|
Denise Herzing
Denise L. Herzing is the founder and Research Director of the Wild Dolphin Project, a non-profit which funds the study of the natural behaviors and communication of Atlantic spotted dolphins in the wild. Herzing has earned her Ph.D. in Behavioral Biology/Environmental Studies, her M.A. in Behavioral Biology, and her B.S. in Marine Zoology Herzing's aim is to achieve two-way communication between humans and dolphins. She hopes to use a wearable underwater computer to record and make dolphin sounds. The computer aims to create synthesized dolphin sounds that can be established between sound and object. The object is to enable dolphins to imitate the sound in order to make requests from people. In the field of dolphin intelligence and communication, Herzing has recorded observations of dolphins expressing teaching behaviors. She also worked as part of a team that developed a new camera/hydrophone system which allows researchers to identify which dolphin on a recording made whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Spotted Dolphin
The Atlantic spotted dolphin (''Stenella frontalis'') is a dolphin found in warm temperate and tropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Older members of the species have a very distinctive spotted coloration all over their bodies. Taxonomy The Atlantic spotted dolphin was first described by Cuvier in 1828. Considerable variation in the physical form of individuals occurs in the species, and specialists have long been uncertain as to the correct taxonomic classification. Currently, just one species is recognised, but a large, particularly spotty variant commonly found near Florida quite possibly may be classified as a formal subspecies or indeed a species in its own right. Atlantic spotted dolphins in the Bahamas have been observed mating with bottlenose dolphins. Rich LeDuc has published data that suggest the Atlantic spotted dolphin may be more closely related to the bottlenose dolphins (genus ''Tursiops'') than to other members of the genus ''Stenella''. More recent studies in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioral Biology
Ethology is a branch of zoology that studies the behaviour of non-human animals. It has its scientific roots in the work of Charles Darwin and of American and German ornithologists of the late 19th and early 20th century, including Charles O. Whitman, Oskar Heinroth, and Wallace Craig. The modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of the Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and the Austrian biologists Konrad Lorenz and Karl von Frisch, the three winners of the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Ethology combines laboratory and field science, with a strong relation to neuroanatomy, ecology, and evolutionary biology. Etymology The modern term ''ethology'' derives from the Greek language: ἦθος, ''ethos'' meaning "character" and , ''-logia'' meaning "the study of". The term was first popularized by the American entomologist William Morton Wheeler in 1902. History The beginnings of ethology Etholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biology
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms that inhabit the sea. Given that in biology many scientific classification, phyla, family (biology), families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment (biophysical), environment rather than on taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. A large proportion of all life, life on Earth lives in the ocean. The exact size of this "large proportion" is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world, covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wearable Computer
A wearable computer, also known as a body-borne computer, is a computing device worn on the body. The definition of 'wearable computer' may be narrow or broad, extending to smartphones or even ordinary wristwatches. Wearables may be for general use, in which case they are just a particularly small example of mobile computing. Alternatively, they may be for specialized purposes such as fitness trackers. They may incorporate special sensors such as accelerometers, heart rate monitors, or on the more advanced side, Electrocardiography, electrocardiogram (ECG) and Oxygen saturation (medicine), blood oxygen saturation (SpO2) monitors. Under the definition of wearable computers, we also include novel user interfaces such as Google Glass, an optical head-mounted display controlled by gestures. It may be that specialized wearables will evolve into general all-in-one devices, as happened with the convergence of Personal digital assistant, PDAs and mobile phones into smartphones. Wearables ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
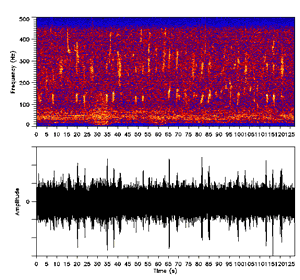
Dolphin Sound
Whales use a variety of sounds for communication and sensation. The mechanisms used to produce sound vary from one family of cetaceans to another. Marine mammals, including whales, dolphins, and porpoises, are much more dependent on sound than land mammals due to the limited effectiveness of other senses in water. Sight is less effective for marine mammals because of the way particulates in the ocean scatter light. Smell is also limited, as molecules diffuse more slowly in water than in air, which makes smelling less effective. However, the speed of sound is roughly four times greater in water than in the atmosphere at sea level. As sea mammals are so dependent on hearing to communicate and feed, environmentalists and cetologists are concerned that they are being harmed by the increased ambient noise in the world's oceans caused by ships, sonar and marine seismic surveys. The word "song" is used to describe the pattern of regular and predictable sounds made by some species o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacean Intelligence
Cetacean intelligence is the overall intelligence and derived cognitive ability of aquatic mammals belonging in the infraorder Cetacea (cetaceans), including baleen whales, porpoises, and dolphins. In 2014, a study found that the long-finned pilot whale has more neocortical neurons than any other mammal, including humans, examined to date. Brain Size Brain size was previously considered a major indicator of the intelligence of an animal. However, many other factors also affect intelligence, and recent discoveries concerning bird intelligence have called into question the influence of brain size. Since most of the brain is used for maintaining bodily functions, greater ratios of brain to body mass may increase the amount of brain mass available for more complex cognitive tasks. Allometric analysis indicates that in general, mammalian brain size scales at approximately the or exponent of body mass. Comparison of actual brain size with the size expected from allometry provides an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophone
A hydrophone () is a microphone designed for underwater use, for recording or listening to underwater sound. Most hydrophones contains a piezoelectric transducer that generates an electric potential when subjected to a pressure change, such as a sound wave. A hydrophone can also detect airborne sounds but is insensitive of them because it is designed to match the acoustic impedance of water, a denser fluid than air. Sound travels 4.3 times faster in water than in air, and a sound wave in water exerts a pressure 60 times more than what is exerted by a wave of the same amplitude in air. Similarly, a standard microphone can be buried in the ground, or immersed in water if it is put in a waterproof container but will give poor performance because of the similarly-bad acoustic impedance match. History The first hydrophones consisted of a tube with a thin membrane covering the submerged end and the observer's ear of the equipment. The design of effective hydrophones must take into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Direction
In geometry, direction, also known as spatial direction or vector direction, is the common characteristic of all ray (geometry), rays which coincide when translation (geometry), translated to share a common endpoint; equivalently, it is the common characteristic of vector (geometry), vectors (such as the relative position between a pair of points) which can be made equal by scaling (geometry), scaling (by some positive scalar multiplication, scalar multiplier). Two vectors sharing the same direction are said to be ''codirectional'' or ''equidirectional''. All codirectional line segments sharing the same size (length) are said to be ''equipollent (geometry), equipollent''. Two equipollent segments are not necessarily coincident; for example, a given direction can be evaluated at different starting Position (geometry), positions, defining different unit directed line segments (as a bound vector instead of a free vector). A direction is often represented as a unit vector, the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Cognition
Animal cognition encompasses the mental capacities of non-human animals, including insect cognition. The study of animal conditioning and learning used in this field was developed from comparative psychology. It has also been strongly influenced by research in ethology, behavioral ecology, and evolutionary psychology; the alternative name cognitive ethology is sometimes used. Many behaviors associated with the term ''animal intelligence'' are also subsumed within animal cognition. Researchers have examined animal cognition in mammals (especially primates, cetaceans, elephants, bears, dogs, cats, pigs, horses, cattle, raccoons and rodents), birds (including parrots, fowl, corvids and pigeons), reptiles ( lizards, snakes, and turtles), fish and invertebrates (including cephalopods, spiders and insects). Historical background Earliest inferences The mind and behavior of non-human animals has captivated the human imagination for centuries. Many writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetologists
Cetology (from Greek , ''kētos'', "whale"; and , ''-logia'') or whalelore (also known as whaleology) is the branch of marine mammal science that studies the approximately eighty species of whales, dolphins, and porpoises in the scientific infraorder Cetacea. Cetologists, or those who practice cetology, seek to understand and explain cetacean evolution, distribution, morphology, behavior, community dynamics, and other topics. History Observations about Cetacea have been recorded since at least classical times. Ancient Greek fishermen created an artificial notch on the dorsal fin of dolphins entangled in nets so that they could tell them apart years later. Approximately 2,300 years ago, Aristotle carefully took notes on cetaceans while traveling on boats with fishermen in the Aegean Sea. In his book ''Historia animalium'' (''History of Animals''), Aristotle was careful enough to distinguish between the baleen whales and toothed whales, a taxonomical separation still used toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |