|
Chlorohydrin
In organic chemistry a halohydrin (also a haloalcohol or β-halo alcohol) is a functional group in which a halogen and a hydroxyl are bonded to adjacent carbon atoms, which otherwise bear only hydrogen or hydrocarbyl groups (e.g. 2-chloroethanol, 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol). The term only applies to saturated motifs, as such compounds like 2-chlorophenol would not normally be considered halohydrins. Megatons of some chlorohydrins, e.g. propylene chlorohydrin, are produced annually as precursors to polymers. Halohydrins may be categorized as chlorohydrins, bromohydrins, fluorohydrins or iodohydrins depending on the halogen present. Synthesis From alkenes Halohydrins are usually prepared by treatment of an alkene with a halogen, in the presence of water. The reaction is a form of electrophilic addition, similar to the halogen addition reaction and proceeds with anti addition, leaving the newly added X and OH groups in a trans configuration. The chemical equation for the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroethanol
2-Chloroethanol (also called ethylene chlorohydrin or glycol chlorohydrin) is an organic chemical compound with the chemical formula HOCH2CH2Cl and the ''simplest'' beta-halohydrin (chlorohydrin). This colorless liquid has a pleasant ether-like odor. It is miscible with water. The molecule is bifunctional, consisting of both an alkyl chloride and an alcohol functional group. Synthesis and applications 2-Chloroethanol is produced by treating ethylene with hypochlorous acid: : 2-Chloroethanol was once produced on a large scale as a precursor to ethylene oxide: : :HOCH2CH2Cl + NaOH → C2H4O + NaCl + H2O This application has been supplanted by the more economic direct oxidation of ethylene. Otherwise chloroethanol is still used in the production of pharmaceuticals, biocides, and plasticizers. Many of these applications entail its use in installing 2-hydroxyethyl groups. Several dyes are prepared by the alkylation of aniline derivatives with chloroethanol. It is also used for manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-MCPD
3-MCPD (3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol or 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol) is an organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid. It is a versatile multifunctional building block. The compound has attracted attention as the most common member of chemical food contaminants known as chloropropanols. It is suspected to be carcinogenic in humans. It is produced in foods treated at high temperatures with hydrochloric acid to speed up protein hydrolysis. As a byproduct of this process, chloride can react with the glycerol backbone of lipids to produce 3-MCPD. 3-MCPD can also occur in foods that have been in contact with materials containing epichlorohydrin-based wet-strength resins which are used in the production of some tea bags and sausage casings. In 2009, 3-MCPD was found in some East Asian and Southeast Asian sauces such as oyster sauce, Hoisin sauce, and soy sauce. Using hydrochloric acid is far faster than traditional slow fermentation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propylene Chlorohydrin
Propylene chlorohydrin usually refers to the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CH2Cl. A related compound, an isomer, is CH3CH(Cl)CH2OH. Both isomers are colorless liquids that are soluble in organic solvents. They are classified as chlorohydrins. Both are generated on a large scale as intermediates in the production of propylene oxide.Gordon Y. T. Liu, W. Frank Richey, Joanne E. Betso, Brian Hughes, Joanna Klapacz, and Joerg Lindner "Chlorohydrins" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. {{doi, 10.1002/14356007.a06_565.pub2 The reaction of aqueous solution of chlorine with propene Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH=CH2. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petrole ... gives a 10:1 ratio of CH3CH(OH)CH2Cl and CH3CH(Cl)CH2OH. These compounds are treated with lime to give prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
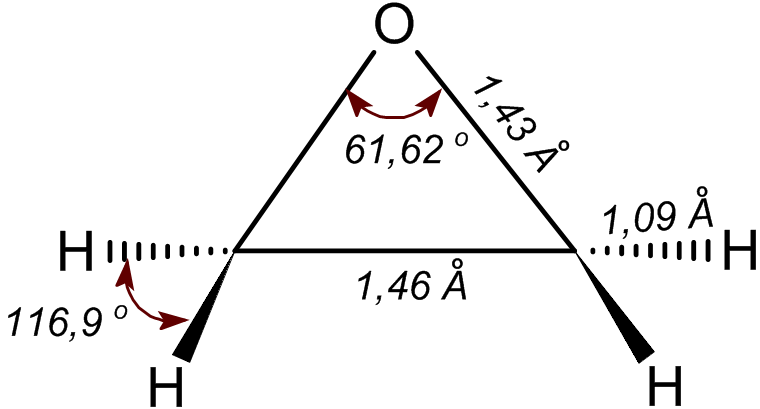
Ethylene Oxide
Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the formula . It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of silver catalyst. The reactivity that is responsible for many of ethylene oxide's hazards also makes it useful. Although too dangerous for direct household use and generally unfamiliar to consumers, ethylene oxide is used for making many consumer products as well as non-consumer chemicals and intermediates. These products include detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and various organic chemicals such as ethylene glycol, ethanolamines, simple an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halohydrin
In organic chemistry a halohydrin (also a haloalcohol or β-halo alcohol) is a functional group in which a halogen and a hydroxyl are bonded to adjacent carbon atoms, which otherwise bear only hydrogen or hydrocarbyl groups (e.g. 2-chloroethanol, 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol). The term only applies to saturated motifs, as such compounds like 2-chlorophenol would not normally be considered halohydrins. Megatons of some chlorohydrins, e.g. propylene chlorohydrin, are produced annually as precursors to polymers. Halohydrins may be categorized as chlorohydrins, bromohydrins, fluorohydrins or iodohydrins depending on the halogen present. Synthesis From alkenes Halohydrins are usually prepared by treatment of an alkene with a halogen, in the presence of water. The reaction is a form of electrophilic addition, similar to the halogen addition reaction and proceeds with anti addition, leaving the newly added X and OH groups in a trans configuration. The chemical equation for the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionyl Chloride
Propionyl chloride (also propanoyl chloride) is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2C(O)Cl. It is the acyl chloride derivative of propionic acid. It undergoes the characteristic reactions of acyl chlorides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. It is used as a reagent for organic synthesis. In derived chiral amides and esters, the methylene protons are diastereotopic. Synthesis Propionyl chloride is industrially produced by chlorination of propionic acid with phosgene Phosgene is the organic chemical compound with the formula COCl2. It is a toxic, colorless gas; in low concentrations, its musty odor resembles that of freshly cut hay or grass. Phosgene is a valued and important industrial building block, espe ...: :CH3CH2CO2H + COCl2 → CH3CH2COCl + HCl + CO2 References {{reflist, 30em Acyl chlorides Reagents for organic chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
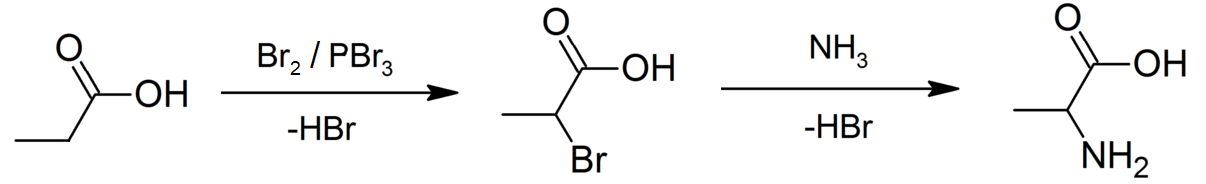
Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky Halogenation
The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky halogenation reaction is a chemical transformation that involves the halogenation of a carboxylic acid at the α carbon. For this reaction to occur the α carbon must bear at least one proton. The reaction is named after the German chemists Carl Magnus von Hell (1849–1926) and Jacob Volhard (1834–1910) and the Russian chemist Nikolay Zelinsky (1861–1953). : An example of the Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction can be seen in the preparation of alanine from propionic acid. In the first step, a combination of bromine and phosphorus tribromide (catalyst) is used in the Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky reaction to prepare 2-bromopropanoic acid, which in the second step is converted to a racemic mixture of the amino acid product by ammonolysis. :: Mechanism The reaction is initiated by addition of a catalytic amount of PBr3, after which one molar equivalent of Br2 is added. : PBr3 replaces the carboxylic OH with a bromide, resulting in a carboxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiomerically
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode – is one of two stereoisomers that are non-superposable onto their own mirror image. Enantiomers are much like one's right and left hands, when looking at the same face, they cannot be superposed onto each other. No amount of reorientation will allow the four unique groups on the chiral carbon (see Chirality (chemistry)) to line up exactly. The number of stereoisomers a molecule has can be determined by the number of chiral carbons it has. Stereoisomers include both enantiomers and diastereomers. Diastereomers, like enantiomers, share the same molecular formula and are non-superposable onto each other however, they are not mirror images of each other. A molecule with chirality rotates plane-polarized light. A mixture of equals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxide
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy'', but such materials do not contain epoxide groups (or contain only a few residual epoxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |