|
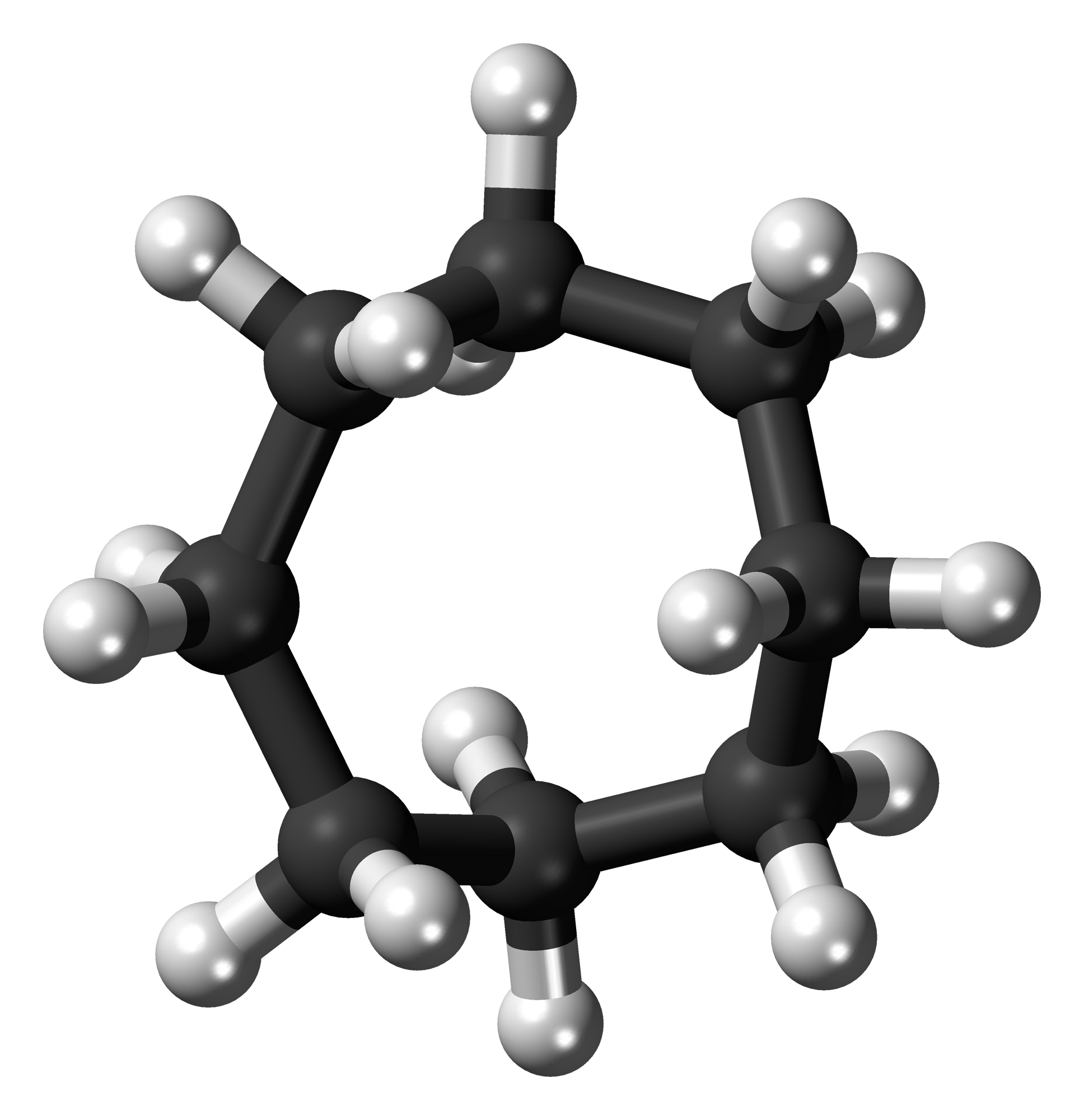
Cyclooctane Twist Chair-chair Conformation
Cyclooctane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)8. It is a simple colourless hydrocarbon, but it is often a reference compound for saturated eight-membered ring compounds in general. Cyclooctane has a camphoraceous odor. Conformations The conformational isomer, conformation of cyclooctane has been studied extensively using computational chemistry, computational methods. Hendrickson noted that "cyclooctane is unquestionably the conformationally most complex cycloalkane owing to the existence of many conformers of comparable energy". The boat-chair conformation (below) is the most stable form. Allinger and co-workers confirmed this. The crown conformation (below) is slightly less stable. Among the many compounds exhibiting the crown conformation (structure II) is S8, elemental sulfur. : Synthesis and reactions The main route to cyclooctane derivatives involves the dimerization of butadiene, catalysed by nickel(0) complexes such as nickel bis(cyclooctadiene). This pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloalkane
In organic chemistry, the cycloalkanes (also called naphthenes, but distinct from naphthalene) are the ring (chemistry), monocyclic Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, a cycloalkane consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring (possibly with side chains), and all of the carbon-carbon bonds are single bond, single. The larger cycloalkanes, with more than 20 carbon atoms are typically called ''cycloparaffins''. All cycloalkanes are isomers of alkenes. The cycloalkanes without side chains (also known as monocycloalkanes) are classified as small (cyclopropane and cyclobutane), common (cyclopentane, cyclohexane, and cycloheptane), medium (cyclooctane through cyclotridecane), and large (all the rest). Besides this standard definition by IUPAC, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), in some authors' usage the term ''cycloalkane'' includes also those saturated hydrocarbons th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctane Twist Boat-chair Conformation
Cyclooctane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)8. It is a simple colourless hydrocarbon, but it is often a reference compound for saturated eight-membered ring compounds in general. Cyclooctane has a camphoraceous odor. Conformations The conformation of cyclooctane has been studied extensively using computational methods. Hendrickson noted that "cyclooctane is unquestionably the conformationally most complex cycloalkane owing to the existence of many conformers of comparable energy". The boat-chair conformation (below) is the most stable form. Allinger and co-workers confirmed this. The crown conformation (below) is slightly less stable. Among the many compounds exhibiting the crown conformation (structure II) is S8, elemental sulfur. : Synthesis and reactions The main route to cyclooctane derivatives involves the dimerization of butadiene, catalysed by nickel(0) complexes such as nickel bis(cyclooctadiene). This process affords, among other products, 1,5-cyclo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloalkanes
In organic chemistry, the cycloalkanes (also called naphthenes, but distinct from naphthalene) are the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons. In other words, a cycloalkane consists only of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a structure containing a single ring (possibly with side chains), and all of the carbon-carbon bonds are single. The larger cycloalkanes, with more than 20 carbon atoms are typically called ''cycloparaffins''. All cycloalkanes are isomers of alkenes. The cycloalkanes without side chains (also known as monocycloalkanes) are classified as small (cyclopropane and cyclobutane), common (cyclopentane, cyclohexane, and cycloheptane), medium (cyclooctane through cyclotridecane), and large (all the rest). Besides this standard definition by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), in some authors' usage the term ''cycloalkane'' includes also those saturated hydrocarbons that are polycyclic. In any case, the general form of the chemical formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The American Chemical Society
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' (also known as JACS) is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytical and Applied Chemistry'' (July 1893) and the ''American Chemical Journal'' (January 1914). It covers all fields of chemistry. Since 2021, the editor-in-chief is Erick M. Carreira (ETH Zurich). In 2014, the journal moved to a hybrid open access publishing model. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 14.4. Editors-in-chief The following people are or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Radical Halogenation
In organic chemistry, free-radical halogenation is a type of halogenation. This chemical reaction is typical of alkanes and alkyl-substituted aromatics under application of UV light. The reaction is used for the industrial synthesis of chloroform (CHCl3), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), and hexachlorobutadiene. It proceeds by a free-radical chain mechanism. General mechanism The chain mechanism is as follows, using the chlorination of methane as an example: ; Initiation: Ultraviolet radiation splits ( homolyzes) a chlorine molecule to two chlorine atom radicals. ; Chain propagation (two steps): A radical abstracts a hydrogen atom from methane, leaving a primary methyl radical. The methyl radical then abstracts Cl• from Cl2 to give the desired product and another chlorine radical. The radical will then participate in another propagation reaction: the radical chain. Other products such as CH2Cl2 may also form. ; Chain termination: Two free radicals (chlorine and chlorine, chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While activation energy must be supplied to initiate combustion (e.g., using a lit match to light a fire), the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. The study of combustion is known as combustion science. Combustion is often a complicated sequence of elementary reaction, elementary Radical (chemistry), radical reactions. Solid fuels, such as wood and coal, first undergo endothermic pyrolysis to produce gaseous fuels whose combustion then supplies the heat required to produce more of them. Combustion is often hot e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous Catalysis
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the catalyst is in same phase as reactants, principally by a soluble catalyst in a solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid and gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is an established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts. Examples Acid catalyst The proton is a pervasive homogeneous catalyst because water is the most common solvent. Water forms protons by the process of self-ionization of water. In an illustrative case, acids accelerate (catalyze) the hydrolysis of esters: :CH3CO2CH3 + H2O CH3CO2H + CH3OH At neutral pH, aqueous solutions of most esters do not hydrolyze at practical rates. Transition met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,5-Cyclooctadiene
1,5-Cyclooctadiene (also known as cycloocta-1,5-diene) is a cyclic compound, cyclic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , specifically . There are three configurational isomers with this structure, that differ by the arrangement of the four C–C single bonds adjacent to the double bonds. Each pair of single bonds can be on the same side () or on opposite sides () of the double bond's plane; the three possibilities are denoted , , and ; or (), (), and (). (Because of overall symmetry, is the same configuration as .) Generally abbreviated COD, the isomer of this diene is a useful precursor to other organic compounds and serves as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid with a strong odor. 1,5-Cyclooctadiene can be prepared by dimerization of butadiene in the presence of a nickel catalyst, a coproduct being 4-Vinylcyclohexene, vinylcyclohexene. Approximately 10,000 tons were produced in 2005. Organic reactions COD reacts with borane to give 9-Borabicy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Bis(cyclooctadiene)
Bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(C8H12)2, also written Ni(cod)2. It is a diamagnetic coordination complex featuring tetrahedral nickel(0) bound to the alkene groups in two 1,5-cyclooctadiene ligands. This highly air-sensitive yellow solid is a common source of Ni(0) in chemical synthesis. Preparation and properties The complex is prepared by reduction of anhydrous nickel(II) acetylacetonate in the presence of the diolefin: :Ni(acac)2 + 2 cod + 2 AlEt3 → Ni(cod)2 + 2 acacAlEt2 + C2H6 + C2H4 Ni(cod)2 is moderately soluble in several organic solvents. If exposed to air, the solid oxidizes in a few minutes to nickel(II) oxide. As a result, this compound is generally handled in a glovebox. Reactions The reactivity of Ni(cod)2 has been extensively examined. One or both 1,5-cyclooctadiene ligands are readily displaced by phosphines, phosphites, bipyridine, and isocyanides. Oxidation gives the highly reactive monocation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butadiene
1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene. Although butadiene breaks down quickly in the atmosphere, it is nevertheless found in ambient air in urban and suburban areas as a consequence of its constant emission from motor vehicles. The name butadiene can also refer to the isomer, 1,2-butadiene, which is a cumulated diene with structure H2C=C=CH−CH3. This allene has no industrial significance. History In 1863, French chemist E. Caventou isolated butadiene from the pyrolysis of amyl alcohol. This hydrocarbon was identified as butadiene in 1886, after Henry Edward Armstrong isolated it from among the pyrolysis products of petroleum. In 1910, the Russian chemist Sergei Lebedev polymerized butadiene and obtained a material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctane Twist Chair-chair Conformation
Cyclooctane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)8. It is a simple colourless hydrocarbon, but it is often a reference compound for saturated eight-membered ring compounds in general. Cyclooctane has a camphoraceous odor. Conformations The conformational isomer, conformation of cyclooctane has been studied extensively using computational chemistry, computational methods. Hendrickson noted that "cyclooctane is unquestionably the conformationally most complex cycloalkane owing to the existence of many conformers of comparable energy". The boat-chair conformation (below) is the most stable form. Allinger and co-workers confirmed this. The crown conformation (below) is slightly less stable. Among the many compounds exhibiting the crown conformation (structure II) is S8, elemental sulfur. : Synthesis and reactions The main route to cyclooctane derivatives involves the dimerization of butadiene, catalysed by nickel(0) complexes such as nickel bis(cyclooctadiene). This pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |