|
Corycida
Corycidia (alternatively spelt Corycida) is a clade of amoeboid protists within the eukaryotic supergroup (biology), supergroup Amoebozoa. It contains all amoebae of the families Microcoryciidae, which was previously regarded as Arcellinida (an order of testate amoebae), and Trichosphaeriidae, which contains the sole genus ''Trichosphaerium''. Taxonomy Corycidia is defined as the least inclusive clade containing ''Amphizonella'', ''Diplochlamys (protist), Diplochlamys'' and ''Trichosphaerium''. It was discovered in 2017 through a phylogenomic study by Senghuo Kang and coauthors, published in the journal ''Molecular Biology and Evolution''. It is supported by independent analyses. As of 2019, it is accepted by the International Society of Protistologists as part of the modern cladistic classification of eukaryotes, although under the alternative spelling Corycida. The name Corycidia is derived , referring to the "leathery" test (biology), test that members of the clade have. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplochlamys (protist)
Corycidia (alternatively spelt Corycida) is a clade of amoeboid protists within the eukaryotic supergroup Amoebozoa. It contains all amoebae of the families Microcoryciidae, which was previously regarded as Arcellinida (an order of testate amoebae), and Trichosphaeriidae, which contains the sole genus '' Trichosphaerium''. Taxonomy Corycidia is defined as the least inclusive clade containing '' Amphizonella'', '' Diplochlamys'' and '' Trichosphaerium''. It was discovered in 2017 through a phylogenomic study by Senghuo Kang and coauthors, published in the journal ''Molecular Biology and Evolution''. It is supported by independent analyses. As of 2019, it is accepted by the International Society of Protistologists as part of the modern cladistic classification of eukaryotes, although under the alternative spelling Corycida. The name Corycidia is derived , referring to the "leathery" test that members of the clade have. Evolution Corycidia is located in the eukaryotic super ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinamoebida
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba'', '' Arcella'', '' Difflugia'' and '' Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists such as Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed Lobosea ''sensu stric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcoryciidae
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba (genus), Amoeba'', ''Arcella'', ''Difflugia'' and ''Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists such as Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyly, polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulinea
The Tubulinea are a major grouping of Amoebozoa, including most of the more familiar amoebae genera like ''Amoeba'', '' Arcella'', '' Difflugia'' and '' Hartmannella''. Characteristics During locomotion most Tubulinea have a roughly cylindrical form or produce numerous cylindrical pseudopods. Each cylinder advances by a single central stream of cytoplasm, granular in appearance, and has no subpseudopodia. This distinguishes them from other amoeboid groups, although in some members this is not the normal type of locomotion. Classification This class was anticipated by some biologists such as Jahn, who grouped all amoebae with granular pseudopodia together, but most split the lobose amoebae into testate Testacealobosia and naked Gymnamoebia. These latter are polyphyletic, but molecular trees by Bolivar ''et al.'' identified a core monophyletic subgroup. Subsequent studies showed the testate lobose amoebae belong to the same group, which was thus renamed Lobosea ''sensu stric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
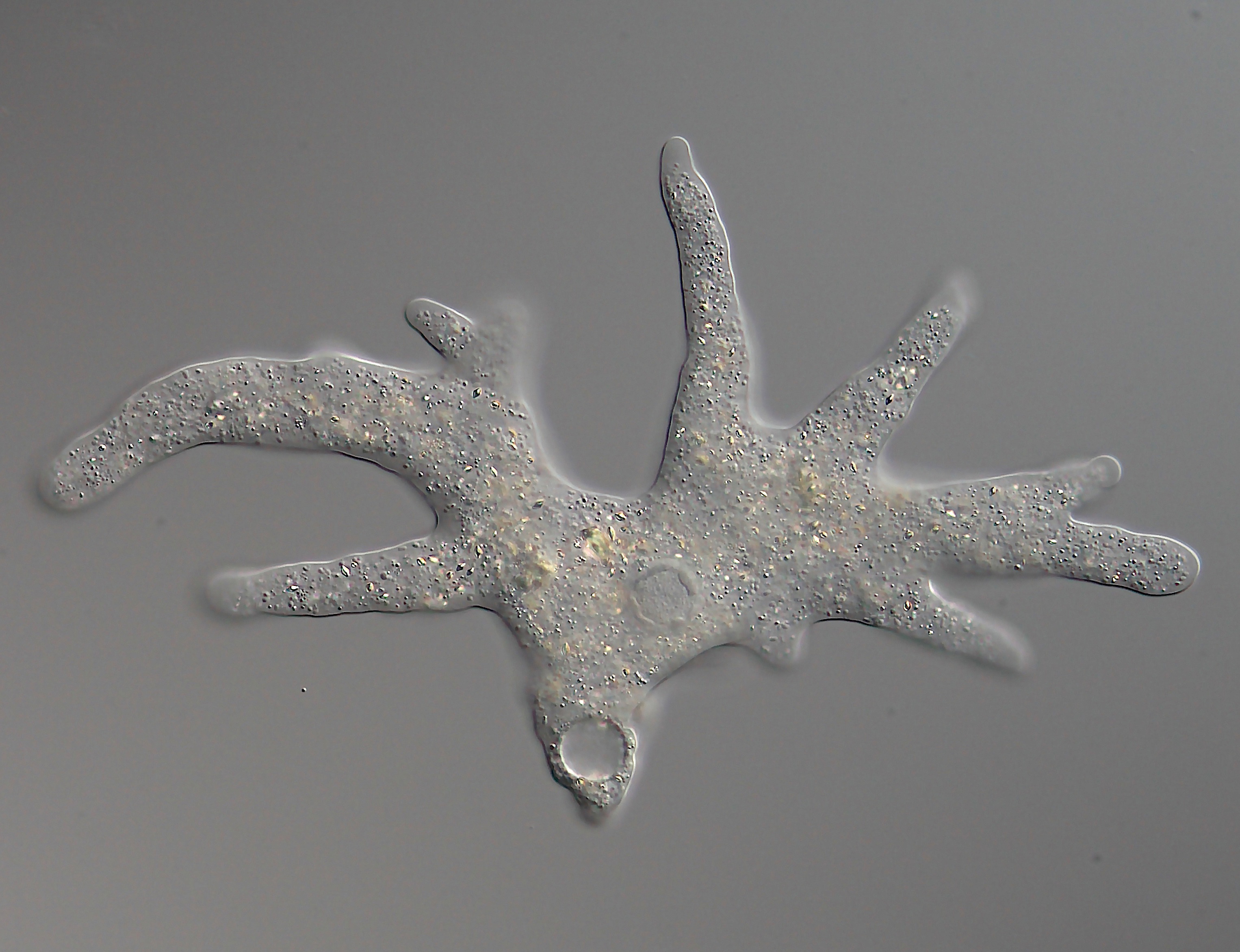
Trichosphaerium 1c Microbiolres-14
''Trichosphaerium'' is a genus of amoebozoan protists that present extraordinary morphological transformations, both in size and shape, during their life cycle. They can present a test that may or may not be covered in spicules. They are related to the family Microcoryciidae, which contains other amoebae with tests, within the clade Corycidia of the phylum Amoebozoa. Morphology ''Trichosphaerium'' is a genus of amoebae characterized from other Amoebozoa by a multiporous test and a specialized non-motile pseudopodium, known as a dactylopodium, shaped like a digit. The dactylopodium is considered a sensory structure. Its morphology, behavior and life cycle are extraordinary in comparison with other protists. During its poorly understood life cycle, ''Trichosphaerium'' undergoes dramatic changes in shape and size. They can grow from as small as 10 μm to giant cell sizes of over 1 mm, observable by the naked eye. They can display such varied recognizable morphotypes that they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discosea
Discosea is a class of Amoebozoa, consisting of naked amoebae with a flattened, discoid body shape. Members of the group do not produce tubular or subcylindrical pseudopodia, like amoebae of the class Tubulinea. When a discosean is in motion, a transparent layer called ''hyaloplasm'' forms at the leading edge of the cell (see lamellipodium). In some discoseans, short "subpseudopodia" may be extended from this hyaloplasm, but the granular contents of the cell do not flow into these, as in true pseudopodia. Discosean amoebae lack hard shells, but some, like ''Cochliopodium'' and '' Korotnevella'' secrete intricate organic scales which may cover the upper (dorsal) surface of the cell. No species have flagella or flagellated stages of life. The composition of Discosea is similar to that of the class Flabellinea, proposed by Alexey Smirnov and his collaborators in 2005. However, Discosea is a more comprehensive taxon, including several groups not included in Flabellinea. In 2011, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physarum Album 252229345
''Physarum'' is a genus of mycetozoan slime molds in the family Physaraceae. It contains the following species: *'' Physarum albescens'' *'' Physarum album'' *'' Physarum andinum'' *'' Physarum bivalve'' *'' Physarum bogoriense'' *'' Physarum cinereum'' *'' Physarum citrinum'' *'' Physarum compressum'' *'' Physarum confertum'' *'' Physarum conglomeratum'' *'' Physarum crateriforme'' *'' Physarum daamsii'' *'' Physarum didermoides'' *''Physarum digitatum'' *'' Physarum flavicomum'' *'' Physarum florigerum'' *'' Physarum globuliferum'' *''Physarum gyrosum'' *''Physarum hongkongense'' *''Physarum lakhanpalii'' *''Physarum lateritium'' *''Physarum leucophaeum'' *''Physarum loratum'' *''Physarum luteolum'' *''Physarum melleum'' *''Physarum mortonii'' *''Physarum mutabile'' *'' Physarum nigripodum'' *'' Physarum nucleatum'' *'' Physarum oblatum'' *'' Physarum plicatum'' *''Physarum polycephalum'' *''Physarum psittacinum'' *'' Physarum pulcherrimum'' *''Physarum pusillum'' *'' Physarum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evosea
Evosea is a diverse clade of amoeboid protists discovered through molecular analyses. Along with Tubulinea and Discosea, Evosea is one of the three major groups within Amoebozoa, an important clade of eukaryotic organisms. It contains unicellular organisms that display a wide variety of life cycles and cell shapes, including amoebae, flagellates and different kinds of slime molds. Characteristics Evosea is a strongly supported clade of eukaryotes containing four large groups of amoebozoans: Eumycetozoa or "true" slime molds, Variosea, Cutosea and Archamoebae. It is defined on a node-based approach as the least-inclusive clade containing '' Dictyostelium discoideum'' (a true slime mold), '' Protostelium nocturnum'' (a variosean), '' Squamamoeba japonica'' (a cutosean), and '' Entamoeba histolytica'' (an archamoeba). Within Evosea, organisms can vary across almost the entire range of morphologies seen in Amoebozoa. Many members have complex life cycles that include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or Taxon, taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In other words, it is a branching diagram or a tree (graph theory), tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. In evolutionary biology, all life on Earth is theoretically part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. Phylogenetics is the study of phylogenetic trees. The main challenge is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of species or taxa. computational phylogenetics, Computational phylogenetics (also phylogeny inference) focuses on the algorithms involved in finding optimal phylogenetic tree in the phylogenetic landscape. Phylogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Group
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |