|
Christopher Evans (businessman)
Sir Christopher Thomas Evans (born 29 November 1957) is a Welsh professor, scientist and biotechnology entrepreneur. Evans has founded and co-founded numerous biotech companies in the United Kingdom. Since the 1980s, Evans has launched and supported more than 50 companies in the biotechnology sector, including 20 listed on six different stock markets. Many have specialized in their goal of creating unique products and medicines, as well as conducting clinical trials. These include an S-Ketoprofen anti-inflammatory pharmaceutical, single isomer chiral synthons for use in new anti-viral drugs, a single-isomer levobupivacaine for local anaesthesia, the pre-eminent rapid bioluminescent test for bacterial contamination, numerous enzymes and proteins for use in clinical diagnostic tests, as well as stem cell therapies, immunotherapeutics, oncology drugs and respiratory devices. Early life and education Evans was born in 1957, in Port Talbot, to Cyril and Jeanette (née Cottey) Eva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burke's Peerage
Burke's Peerage Limited is a British genealogical publisher, considered an authority on the order of precedence of noble families and information on the lesser nobility of the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1826, when the Anglo-Irish genealogist John Burke began releasing books devoted to the ancestry and heraldry of the peerage, baronetage, knightage and landed gentry of Great Britain and Ireland. His first publication, a ''Genealogical and Heraldic Dictionary of the Peerage and Baronetage of the United Kingdom'', was updated sporadically until 1847, when the company began publishing new editions every year as ''Burke's Peerage, Baronetage and Knightage'' (often shortened and known as ''Burke's Peerage''). Other books followed, including '' Burke's Landed Gentry'', '' Burke's Colonial Gentry'', and '' Burke's General Armory''. In addition to its peerage publications, the ''Burke's'' publishing company produced books on Royal families of Europe and Latin America, rulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world. The agency was established in London in 1851 by Paul Reuter. The Thomson Corporation of Canada acquired the agency in a 2008 corporate merger, resulting in the formation of the Thomson Reuters Corporation. In December 2024, Reuters was ranked as the 27th most visited news site in the world, with over 105 million monthly readers. History 19th century Paul Julius Reuter worked at a book-publishing firm in Berlin and was involved in distributing radical pamphlets at the beginning of the Revolutions of 1848. These publications brought much attention to Reuter, who in 1850 developed a prototype news service in Aachen using homing pigeons and electric telegraphy from 1851 on, in order to transmit messages between Brussels and Aachen, in what today is Aa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50 to 150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. '' In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ReNeuron
ReNeuron is a UK-based stem cell research company whose shares were listed on the Alternative Investment Market, until it delisted in August 2024 after entering administration. Its focus is on the development of stem-cell therapies targeting areas of poorly-met medical need, including peripheral arterial disease, strokes, and retinal diseases. As of 2010 ReNeuron was testing the effects of neural stem cells on spinal cords for neuroregeneration Neuroregeneration is the regrowth or repair of nervous tissues, cells or cell products. Neuroregenerative mechanisms may include generation of new neurons, glia, axons, myelin, or synapses. Neuroregeneration differs between the peripheral nervous .... They were also testing the use of fetal stem cells on stroke patients. References External links * Biotechnology companies of the United Kingdom Biotechnology companies established in 1997 1997 establishments in the United Kingdom {{UK-company-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclacel
Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals Inc. is a biotechnology firm based in Dundee, Scotland, and Short Hills, New Jersey, developing cancer drugs and treatments. Cyclacel was founded in 1996 by David Lane, Merlin Ventures and Cancer Research Campaign Technology with the University of Dundee and the University of Glasgow. Company overview Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is a biopharmaceutical company developing oral therapies that target the various phases of cell cycle control for the treatment of cancer and other serious diseases. Sir David Lane, a recognized leader in the field of tumor suppressor biology, who discovered the p53 protein, founded the company in 1996. In 1999, Cyclacel Pharmaceuticals was joined by David Glover, a recognized leader in the mechanism of mitosis or cell division, who discovered, among other cell cycle targets, the mitotic kinases, Polo and Aurora, enzymes that act in the mitosis phase of the cell cycle. Three product candidates are currently in clinical devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Funding
Seed money, also known as seed funding or seed capital, is a form of securities offering in which an investor puts capital in a startup company in exchange for an equity stake or convertible note stake in the company. The term ''seed'' suggests that this is a very early investment, meant to support the business until it can generate cash of its own (see cash flow), or until it is ready for further investments. Seed money options include friends and family funding, seed venture capital funds, angel funding, and crowdfunding. Usage Traditionally, companies that have yet to meet listing requirements or qualify for bank loans, recognize VC as providers of financial support and value added services. Seed money can be used to pay for preliminary operations such as market research and product development. Investors can be the founders themselves, using savings and loans. They can be family members and friends of the founders. Investors can also be outside angel investors, venture capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celltech
Celltech Group plc was a leading British-based biotechnology business based in Slough. It was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. Celltech was instrumental in changing the UK's system of technology transfer from research to business, and in creating the biotechnology industry. History Celltech was formed in 1980 in response to the concern that Britain was failing to commercialise its science and was missing out on the potential of the new biotechnology. There was especial concern that whereas US firms had been creating rapidly growing firms such as Genentech around scientific discoveries in biotechnology, the UK had missed opportunities such as that believed to be provided by the Nobel Prize-winning discovery of the production technique for Monoclonal antibody by Cesar Milstein and Georges Kohler at Cambridge University. The creation of Celltech was complicated, involving the National Enterprise Board, the National Research Devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initial Public Offering
An initial public offering (IPO) or stock launch is a public offering in which shares of a company are sold to institutional investors and usually also to retail (individual) investors. An IPO is typically underwritten by one or more investment banks, who also arrange for the shares to be listed on one or more stock exchanges. Through this process, colloquially known as ''floating'', or ''going public'', a privately held company is transformed into a public company. Initial public offerings can be used to raise new equity capital for companies, to monetize the investments of private shareholders such as company founders or private equity investors, and to enable easy trading of existing holdings or future capital raising by becoming publicly traded. After the IPO, shares are traded freely in the open market at what is known as the free float. Stock exchanges stipulate a minimum free float both in absolute terms (the total value as determined by the share price multiplied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and also published digitally that focuses on business and economic Current affairs (news format), current affairs. Based in London, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Nikkei, Inc., Nikkei, with core editorial offices across Britain, the United States and continental Europe. In July 2015, Pearson plc, Pearson sold the publication to Nikkei for Pound sterling, £844 million (US$1.32 billion) after owning it since 1957. In 2019, it reported one million paying subscriptions, three-quarters of which were digital subscriptions. In 2023, it was reported to have 1.3 million subscribers of which 1.2 million were digital. The newspaper has a prominent focus on Business journalism, financial journalism and economic analysis rather than News media, generalist reporting, drawing both criticism and acclaim. It sponsors an Financial Times and McKinsey Business Book of the Year Award, annual book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
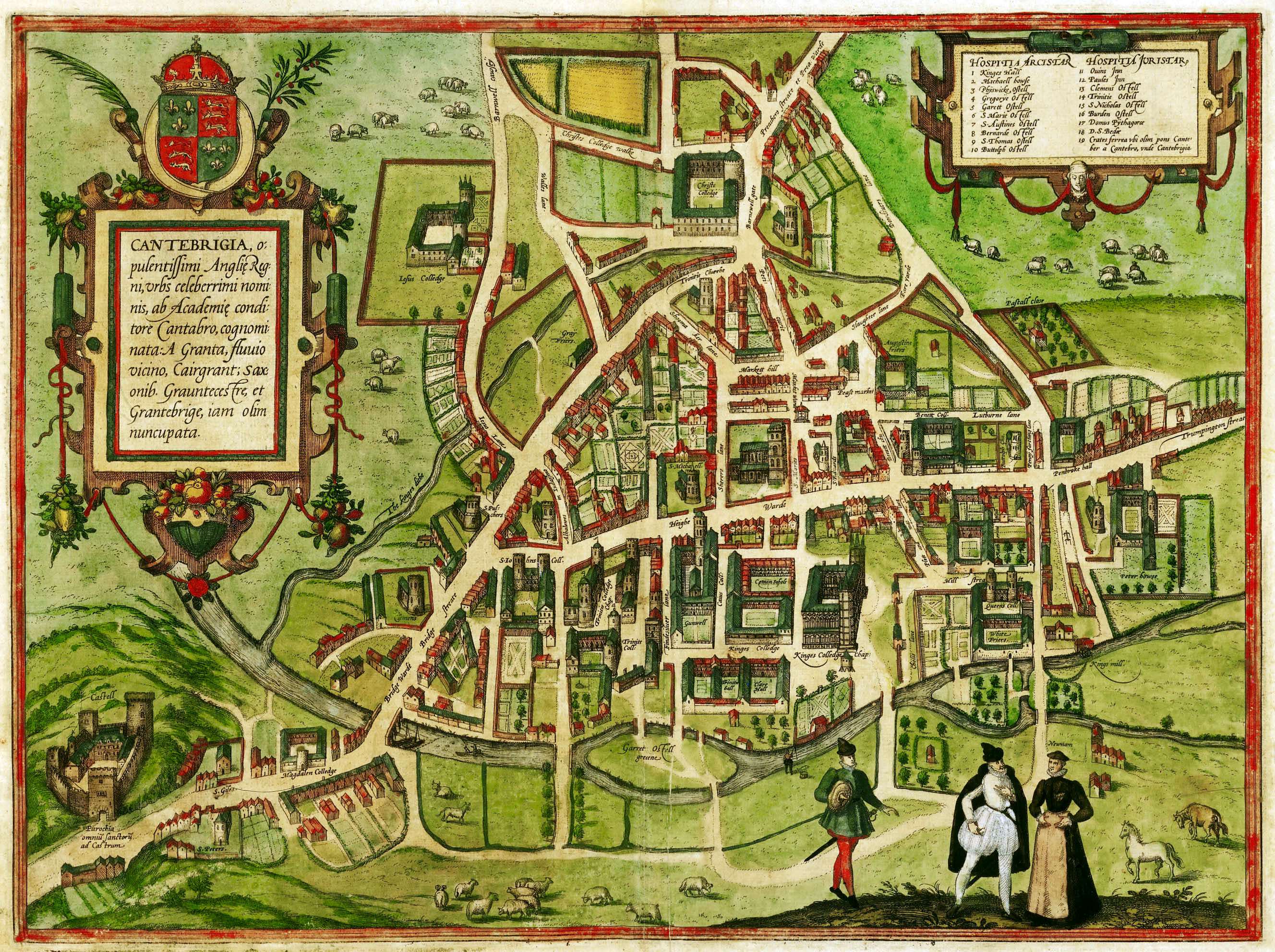
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles River Laboratories
Charles River Laboratories International, Inc. is an American pharmaceutical company specializing in preclinical and clinical laboratory, gene therapy and cell therapy services and supplies for the pharmaceutical, medical device and biotechnology industries. The company has over 150 facilities, operates in 21 countries, and employs over 21,000 people worldwide. Charles River Laboratories frequently criticized by animal rights activists, who condemn the company's use of dogs and primates for pharmaceutical research. The company is also a major harvester of blood from horseshoe crabs. History Charles River was founded in 1947 by Henry Foster, a young veterinarian who purchased one thousand rat cages from a Virginia farm and set up a one-person laboratory in Boston overlooking the Charles River. He supplied local researchers with laboratory animal models. In 1955, the company's headquarters were relocated to their current home in Wilmington, Massachusetts. The organization b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |