|
Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Syndrome
Presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS) is a syndrome affecting the eye, which is characterized by peripheral atrophic chorioretinal scars, atrophy or scarring adjacent to the optic disc and maculopathy. The loss of vision in POHS is caused by choroidal neovascularization. Presentation The diagnosis of POHS is based on the clinical triad of multiple white, atrophic choroidal scars, peripapillary pigment changes (dark spots around optic disc of the eye), and a maculopathy caused by choroidal neovascularization. Completely distinct from POHS, acute ocular histoplasmosis may rarely occur in immunodeficiency. Causes Despite its name, the "presumed" relationship of POHS to ''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is controversial and has been questioned by a number of medical professionals. The fungus has rarely been isolated from cases with POHS, Presumed Ocular Histoplasmosis Synd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Disc
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye. The ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. The optic disc represents the beginning of the optic nerve and is the point where the axons of retinal ganglion cells come together. The optic disc in a normal human eye carries 1–1.2 million afferent nerve fibers from the eye toward the brain. The optic disc is also the entry point for the major arteries that supply the retina with blood, and the exit point for the veins from the retina. Structure The optic disc is located 3 to 4 mm to the nasal side of the fovea. It is a vertical oval, with average dimensions of 1.76mm horizontally by 1.92mm vertically. There is a central depression, of variable size, called the optic cup. This depression can be a variety of shapes from a shallow indent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. With time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance it is no longer necessary to use a contrast. The word itself comes from the Greek words ἀνγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessels is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely. The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography and newer vascular ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
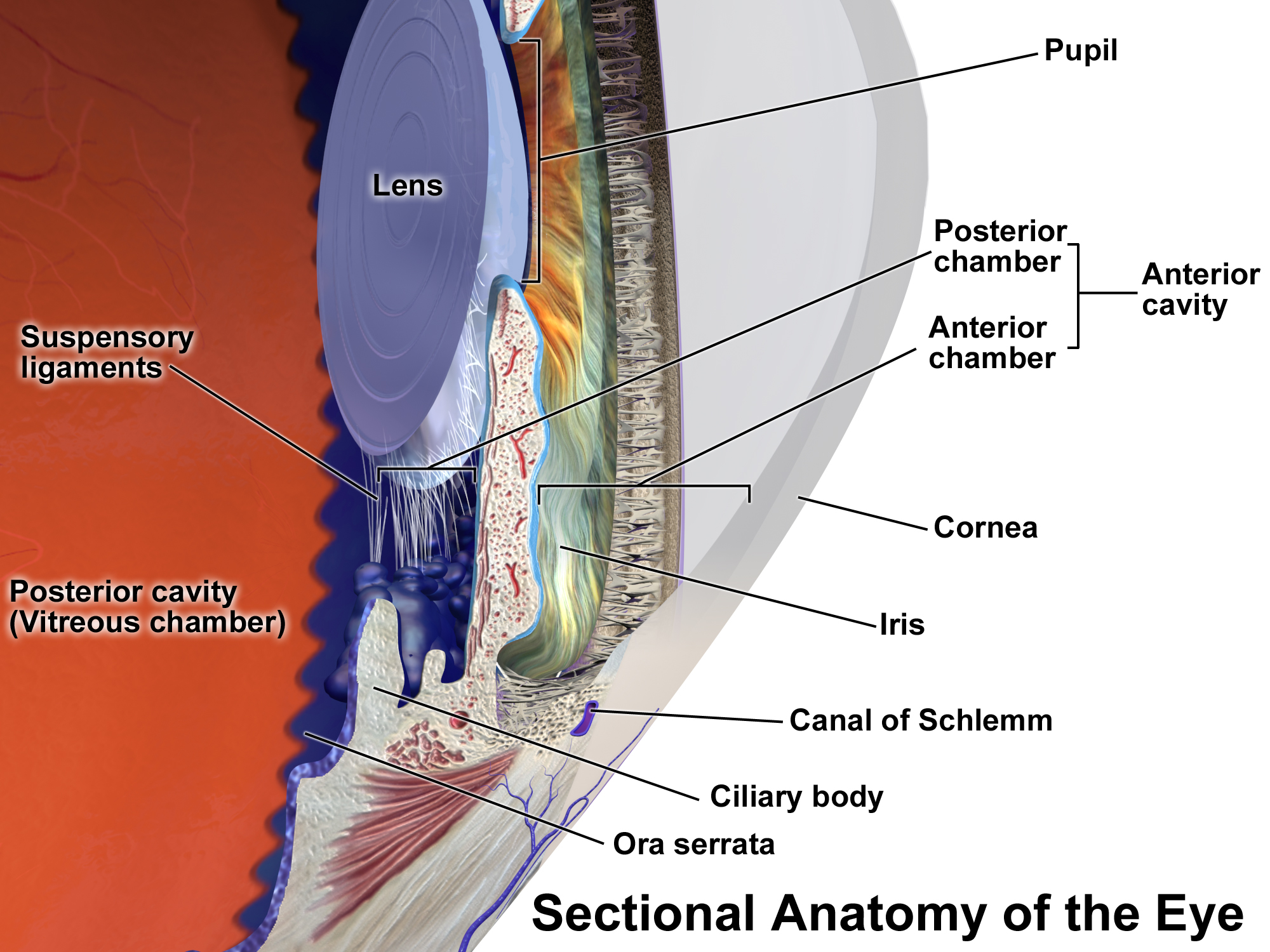
Uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and includes the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis is described anatomically, by the part of the eye affected, as anterior, intermediate or posterior, or panuveitic if all parts are involved. Anterior uveitis ( iridocyclitis) is the most common, with the incidence of uveitis overall affecting approximately 1:4500, most commonly those between the ages of 20–60. Symptoms include eye pain, eye redness, floaters and blurred vision, and ophthalmic examination may show dilated ciliary blood vessels and the presence of cells in the anterior chamber. Uveitis may arise spontaneously, have a genetic component, or be associated with an autoimmune disease or infection. While the eye is a relatively protected environment, its immune mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF, ), originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF), is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of Cystine knot, cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis (the ''De novo synthesis, de novo'' formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). It is part of the system that restores the oxygen supply to tissues when blood circulation is inadequate such as in hypoxic conditions. Serum concentration of VEGF is high in bronchial asthma and diabetes mellitus. VEGF's normal function is to create new blood vessels during embryonic development, new blood vessels after injury, muscle following exercise, and new vessels (collateral circulation) to bypass blocked vessels. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologists
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a form of phototherapy involving light and a photosensitizing chemical substance used in conjunction with molecular oxygen to elicit cell death ( phototoxicity). PDT is used in treating acne, wet age-related macular degeneration, psoriasis, and herpes. It is used to treat malignant cancers, including head and neck, lung, bladder and skin. Advantages lessen the need for delicate surgery and lengthy recuperation and minimal formation of scar tissue and disfigurement. A side effect is the associated photosensitisation of skin tissue. Basics PDT applications involve three components: a photosensitizer, a light source and tissue oxygen. The wavelength of the light source needs to be appropriate for exciting the photosensitizer to produce radicals and/or reactive oxygen species. These are free radicals (Type I) generated through electron abstraction or transfer from a substrate molecule and highly reactive state of oxygen known as singlet oxygen ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis Inhibitor
An angiogenesis inhibitor is a substance that inhibits the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Some angiogenesis inhibitors are endogenous and a normal part of the body's control and others are obtained exogenously through pharmaceutical drugs or diet. While angiogenesis is a critical part of wound healing and other favorable processes, certain types of angiogenesis are associated with the growth of malignant tumors. Thus angiogenesis inhibitors have been closely studied for possible cancer treatment. Angiogenesis inhibitors were once thought to have potential as a "silver bullet" treatment applicable to many types of cancer, but the limitations of anti-angiogenic therapy have been shown in practice. Currently, angiogenesis inhibitors are recognized for their improvement of cancer immunotherapy by overcoming endothelial cell anergy. Angiogenesis inhibitors are also used to effectively treat macular degeneration in the eye, and other diseases that involve a proliferatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between the two forms is categorized by the change in the macula. Those with dry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescein Angiography
Fluorescein angiography (FA), fluorescent angiography (FAG), or fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid (parts of the fundus) using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. Sodium fluorescein is added into the systemic circulation, the retina is illuminated with blue-green light at a wavelength of 490 nanometers, and an angiogram is obtained by photographing the fluorescent green light that is emitted by the dye. The fluorescein is administered intravenously in intravenous fluorescein angiography (IVFA) and orally in oral fluorescein angiography (OFA). The test is a dye tracing method. The fluorescein dye also reappears in the patient urine, causing the urine to appear darker, and sometimes orange. It can also cause discolouration of the saliva. Fluorescein angiography is one of several health care applications of this dye, all of which have a risk of severe adverse effects. See fluorescein safety in h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maculopathy
A maculopathy is any pathological condition of the macula, an area at the centre of the retina that is associated with highly sensitive, accurate vision. Forms of maculopathies * Age-Related Macular Degeneration is a degenerative maculopathy associated with progressive sight loss. It is characterised by changes in pigmentation in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium, the appearance of drusen on the retina of the eye and choroidal neovascularization. AMD has two forms; 'dry' or atrophic/non-exudative AMD, and 'wet' or exudative/neovascular AMD. * Malattia Leventinese (or Doyne’s honeycomb retinal dystrophy) is another maculopathy with a similar pathology to wet AMD. * Hypotony maculopathy: Maculopathy due to very low intraocular pressure ( ocular hypotony). *Cellophane Maculopathy A fine glistening membrane forms over the macula, obscuring the vision. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco Smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed to have begun as early as 5000–3000 BC in Mesoamerica and South America. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia in the late 17th century by European colonists, where it followed common trade routes. The practice encountered criticism from its first import into the Western world onward but embedded itself in certain strata of several societies before becoming widespread upon the introduction of automated cigarette-rolling apparatus. Smoking is the most common method of consuming tobacco, and tobacco is the most common substance smoked. The agricultural product is often mixed with additives and then combusted. The resulting smoke, which contains various active substances, the most significant of which is the addictive psychostimulant drug nicotine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histoplasma Capsulatum
''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is a species of dimorphic fungus. Its sexual form is called ''Ajellomyces capsulatus''. It can cause pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis. ''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is "distributed worldwide, except in Antarctica, but most often associated with river valleys" and occurs chiefly in the " Central and Eastern United States" followed by " Central and South America, and other areas of the world". It is most prevalent in the Ohio and Mississippi River valleys. It was discovered by Samuel Taylor Darling in 1906. Growth and morphology ''Histoplasma capsulatum'' is an ascomycetous fungus closely related to '' Blastomyces dermatitidis''. It is potentially sexual, and its sexual state, ''Ajellomyces capsulatus'', can readily be produced in culture, though it has not been directly observed in nature. ''H. capsulatum'' groups with ''B. dermatitidis'' and the South American pathogen '' Paracoccidioides brasiliensis'' in the recently recognized fungal fami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |