway to further develop and test technologies that can produce
Multiple deep hot dry rock wells have been drilled around the world, including the US, Japan, Australia, France, and the UK. Whereas hydrothermal energy production can exploit already present hot fluids, HDR recovers heat from dry rock via the circulation of an artificially introduced working fluid. Ongoing efforts are underway to further develop and test technologies that can produce
geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for m ...
system containing subsurface working fluid that is heated in a hot rock reservoir without direct contact with rock pores and fractures.: Instead, the subsurface working fluid stays inside a closed loop of deeply buried pipes that conduct Earth’s heat. Closed-loop geothermal systems are one of the prominent categories of next-generation geothermal systems in development today.
 Like all geothermal systems, closed-loop geothermal systems provide
Like all geothermal systems, closed-loop geothermal systems provide renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
, and primarily operate as baseload resources that produce energy at a constant rate. Unlike conventional geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for m ...
plants, closed-loop geothermal plants can be placed anywhere in the world, depending only on the depth of the hot rock resource.
Closed-loop geothermal projects are under development in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
.
Technology
 Closed-loop geothermal companies use a wide variety of engineered systems to produce geothermal energy. These systems primarily vary based on the length and geometry of the closed-loop wells placed subsurface, but can also vary in the materials used in well construction and the working fluid used.
Two commons designs of closed-loop geothermal systems are the U-tube and the tube-in-tube:
* U-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, cool water is pumped down one deep vertical pipe, which then extends horizontally for a certain distance at a depth where the rock is hot and then comes up in a different location. The horizontal section may be composed of one or multiple lateral (horizontal) well sections.
* Tube-in-a-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, the cool water is pumped down along the outer layer of a pipe to a certain depth, at which point the pipe may extend an additional horizontal distance at that depth. When the hot water hits the end of the pipe it is pushed into the inner pipe, through which the hot water returns to the surface. Also called a coaxial or pipe-in-pipe system.
Closed-loop geothermal companies use a wide variety of engineered systems to produce geothermal energy. These systems primarily vary based on the length and geometry of the closed-loop wells placed subsurface, but can also vary in the materials used in well construction and the working fluid used.
Two commons designs of closed-loop geothermal systems are the U-tube and the tube-in-tube:
* U-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, cool water is pumped down one deep vertical pipe, which then extends horizontally for a certain distance at a depth where the rock is hot and then comes up in a different location. The horizontal section may be composed of one or multiple lateral (horizontal) well sections.
* Tube-in-a-tube closed-loop geothermal: In this system, the cool water is pumped down along the outer layer of a pipe to a certain depth, at which point the pipe may extend an additional horizontal distance at that depth. When the hot water hits the end of the pipe it is pushed into the inner pipe, through which the hot water returns to the surface. Also called a coaxial or pipe-in-pipe system.
Research and development
Several closed-loop geothermal systems have been demonstrated globally. One commercial closed-loop geothermal project is under construction in Geretsried, Germany.Advantages
The advantages of a deep, closed-loop geothermal circuit include # No need for a geofluid # No need for the hot rock to be permeable or porous # All the introduced working fluid can be recirculated with zero loss # Nofracking
Fracking (also known as hydraulic fracturing, fracing, hydrofracturing, or hydrofracking) is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of formations in bedrock by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure inje ...
or stimulation is required to establish the engineered geothermal reservoir.
These advantages mean closed-loop geothermal systems can be placed anywhere in the world as a source of carbon-free, baseload energy, with no impact to natural water resources and significantly reduced risk of induced seismicity
Induced seismicity is typically earthquakes and tremors that are caused by human activity that alters the stresses and strains on Earth's crust. Most induced seismicity is of a low magnitude. A few sites regularly have larger quakes, such as The ...
.
Related terminology
Hot dry rock
Hot dry rock (HDR) is an abundant source ofgeothermal energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for m ...
, but it is typically difficult to access. Hot, dry crystalline basement
A basement is any Storey, floor of a building that is not above the grade plane. Especially in residential buildings, it often is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, water heating, ...
rocks are found almost everywhere sufficiently far beneath the surface. Multiple deep hot dry rock wells have been drilled around the world, including the US, Japan, Australia, France, and the UK. Whereas hydrothermal energy production can exploit already present hot fluids, HDR recovers heat from dry rock via the circulation of an artificially introduced working fluid. Ongoing efforts are underway to further develop and test technologies that can produce
Multiple deep hot dry rock wells have been drilled around the world, including the US, Japan, Australia, France, and the UK. Whereas hydrothermal energy production can exploit already present hot fluids, HDR recovers heat from dry rock via the circulation of an artificially introduced working fluid. Ongoing efforts are underway to further develop and test technologies that can produce geothermal energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for m ...
from hot dry rock, including Enhanced Geothermal Systems
An enhanced geothermal system (EGS) generates geothermal electricity without natural convective hydrothermal resources. Traditionally, geothermal power systems operated only where naturally occurring heat, water, and rock permeability are suffici ...
and Closed-Loop Geothermal Systems.
Closed-loop geothermal systems vs. ground source heat pumps
Closed-loop geothermal systems are not to be confused with theground source heat pump
A ground source heat pump (also geothermal heat pump) is a heating/cooling system for buildings that use a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through t ...
s used for small-scale, largely residential heating and cooling. While both systems use underground closed-loop circuits of working fluid, there are important differences in the depth, temperature, scale, and applications for each system:
* Depth: Ground source heat pumps are placed at shallow depths, less than 400 feet (122 meters). Closed-loop geothermal systems are drilled much deeper, greater than 1640 feet (500 meters), to access the hotter rock found at greater depths (see: geothermal gradient
Geothermal gradient is the rate of change in temperature with respect to increasing depth in Earth's interior. As a general rule, the crust temperature rises with depth due to the heat flow from the much hotter mantle; away from tectonic plat ...
).
* Temperature: Ground source heat pumps target shallow ground temperatures, which vary seasonally from 45 °F (7 °C) to 75 °F (21 °C). Closed-loop geothermal systems target much hotter underground temperatures, greater than 212 °F (100 °C), to produce larger volumes of energy.
* Scale: Ground source heat pumps are used for small-scale residential heating and cooling and typically produce less than 1 kilowatt of thermal energy. Closed-Loop Geothermal Systems are used for utility-scale commercial and industrial energy production and typically produce greater than 1 megawatt of thermal energy.
* Application: Ground source heat pumps are most often used for small-scale residential and commercial buildings, and are only used for heating and cooling applications. Closed-loop geothermal systems are most suitable for large-scale commercial and industrial use, and can be used for electricity production, in addition to 'direct use' heating and cooling.
See the glossary of geothermal heating and cooling page for further clarification.
References
{{reflist Geothermal energy Technology