|
DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY
DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY is a drug of the phenethylamine, DOx, and FLY families with an unusual furo ,3-ghromene core structure which acts as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist. It was first synthesised by David E. Nichols and colleagues in 2008, and while it is weaker than similar compounds such as Bromo-DragonFLY it is still the most potent among a number of related derivatives. See also * 2C-B-BUTTERFLY * 2C-B-DRAGONFLY * 2C-B-FLY * 2C-E-FLY * DOB-FLY * NBOMe-2C-B-FLY * TFMFly * Substituted benzofuran The substituted benzofurans are a class of chemical compounds based on the heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic and polycyclic compound, polycyclic compound benzofuran. Many medicines use the benzofuran core as a scaffold, but most commonly the t ... References 5-HT2A agonists Benzofurans Bromoarenes Designer drugs DOx (psychedelics) FLY (psychedelics) Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings Psychedelic phenethylamines Serotonin receptor agonists {{Halluci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Benzofuran
The substituted benzofurans are a class of chemical compounds based on the heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic and polycyclic compound, polycyclic compound benzofuran. Many medicines use the benzofuran core as a scaffold, but most commonly the term is used to refer to the simpler compounds in this class which include numerous psychoactive drugs, including stimulants, psychedelic drug, psychedelics and empathogen-entactogen, empathogens. In general, these compounds have a benzofuran core to which a 2-aminoethyl group is attached (at any position), and combined with a range of other substituents. Some psychoactive derivatives from this family have been sold under the name ''Benzofury (other), Benzofury''. List of substituted benzofurans The derivatives may be produced by substitutions at six locations of the benzofuran molecule, as well as saturation of the 2,3- double bond. The following table displays notable derivatives that have been reported: Legislation Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLY (psychedelics)
FLY is a family of substituted phenethylamine, phenethylamine and substituted benzofuran, benzofuran psychedelic drug, psychedelics possessing a benzodifuran or similar ring system. The FLY drugs were so-named because of the resemblance of their chemical structures to flying insects like dragonfly, dragonflies and butterfly, butterflies. They are structural analog, analogues of 2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamines in which the 2- and 5-position methoxy groups have been cyclic compound, cyclized into furan and/or tetrahydrofuran ring (chemistry), rings. They may be 2C (drug), 2C, DOx, 25-NB, or other FLY versions of psychedelic phenethylamines. Examples of different types of FLY drugs, in the case of the base psychedelic 2C-B, include 2C-B-FLY, 2C-B-DRAGONFLY, 2C-B-BUTTERFLY, and 2C-B-MOTH. BromoDragonFLY (DOB-DragonFLY) is known for its very high potency (pharmacology), potency and its toxicity in overdose. 2C-B-FLY was Ann Shulgin's favorite research chemical. According to Alexander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromo-DragonFLY
Bromo-DragonFLY, also known as 3C-Bromo-Dragonfly or DOB-Dragonfly, psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine, DOx, and FLY families. It acts as a potent full agonist of the 5-HT2A receptor. Use Data on toxicological significance and dosage of Bromo-DragonFLY remains elusive due to lack of human consumption, however commonly reported recreational dose of this substance is in the range of 500 to 1000μg. However, a death has been reported at approximately 700μg Bromo-DragonFLY. Overdose and toxicity The toxicity of Bromo-DragonFLY appears to be fairly high for humans, with reports of at least five deaths believed to have resulted from Bromo-DragonFLY in Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland and the United States. Laboratory testing has confirmed that in October 2009, a batch of Bromo-DragonFLY was distributed, mislabeled as the related compound 2C-B-FLY, which is around 20x less potent than BDF by weight. This mistake is believed to have contributed to several lethal overdoses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2C-B-DRAGONFLY
2C-B-DRAGONFLY (2C-B-DFLY) is a recreational designer drug with psychedelic effects of the phenethylamine, 2C, and FLY families. It can be regarded as the fully aromatic derivative of 2C-B-FLY. 2C-B-DRAGONFLY is stronger than 2C-B or 2C-B-FLY with around 2–3x the potency of 2C-B in animal studies, demonstrating the importance of the fully aromatic benzodifuran ring system for optimum receptor binding at 5-HT2A, but it is still considerably less potent than its alpha-methyl derivative Bromo-DragonFLY. See also * 2C-B-aminorex * 2C-B-BUTTERFLY * 2C-B-PP * 2C-E-FLY * DOB-FLY * DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY * NBOMe-2C-B-FLY * TFMFly * Substituted benzofuran The substituted benzofurans are a class of chemical compounds based on the heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic and polycyclic compound, polycyclic compound benzofuran. Many medicines use the benzofuran core as a scaffold, but most commonly the t ... References 2C (psychedelics) 5-HT2A agonists Benzof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Phenethylamine
Substituted phenethylamines (or simply phenethylamines) are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative (chemistry), derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substitution reaction, substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents. Phenylethylamines are also generally found to be central nervous system stimulants with many also being entactogens/empathogens, and hallucinogens. Structural classification The structural formula of any substituted phenethylamine contains a phenyl group, phenyl ring that is joined to an amino group, amino (NH) group via a two-carbon substituent, sidechain. Hence, any substituted phenethylamine can be classified according to the substitution of hydrogen atom, hydrogen (H) atoms on phenethylamine's phenyl ring, sidechain, or amino group with a moiety (chemistry), specific group of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NBOMe-2C-B-FLY
2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2C-B-FLY, Cimbi-31) is a drug of the phenethylamine, DOx, and FLY families. It was indirectly derived from the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, and related to benzodifurans like 2C-B-FLY and ''N''-benzylphenethylamines like 25I-NBOMe. It was discovered in 2002, and further researched by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin, and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols. It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor Receptor may refer to: * Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse *Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ... subtype. Analogues and derivatives Legality United Kingdom United States 2CBFly-NBOMe is a controlled substance in Vermont as of January 2016. References {{Phenethylamines 5-HT2A agonists 25-NB (psyched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compounds With 3 Rings
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different chemical element, elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drugs
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union, Australia, and New Zealand, as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these designer drugs were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as a haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide ion (such as fluorine F''−'', chlorine Cl−1,−3,−5, bromine Br−1, or iodine I−). Aryl halides are distinct from haloalkanes (alkyl halides) due to significant differences in their methods of preparation, chemical reactivity, and physical properties. The most common and important members of this class are aryl chlorides, but the group encompasses a wide range of derivatives with diverse applications in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. Classification according to halide Aryl fluorides Aryl fluorides are used as synthetic intermediates, e.g. for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and liquid crystals. The conversion of diazonium salts is a well established route to aryl fluorides. Thus, anilines are precursors to aryl fluorides. In the classic Schiemann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
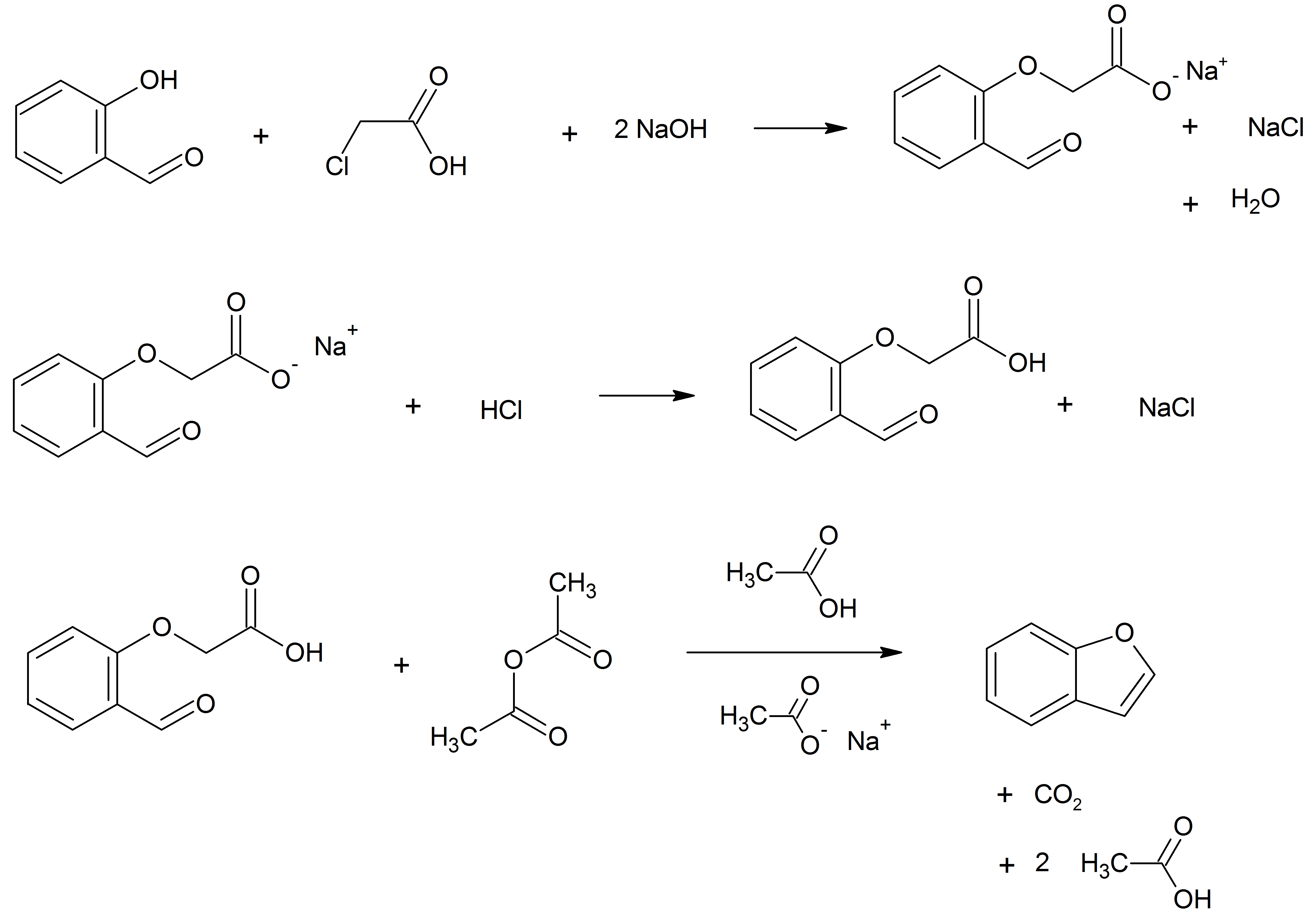
Benzofurans
Benzofuran is the heterocyclic compound consisting of fused benzene and furan rings. This colourless liquid is a component of coal tar. Benzofuran is the structural nucleus (parent compound) of many related compounds with more complex structures. For example, psoralen is a benzofuran derivative that occurs in several plants. Production Benzofuran is extracted from coal tar. It is also obtained by dehydrogenation of 2-ethylphenol. Laboratory methods Benzofurans can be prepared by various methods in the laboratory. Notable examples include: *''O''-alkylation of salicylaldehyde with chloroacetic acid followed by dehydration reaction, dehydration (cyclication) of the resulting ether and decarboxylation. *Perkin rearrangement, where a coumarin is reacted with a hydroxide: : *Diels–Alder reaction of Nitroalkene, nitro vinyl furans with various dienophiles: : *Isomerization, Cycloisomerization of alkyne Arene substitution pattern, ortho-substituted phenols: : Related compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2A Agonists
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFMFly
TFMFly is a drug related of the phenethylamine, DOx, and FLY families related to psychedelics like 2C-B-FLY and 2C-TFM. It was first reported in 2005 by a team at Purdue University led by David Nichols. It acts as a potent agonist at the 5HT2A serotonin receptor subtype, and is a chiral compound with the more active (R) enantiomer having a Ki of 0.12 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor. While the fully aromatic benzodifurans such as Bromo-DragonFLY generally have higher binding affinity than saturated compounds like 2C-B-FLY, the saturated compounds have higher efficacy Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ... as agonists. Legal Status TFMFly is illegal in Latvia. See also * 2C-E-FLY * DOB-FLY References Amines Dihydrofurans FLY (psychedelics) Hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |