|
Chao Yang-class Destroyer
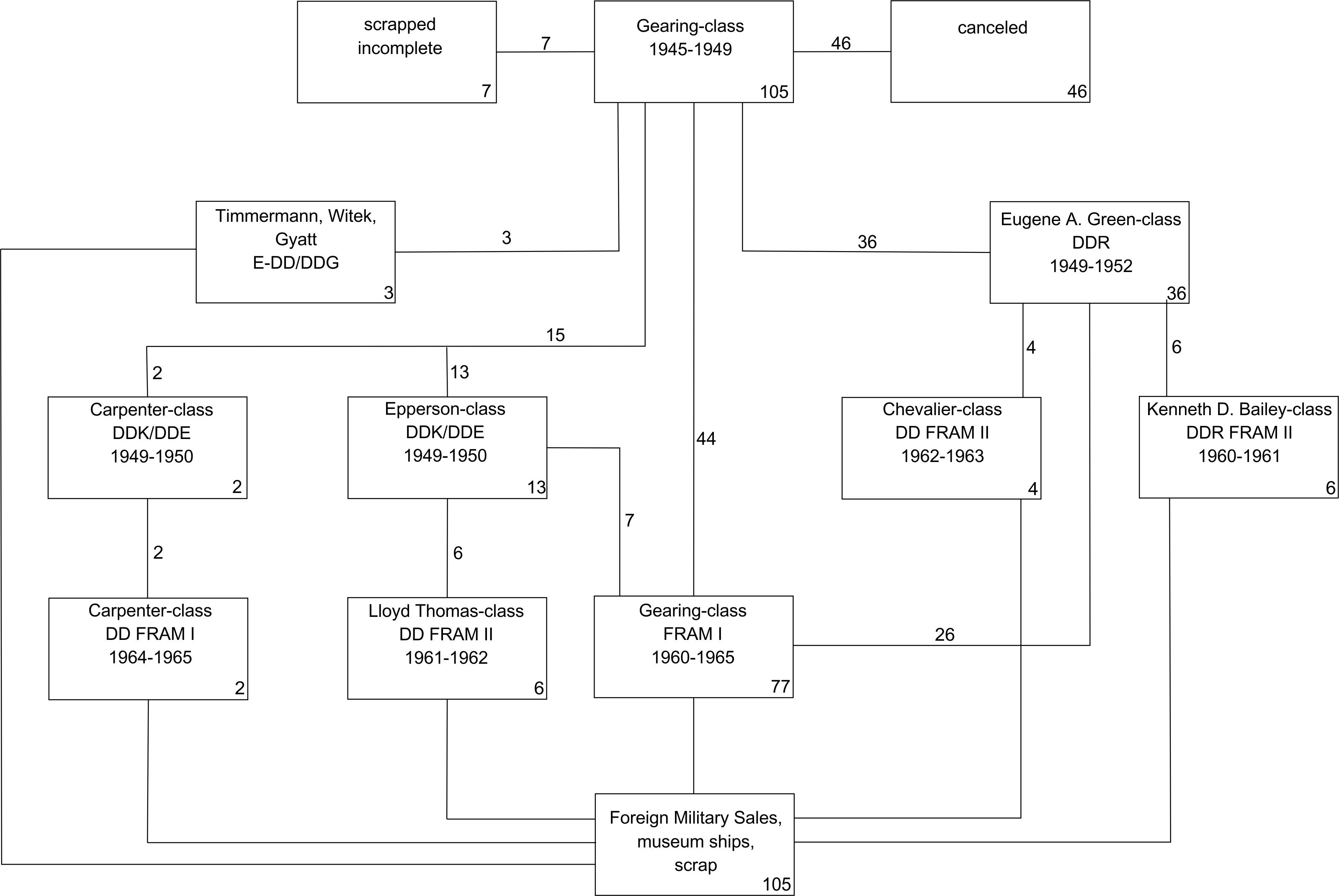
The ''Gearing'' class was a series of 98 destroyers built for the U.S. Navy during and shortly after World War II. The ''Gearing'' design was a minor modification of the , whereby the hull was lengthened by at amidships, which resulted in more fuel storage space and increased the operating range. The first ''Gearings'' were not ready for service until mid-1945 and saw little service in World War II. They continued serving, with a series of upgrades, until the 1970s. At that time many were sold to other nations, where they served many more years. Procurement and construction 31 vessels were authorized on 9 July 1942: * DD-710 to DD-721 awarded to Federal Shipbuilding, Kearny. * DD-742 to DD-743 awarded to Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine. * DD-763 to DD-769 awarded to Bethlehem Steel, San Francisco. * DD-782 to DD-791 awarded to Todd Pacific Shipyards, Seattle. 4 vessels were authorized on 13 May 1942: * DD-805 to DD-808 awarded to Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine. 3 vessels were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bath Iron Works
Bath Iron Works (BIW) is a major United States shipyard located on the Kennebec River in Bath, Maine, founded in 1884 as Bath Iron Works, Limited. Since 1995, Bath Iron Works has been a subsidiary of General Dynamics, one of the world's largest defense companies. BIW has built private, commercial, and military vessels, most of which have been ordered by the United States Navy. History Bath Iron Works was incorporated in 1884 by General Thomas W. Hyde, a native of Bath who served in the American Civil War. After the war, he bought a shop that made windlasses and other iron hardware for the wooden ships built in Bath's many shipyards. He expanded the business by improving its practices, entering new markets, and acquiring other local businesses. By 1882, Hyde Windlass was eyeing the new and growing business of iron shipbuilding, and it incorporated as Bath Iron Works in 1884. On February 28, 1890, BIW won its first contract for complete vessels: two iron gunboats for the Navy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
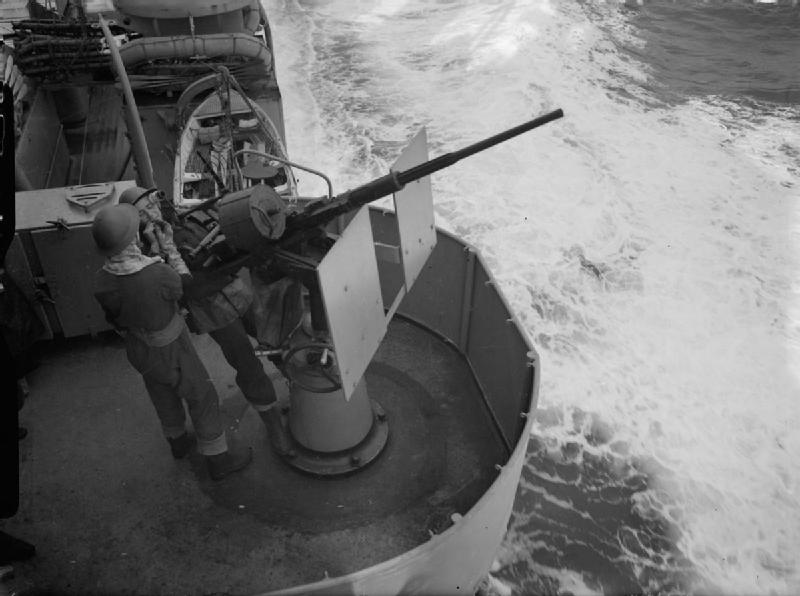
Oerlikon 20 Mm Cannon
The Oerlikon 20 mm cannon is a series of autocannons based on an original German Becker Type M2 20 mm cannon design that appeared very early in World War I. It was widely produced by Oerlikon Contraves and others, with various models employed by both Allied and Axis forces during World War II. Many versions of the cannon are still used. Blowback-operated models History Origins During World War I, the German industrialist Reinhold Becker developed a 20 mm caliber cannon, known now as the 20 mm Becker using the advanced primer ignition blowback (API blowback) method of operation. This used a 20×70mmRB cartridge and had a cyclic rate of fire of 300 rpm. It was used on a limited scale as an aircraft gun on ''Luftstreitkräfte'' warplanes, and an anti-aircraft gun towards the end of that war. Because the Treaty of Versailles banned further production of such weapons in Germany, the patents and design works were transferred in 1919 to the Swiss firm SEMAG (''Seebach M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Depth Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and sodar (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic) to ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
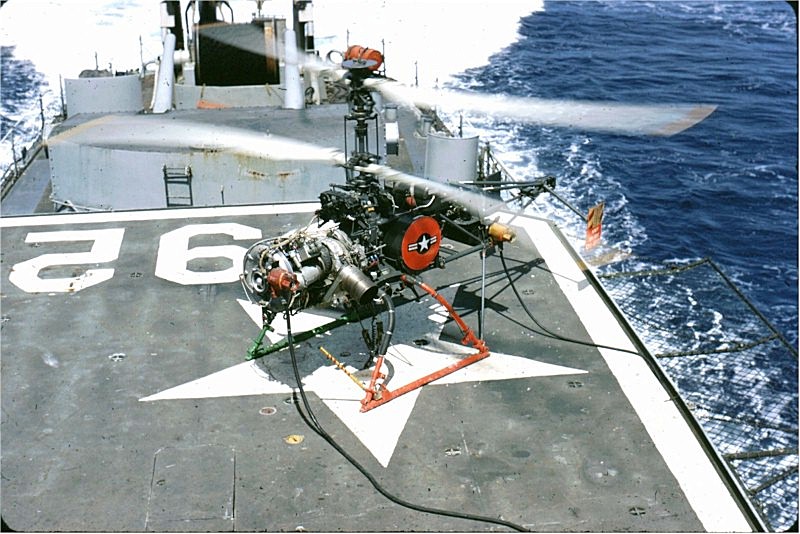
QH-50 DASH
The Gyrodyne QH-50 DASH (''Drone Anti-Submarine Helicopter'') is a small drone helicopter built by Gyrodyne Company of America for use as a long-range anti-submarine weapon on ships that would otherwise be too small to operate a full-sized helicopter. It remained in production until 1969. Several are still used today for various land-based roles. Design and development DASH was a major part of the United States Navy's Fleet Rehabilitation and Modernization (FRAM) program of the late 1950s. FRAM was started because the Soviet Union was building submarines faster than the US could build anti-submarine frigates. Instead of building frigates, the FRAM upgrade series allowed the US to rapidly update by converting older ships that were less useful in modern naval combat. The navy could upgrade the sonar on World War II-era destroyers but needed a stand-off weapon to attack at the perimeter of the sonar's range. The old destroyers had little room for add-ons such as a full flight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 44 Torpedo
The Mark 44 torpedo is a now-obsolete air-launched and ship-launched lightweight torpedo manufactured in the United States, and under licence in Canada, France, Italy, Japan and the United Kingdom, with 10,500 being produced for U.S. service. It was superseded by the Mark 46 torpedo, beginning in the late 1960s. The Royal Australian Navy, however, continued to use it alongside its successor for a number of years, because the Mark 44 was thought to have superior performance in certain shallow-water conditions. It has been deployed by many navies and air forces including the USN, Royal Navy, Royal Australian Navy and the Royal Air Force from various launch vehicles. These include long-range maritime patrol aircraft, e.g. P-3 Orion, RAF Nimrod, Canadair Argus, LAMPS and other embarked naval helicopters, ASROC missiles, Ikara missiles. Development During the 1950s the US Navy ordered development of a new generation of lightweight anti-submarine torpedoes. Two programs were s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 32 Torpedo Tubes
Mark 32 surface vessel torpedo tubes (Mk 32 SVTT) is a torpedo launching system designed for the United States Navy. History The Mark 32 has been the standard anti-submarine torpedo launching system aboard United States Navy surface vessels since its introduction in 1960, and is in use aboard the warships of several other navies. During the FRAM Program, , and destroyers were modernized and fitted with two Mark 32 torpedo tubes on each side of their midship. The torpedo tubes' service extended to multiple other countries such as Mexico, South Korea, Taiwan, Turkey, Egypt and many more due to the fact that decommissioned American ships were bought or transferred over to them throughout the years, notably s. Japan uses the HOS-301 torpedo tubes which are redesignated version of the Mark 32. Design Most versions (referred to as modifications or mods) are triple-tube sets that can be rotated or trained to face a target. The exception is the Mod 9 sets, which only have two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASROC
The RUR-5 ASROC (for "Anti-Submarine Rocket") is an all-weather, all sea-conditions anti-submarine missile system. Developed by the United States Navy in the 1950s, it was deployed in the 1960s, updated in the 1990s, and eventually installed on over 200 USN surface ships, specifically cruisers, destroyers, and frigates. The ASROC has been deployed on scores of warships of many other navies, including Canada, Germany, Italy, Japan, Taiwan, Greece, Pakistan and others. History ASROC started development as the Rocket Assisted Torpedo (RAT) program by Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake in the early 1950s to develop a surface warship anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon to counter the new post-World War II submarines which ran quieter, at much higher speed and could attack from much longer range with high speed homing torpedoes. In addition, the goal was to take advantage of modern sonars with a much larger detection range. An extended range torpedo delivered by parachute from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FRAM I
The Fleet Rehabilitation and Modernization (FRAM) program of the United States Navy extended the lives of World War II-era destroyers by shifting their mission from a surface attack role to that of a submarine hunter. The FRAM program also covered cruisers, aircraft carriers, submarines, amphibious ships, and auxiliaries.Vinock, Eli, CAPT USN "FRAM Fixes the Fleet" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' August 1984 pp.70-73 The United States Coast Guard also used this term in the 1980s for the modernization of its s. Background The program was started by Admiral Arleigh Burke as a response to estimates that the Soviet Navy would have a force of about 300 modern fast-attack submarines by 1957. The U.S. Navy was unable to produce quickly enough the destroyer escorts (redesignated as frigates after 1975) and other antisubmarine warfare ships to counter this threat, given its other priorities in new antiaircraft warfare frigates (redesignated as cruisers after 1975) and air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedgehog (weapon)
The Hedgehog (also known as an ''Anti-Submarine Projector'') was a forward-throwing anti-submarine weapon that was used primarily during the Second World War. The device, which was developed by the Royal Navy, fired up to 24 spigot mortars ahead of a ship when attacking a U-boat. It was deployed on convoy escort warships such as destroyers and corvettes to supplement the depth charges. As the mortar projectiles employed contact fuzes rather than time or bathymetric (depth) fuzes, detonation occurred directly against a hard surface such as the hull of a submarine making it more deadly than depth charges, which relied on damage caused by hydrostatic shockwaves. During World War II out of 5,174 British depth charge attacks there were 85.5 kills, a ratio of 60.5 to 1. In comparison, the Hedgehog made 268 attacks for 47 kills, a ratio of 5.7 to 1. Development The "Hedgehog", so named because the empty rows of its launcher spigots resembled the spines on the back of a hedgeh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
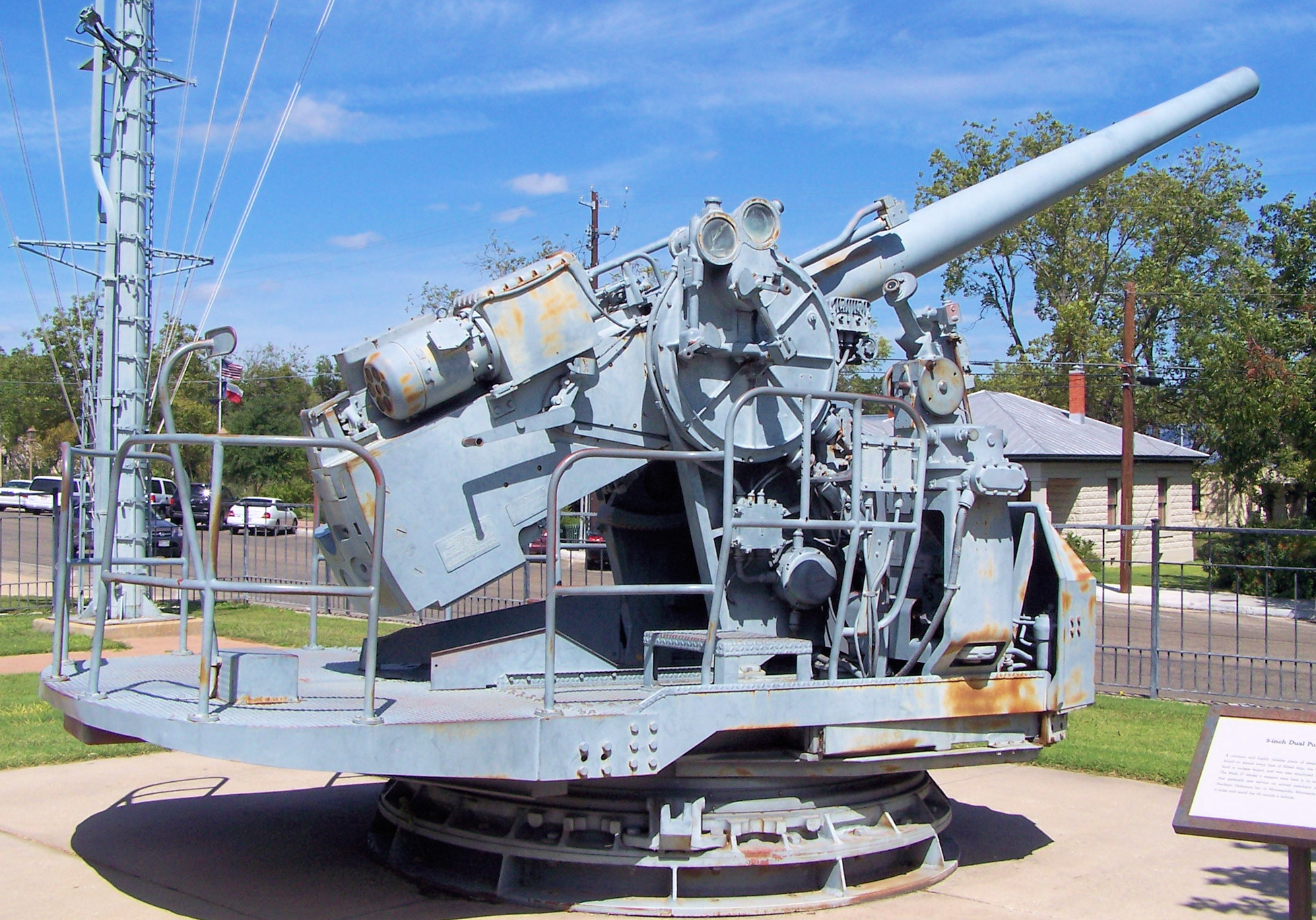
3"/50 Caliber Gun
The 3-inch/50-caliber gun (spoken "three-inch fifty-caliber") in United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile in diameter, and the barrel was 50 Caliber (artillery), calibers long (barrel length is 3 in × 50 = ). Different guns (identified by Mark numbers) of this caliber were used by the U.S. Navy and U.S. Coast Guard from 1900 through to 1990 on a variety of combatant and transport ship classes. The gun is still in use with the Spanish Navy on Serviola-class patrol boat, ''Serviola''-class patrol boats. Early low-angle guns The US Navy's first 3 inch /50-caliber gun (Mark 2) was an early model with a projectile velocity of per second. Low-angle (single-purpose/non-anti-aircraft) mountings for this gun had a range of 7000 yards at the maximum elevation of 15 degrees. The gun entered service around 1900 with the s, and was also fitted to s. By World War II these guns were found only on a few Coast Guard cutters and Defensively Equipped Mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual Purpose Gun
A dual-purpose gun is a naval artillery mounting designed to engage both surface and air targets. Description Second World War-era capital ships had four classes of artillery: the heavy main battery, intended to engage opposing battleships and cruisers of 305 mm to 457 mm (12 inch to 18 inch); a secondary battery for use against enemy destroyers of 152 mm to 203 mm (6 inch to 8 inch); heavy anti-aircraft guns of 76 mm to 127 mm (3 inch to 5 inch), which could create barrages to knock out airplanes at a distance; finally, light rapid-fire anti-aircraft batteries (A/A) to track and bring down aircraft at close range. The light A/A was dispersed throughout the ship and included both automatic cannons of 20 mm to 40 mm (.787 inch to 1.57 inch) and heavy machine guns of 12.7 mm to 14.5 mm (.50 inch to .58 inch). During World War II, the US Navy, Royal Navy, the French Navy, and the Imperial Japanese Navy combined the secondary batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
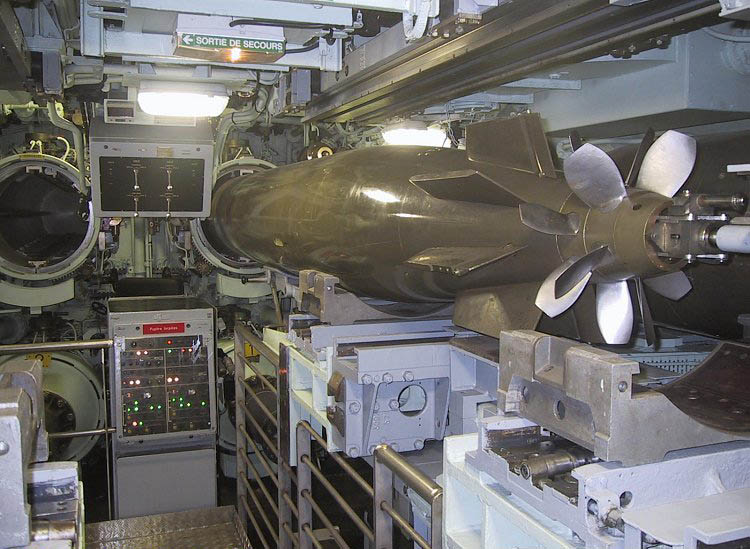
Torpedo Tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes. There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboard surface vessels. Deck-mounted torpedo launchers are usually designed for a specific type of torpedo, while submarine torpedo tubes are general-purpose launchers, and are often also capable of deploying naval mine, mines and cruise missiles. Most modern launchers are standardized on a diameter for light torpedoes (deck mounted aboard ship) or a diameter for heavy torpedoes (underwater tubes), although Torpedo#Classes and diameters, torpedoes of other classes and diameters have been used. Submarine torpedo tube A submarine torpedo tube is a more complex mechanism than a torpedo tube on a surface ship, because the tube has to accomplish the function of moving the torpedo from the normal atmospheric pressure within the submarine into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |