|
Choroiditis
Chorioretinitis is an inflammation of the choroid (thin pigmented vascular coat of the eye) and retina of the eye. It is a form of posterior uveitis. Inflammation of these layers can lead to vision-threatening complications. If only the choroid is inflamed, not the retina, the condition is termed choroiditis. The ophthalmologist's goal in treating these potentially blinding conditions is to eliminate the inflammation and minimize the potential risk of therapy to the patient. Symptoms Symptoms may include the presence of floating black spots, blurred vision, pain or redness in the eye, sensitivity to light, or excessive tearing. Causes Chorioretinitis is often caused by toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus infections (mostly seen in immunodeficient subjects such as people with HIV/AIDS or on immunosuppressant drugs). Congenital toxoplasmosis via transplacental transmission can also lead to sequelae such as chorioretinitis along with hydrocephalus and cerebral calcifications. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy, also called funduscopy, is a test that allows a health professional to see inside the fundus of the eye and other structures using an ophthalmoscope (or funduscope). It is done as part of an eye examination and may be done as part of a routine physical examination. It is crucial in determining the health of the retina, optic disc, and vitreous humor. The pupil is a hole through which the eye's interior can be viewed. For better viewing, the pupil can be opened wider (dilated; mydriasis) before ophthalmoscopy using medicated eye drops ( dilated fundus examination). However, undilated examination is more convenient (albeit not as comprehensive), and is the most common type in primary care. An alternative or complement to ophthalmoscopy is to perform a fundus photography, where the image can be analysed later by a professional. Types There are two major types of ophthalmoscopy: * direct ophthalmoscopy, which produces an upright (unreversed) image of approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disorders Of Choroid And Retina
Disorder may refer to randomness, a lack of intelligible pattern, or: Healthcare * Disorder (medicine), a functional abnormality or disturbance * Mental disorder or psychological disorder, a psychological pattern associated with distress or disability that occurs in a person and is not a part of normal development or culture: :* Anxiety disorder, different forms of abnormal and pathological fear and anxiety :* Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder :* Autism spectrum disorder :* Conversion disorder, neurological symptoms such as numbness, blindness, paralysis, or fits, where no neurological explanation is possible :* Obsessive–compulsive disorder, an anxiety disorder characterized by repetitive behaviors aimed at reducing anxiety :* Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder, obsession with perfection, rules, and organization :* Personality disorder, an enduring pattern of inner experience and behavior that deviates markedly from the expectations of the culture of the person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multifocal Choroiditis And Panuveitis
Multifocal choroiditis and panuveitis (MCP) is an inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology, affecting the choroid, retina, and vitreous of the eye that presents asymmetrically, most often in young myopic women with photopsias, enlargement of the physiologic blind spot and decreased vision. The first description of the disease was written in 1973. Symptoms Symptoms include blurry vision, with or without sensitivity to light, blind spots, floaters, eye discomfort and perceived flashes of light. Diagnosis An ophthalmologist may use a series of imaging techniques. A test called flourescein angiography uses a special dye and camera to study blood flow in the back layers of the eye. When a person has multifocal choroiditis (MFC), lesions in the eye will appear as fluorescent spots. Visual field tests may also show an enlarged blind spot or a decrease in visual clarity. Often, doctors may order blood tests to check if the symptoms are caused by a viral disease rather than MFC. Tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinitis
Retinitis is inflammation of the retina in the eye, which can permanently damage the retina and lead to blindness. The retina is the eye's "sensing" tissue. Retinitis may be caused by a number of different infectious agents. Its most common form, called retinitis pigmentosa, has a prevalence of one in every 2,500–7,000 people. This condition is one of the leading causes that leads to blindness in patients in the age range of 20–60 years old. Retinitis may be caused by several infectious agents, including toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus and candida. Cytomegalovirus retinitis is an important cause of blindness in AIDS The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ... patients. Candida spreading to the retina from the bloodstream usually results in the production of severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
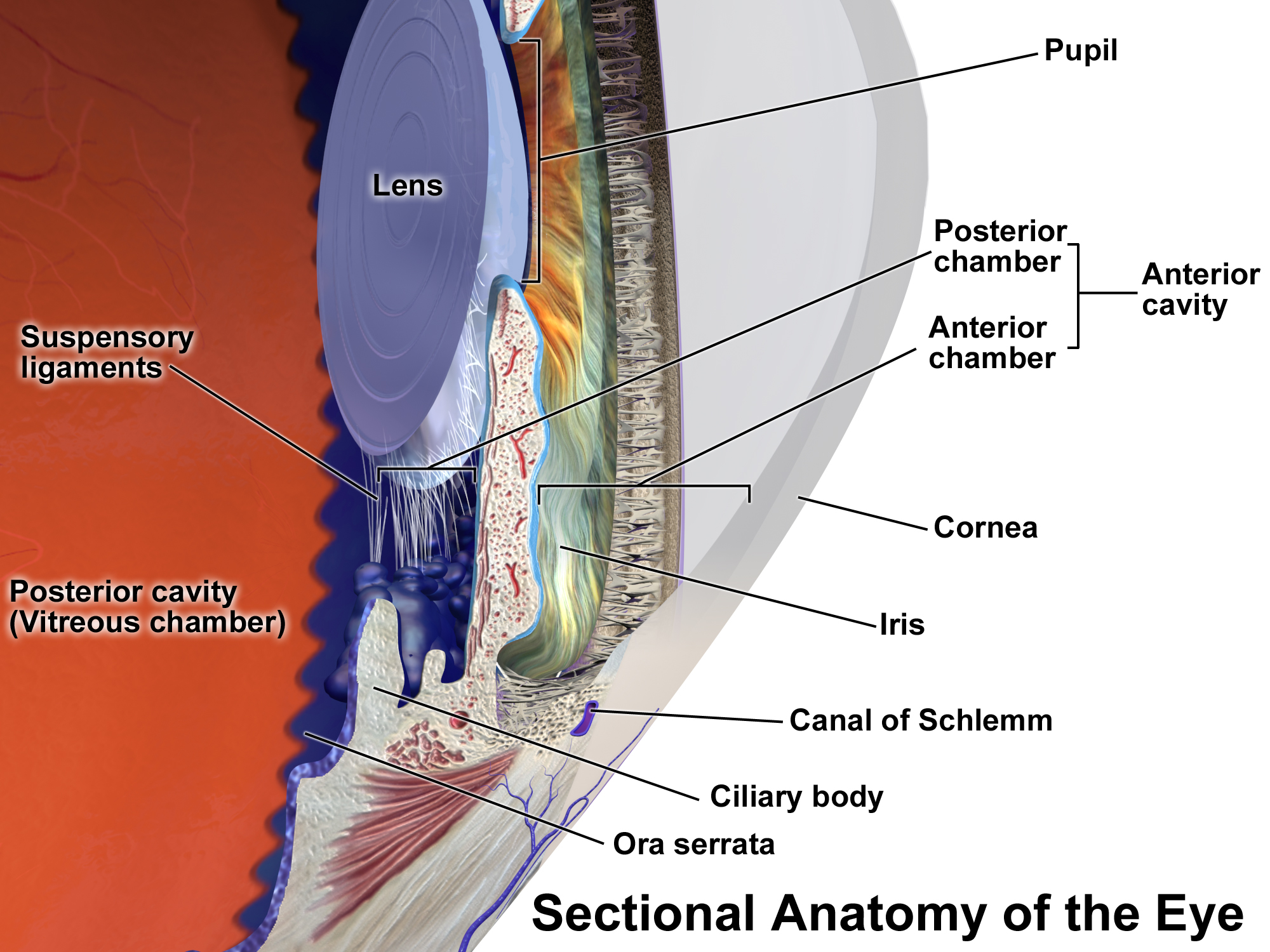
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20–60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivermectin
Ivermectin is an antiparasitic drug. After its discovery in 1975, its first uses were in veterinary medicine to prevent and treat heartworm and acariasis. Approved for human use in 1987, it is used to treat infestations including head lice, scabies, river blindness (onchocerciasis), strongyloidiasis, trichuriasis, ascariasis and lymphatic filariasis. It works through many mechanisms to kill the targeted parasites, and can be taken by mouth, or applied to the skin for external infestations. It belongs to the avermectin family of medications. William Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura were awarded the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for its discovery and applications. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, and is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as an antiparasitic agent. In 2022, it was the 314th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 200,000 prescriptions. It is available as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochrane (organisation)
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes 53 review groups that are based at research institutions worldwide. Cochrane has over volunteer experts from around the world. The group conducts systematic reviews of healthcare interventions and diagnostic tests and publishes them in the Cochrane Library. While Cochrane reviews typically focus on randomized controlled trials, some reviews, particularly in areas such as public and occupational health, also incorporate other study designs. These may include non-randomised observational studies as well as controlled before–after (CBA) studies and interrupted time-series studies. According to the Library, articles are available via one-click access, though some may require registration or a subscription. History Cochrane, prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histoplasma
''Histoplasma'' is a genus of fungi in the order Onygenales. Species are known human pathogens producing yeast-like states under pathogenic conditions. They are the causative agents of histoplasmosis in humans and epizootic lymphangitis in horses. Forms and stages ''Histoplasma'' species have two forms: their environmental form is hyphal with microconidia and tuberculate macroconidia while their pathogenic form is a small intracellular yeast that exhibits narrow-necked budding and no capsule. Infection occurs through inhalation of microconidia or small mycelial fragments. The dimorphic mold-yeast transforms and enters host macrophages Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ... and proliferates within them. Infections are most often seen in immunodeficient individuals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome
Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS) is a syndrome affecting the eye, which is characterized by peripheral atrophic chorioretinal scars, atrophy or scarring adjacent to the optic disc and maculopathy. The loss of vision in POHS is caused by choroidal neovascularization. Presentation The diagnosis of POHS is based on the clinical triad of multiple white, atrophic choroidal scars, peripapillary pigment changes (dark spots around optic disc of the eye), and a maculopathy caused by choroidal neovascularization. Completely distinct from POHS, acute ocular histoplasmosis may rarely occur in immunodeficiency. Causes Despite its name, the "presumed" relationship of POHS to ''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is controversial and has been questioned by a number of medical professionals. The fungus has rarely been isolated from cases with POHS, Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Synd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |