|
Czatkowiella
''Czatkowiella'' is an extinct genus of long-necked archosauromorph known from Early Triassic (Olenekian age) rocks of Czatkowice 1, Poland. It was first named by Magdalena Borsuk−Białynicka and Susan E. Evans in 2009 and the type species is ''Czatkowiella harae''. Phylogeny Cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ... after Borsuk−Białynicka & Evans (2009). Cladogram after Spiekman ''et al.'' 2021: References Archosauromorpha Prehistoric reptile genera Olenekian genera Early Triassic reptiles of Europe Fossils of Poland Fossil taxa described in 2009 {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheus
''Tanystropheus'' (~ 'long' + 'hinged') is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile which lived during the Triassic period, Triassic Period in Europe, Asia, and North America. It is recognisable by its extremely elongated neck, longer than the torso and tail combined. The neck was composed of 13 vertebrae strengthened by extensive cervical ribs. ''Tanystropheus'' is one of the most well-described non-Archosauriformes, archosauriform archosauromorphs, known from numerous fossils, including nearly complete skeletons. Some species within the genus may have reached a total length of , making ''Tanystropheus'' the longest non-archosauriform archosauromorph as well. ''Tanystropheus'' is the namesake of the family Tanystropheidae, a clade collecting many long-necked Triassic archosauromorphs previously described as "Protorosauria, protorosaurs" or "Prolacertiformes, prolacertiforms". ''Tanystropheus'' contains at least two valid species as well as fossils which cannot be referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozimek Volans
''Ozimek'' (named after the Ozimek, town of the same name) is a genus of sharovipterygidae, sharovipterygid archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptile, known from Late Triassic deposits in Poland and closely related to the Kyrgyzstani ''Sharovipteryx''. It contains one species, ''O. volans'', named in 2016 by Jerzy Dzik and Tomasz Sulej. Like ''Sharovipteryx'', ''Ozimek'' had long, slender limbs with the hindlimbs longer than the forelimbs; the hindlimbs likely supported gliding membranes as fossilized in ''Sharovipteryx''. Another unusual characteristic was the shoulder girdle, where the massive coracoids formed a shield-like structure covering the bottom of the shoulder region that would have limited mobility. In other respects, such as its long neck, it was a typical member of the non-natural grouping Protorosauria. Phylogenetic analysis has indicated that it, possibly along with ''Sharovipteryx'', may have been an unusual member of the protorosaur group Tanystropheidae, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
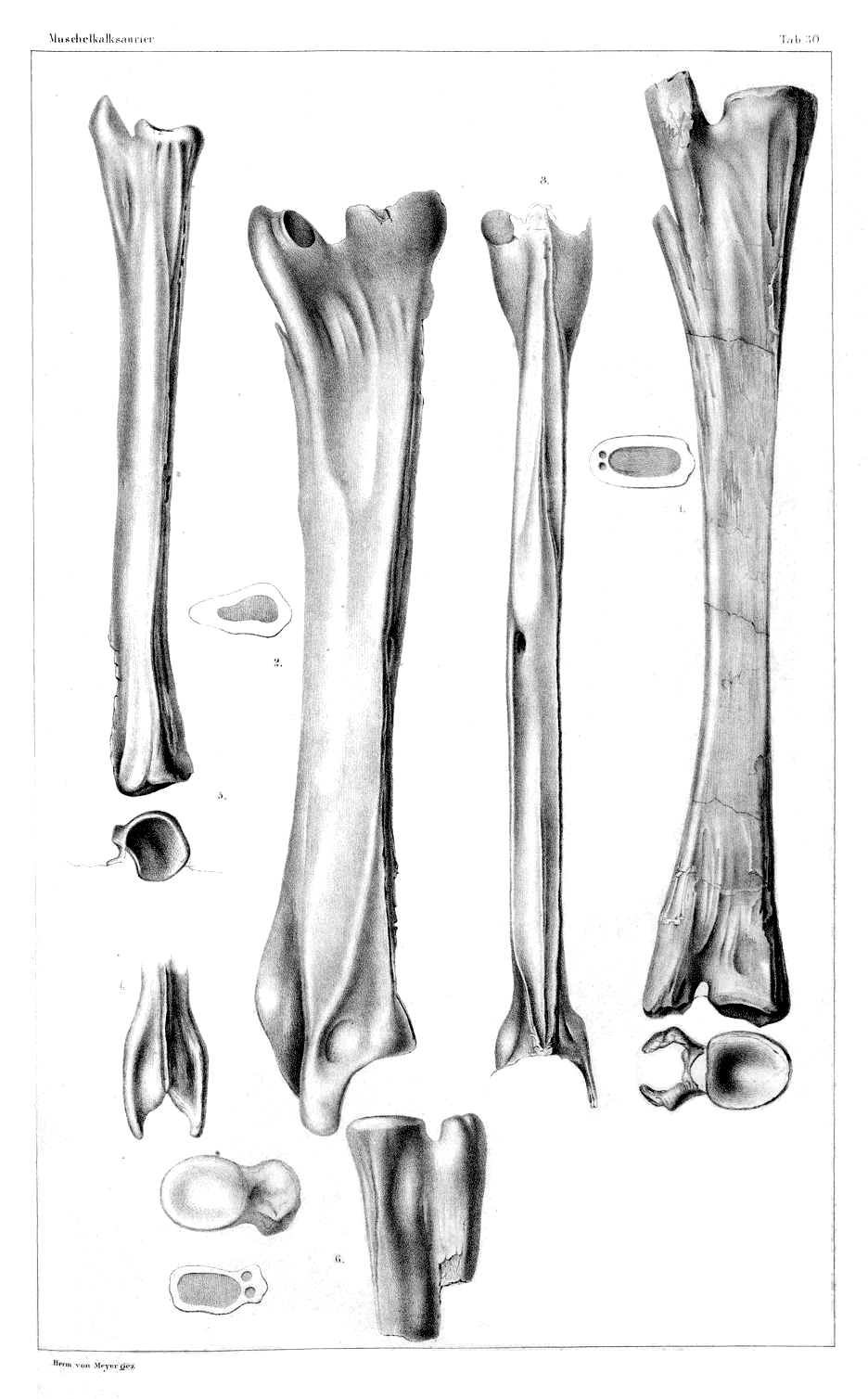
Protorosaurus
''Protorosaurus'' (from , 'earlier' and , 'lizard') is an extinct genus of reptile. Members of the genus lived during the late Permian period in what is now Germany and Great Britain. Once believed to have been an ancestor to lizards, ''Protorosaurus'' is now known to be one of the oldest and most primitive members of Archosauromorpha, the group that would eventually lead to archosaurs such as crocodilians and dinosaurs. Description ''Protorosaurus'' grew up to in length, and was a slender, lizard-like animal, vaguely resembling a monitor lizard, with long legs and a long neck. History ''Protorosaurus'' was one of the first fossil reptiles to be described, being initially described in Latin in 1710 by from a specimen found in Thuringia in Germany, who considered the animal to be a crocodile, and most similar to the Nile crocodile (''C. niloticus''). Over a century later, in publications in 1830 and 1832 Christian Erich Hermann von Meyer, Hermann von Meyer recognised ''Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosauria
Thalattosauria ( Greek for "sea lizards") is an extinct order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic Period. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relationships are unresolved. They are widely accepte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharovipterygidae
Sharovipterygidae is a family of strange gliding archosauromorphs from the mid-Triassic of Eurasia, notable for their short forelimbs and long, wing A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-d ...-like hindlimbs, which supported membranes for gliding. They are represented by '' Sharovipteryx'' and '' Ozimek volans''. A 2019 phylogenetic analysis suggested that ''Ozimek'', and by extension ''Sharovipteryx'', may belong to the Tanystropheidae. References Archosauromorpha Prehistoric reptile families Gliding animals Middle Triassic reptiles of Asia Late Triassic reptiles of Asia Late Triassic reptiles of Europe {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesairosaurus
''Jesairosaurus'' is an extinct genus of early archosauromorph reptile known from the Illizi Province of Algeria. It is known from a single species, ''Jesairosaurus lehmani''. Although a potential relative of the long-necked tanystropheids, this lightly-built reptile could instead be characterized by its relatively short neck as well as various skull features. Etymology and discovery Zarzaïtine fossil material has been known since 1957. Much of the material has been recovered by French expeditions in the late 1950s and 1960s, and deposited at the Laboratoire de Paleontologie (Paleontology department) at the Museum national d'Histoire naturalle in Paris. Algerian fossils were prepared at this institution over subsequent years. Several putative procolophonid skeletons reported in 1971 were later determined to belong to " prolacertiforms" in 1990. The term "prolacertiform" is now considered to refer to an unnatural polyphyletic grouping of early archosauromorphs, distant relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauria
Sauria is the clade of diapsids containing the most recent common ancestor of Archosauria (which includes crocodilians and birds) and Lepidosauria (which includes squamates and the tuatara), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely related to archosaurs than to lepidosaurs as part of Archelosauria, Sauria can be considered the crown group of diapsids, or reptiles in general. Depending on the systematics, Sauria includes all modern reptiles or most of them (including birds, a type of archosaur) as well as various extinct groups. Sauria lies within the larger total group Sauropsida, which also contains various stem-reptiles which are more closely related to reptiles than to mammals. Prior to its modern usage, "Sauria" was used as a name for the suborder occupied by lizards, which before 1800 were considered crocodilians. Systematics Sauria was historically used as a partial equivalent for Squamata (which contains lizards and sna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youngina
''Youngina'' (named after John Young (1823–1900)) is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile from the Late Permian Beaufort Group ('' Tropidostoma''-'' Dicynodon'' zones) of the Karoo Red Beds of South Africa. This, and a few related forms, make up the family Younginidae, within the order Eosuchia (proposed by Broom in 1914). Eosuchia, having become a wastebasket taxon for many probably distantly-related primitive diapsid reptiles ranging from the Late Carboniferous to the Eocene, Romer proposed that it be replaced by Younginiformes (that included Younginidae and the Tangasauridae, ranging from the Permian to the Triassic). Taxonomy ''Youngina'' is known from several specimens. Many of these were attributed to as separate genera and species (such as ''Youngoides'' and ''Youngopsis''), but it was later realized that they were not distinct from ''Y. capensis''. The holotype specimen of ''Youngina'', discovered by Broom himself, was described briefly in 1914. The "''Youngoide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acerosodontosaurus
''Acerosodontosaurus'' is an Extinction, extinct genus of Neodiapsida, neodiapsid Reptile, reptiles that lived during the Late Permian of Madagascar. The only species of ''Acerosodontosaurus'', ''A. piveteaui'', is known from a natural wiktionary:mold_fossil, mold of a single partial skeleton including a crushed skull and part of the body and limbs. The fossil was discovered in deposits of the Lower Sakamena Formation. Based on skeletal characteristics, it has been suggested that ''Acerosodontosaurus'' individuals were at least partially Aquatic animal, aquatic. ''Acerosodontosaurus'' has generally been considered a "Younginiformes, younginiform", part of a Paraphyly, paraphyletic Evolutionary grade, grade of Permian Diapsid, diapsids which linked the most basal ("primitive") diapsids (Araeoscelidia, araeoscelidians such as ''Petrolacosaurus'') to more derived ("advanced") diapsids, including the earliest ancestors of modern reptiles such as Crocodilia, crocodilians and Lizard, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudiosaurus
''Claudiosaurus'' (''claudus'' is Latin for 'lameness' and ''saurus'' means 'lizard') is an extinct genus of diapsid reptiles from the Late Permian Sakamena Formation of the Morondava Basin, Madagascar. It has been suggested to be semi-aquatic. History and discovery ''Claudiosaurus'' is known from the Sakamena Formation of Madagascar. ''Claudiosaurus'' is found from the Late Permian. Although a paper mentions that they have been also found in Early Triassic deposits of Madagascar, citation does not mention that ''Claudiosaurus'' is from Triassic. Description Individuals of ''Claudiosaurus'' reached a body length of approximately . The body form of ''Claudiosaurus'' is generally similar to those of other basal diapsids, although the neck of ''Claudiosaurus'' is somewhat elongated, with 8 cervical vertebrae, and had a proportionally small head. The body has 16 trunk vertebrae with gastralia present on the underside, and the tail has at least 45 caudal vertebrae. The jaws ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orovenator
''Orovenator'' is an extinct genus of diapsid from Lower Permian ( Artinskian stage) deposits of Oklahoma, United States. It is known from two partial skulls from the Richards Spur locality in Oklahoma. The holotype OMNH 74606 consists of a partial skull preserving snout and mandible, and the referred specimen, OMNH 74607, a partial skull preserving the skull roof, vertebrae and palatal elements. It was first named by Robert R. Reisz, Sean P. Modesto and Diane M. Scott in 2011 and the type species is ''Orovenator mayorum''. The generic name means "mountain", ''oro'', in Greek in reference to the Richards Spur locality, which was mountainous during the Permian period and "hunter", ''venator'', in Latin. The specific name honours Bill and Julie May. ''Orovenator'' is the oldest and most basal neodiapsid to date. A 2018 redescription by David Ford and Roger Benson found that ''Orovenator'' shared many similarities with varanopids, a group of reptile-like tetrapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |