Torpedo tube on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching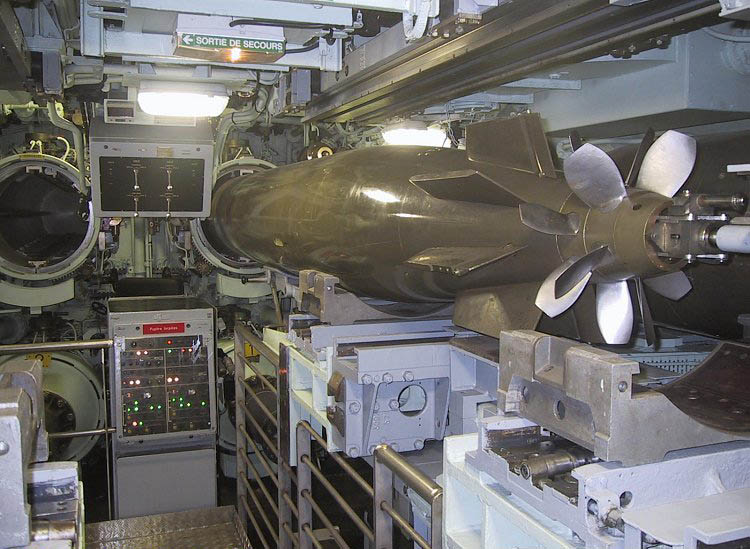  There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to
 The diagram illustrates the operation of a submarine torpedo tube. The diagram is somewhat simplified but does show the working of a submarine torpedo launch.
A torpedo tube has a considerable number of interlocks for safety reasons. For example, an interlock prevents the breech door and muzzle door from opening at the same time.
The submarine torpedo launch sequence is, in simplified form:
The diagram illustrates the operation of a submarine torpedo tube. The diagram is somewhat simplified but does show the working of a submarine torpedo launch.
A torpedo tube has a considerable number of interlocks for safety reasons. For example, an interlock prevents the breech door and muzzle door from opening at the same time.
The submarine torpedo launch sequence is, in simplified form:
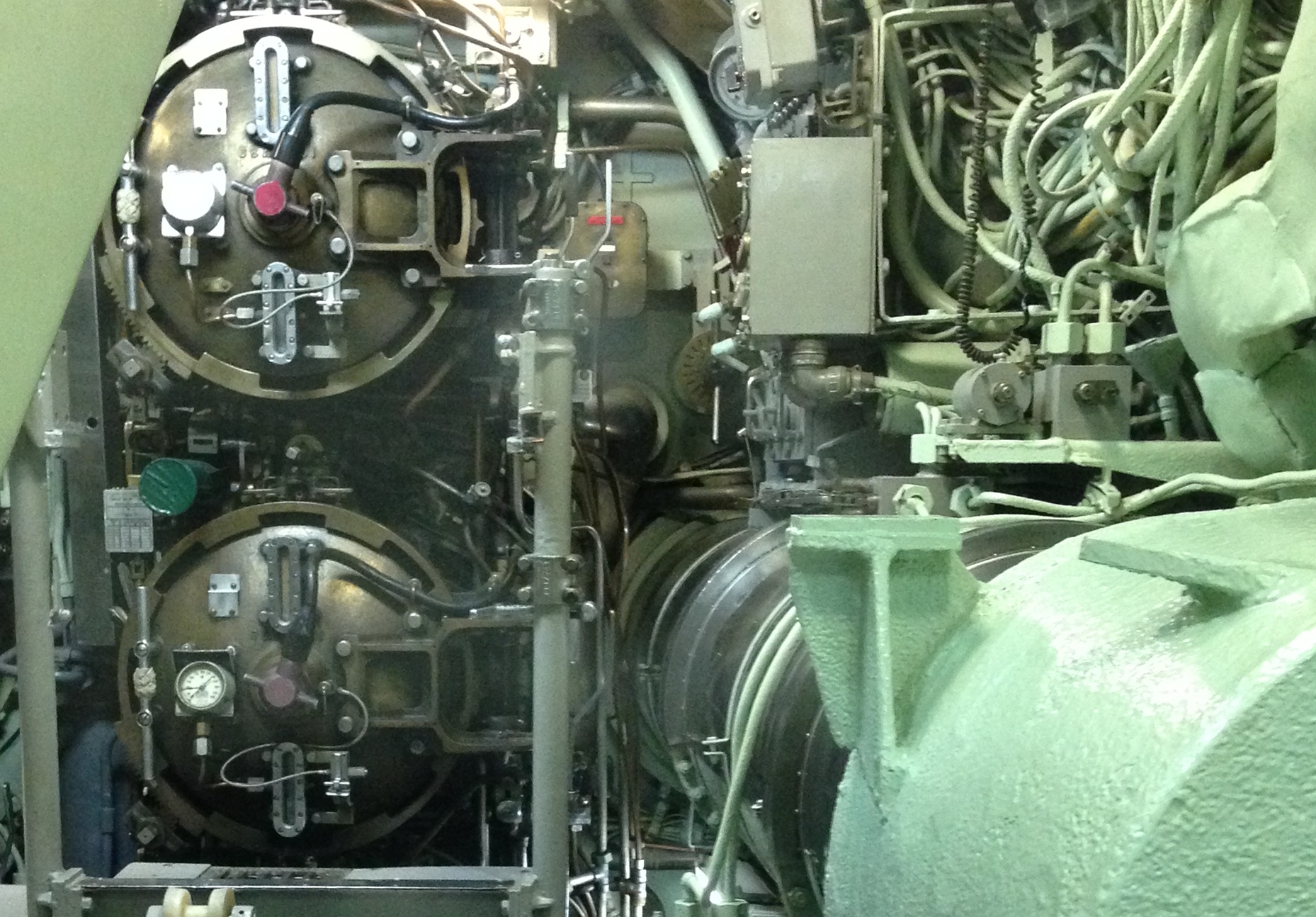
 #Open the breech door in the torpedo room. Load the torpedo into the tube.
#Hook up the wire-guide connection and the torpedo power cable.
#Shut and lock the breech door.
#Turn on power to the torpedo. A minimum amount of time is required for torpedo warmup. Fire control programs are uploaded to the torpedo.
#Flood the torpedo tube. This may be done manually or automatically, from sea or from tanks, depending on the class of submarine. The tube must be vented during this process to allow for complete filling and eliminate air pockets which could escape to the surface or cause damage when firing.
#Open the equalizing
#Open the breech door in the torpedo room. Load the torpedo into the tube.
#Hook up the wire-guide connection and the torpedo power cable.
#Shut and lock the breech door.
#Turn on power to the torpedo. A minimum amount of time is required for torpedo warmup. Fire control programs are uploaded to the torpedo.
#Flood the torpedo tube. This may be done manually or automatically, from sea or from tanks, depending on the class of submarine. The tube must be vented during this process to allow for complete filling and eliminate air pockets which could escape to the surface or cause damage when firing.
#Open the equalizing 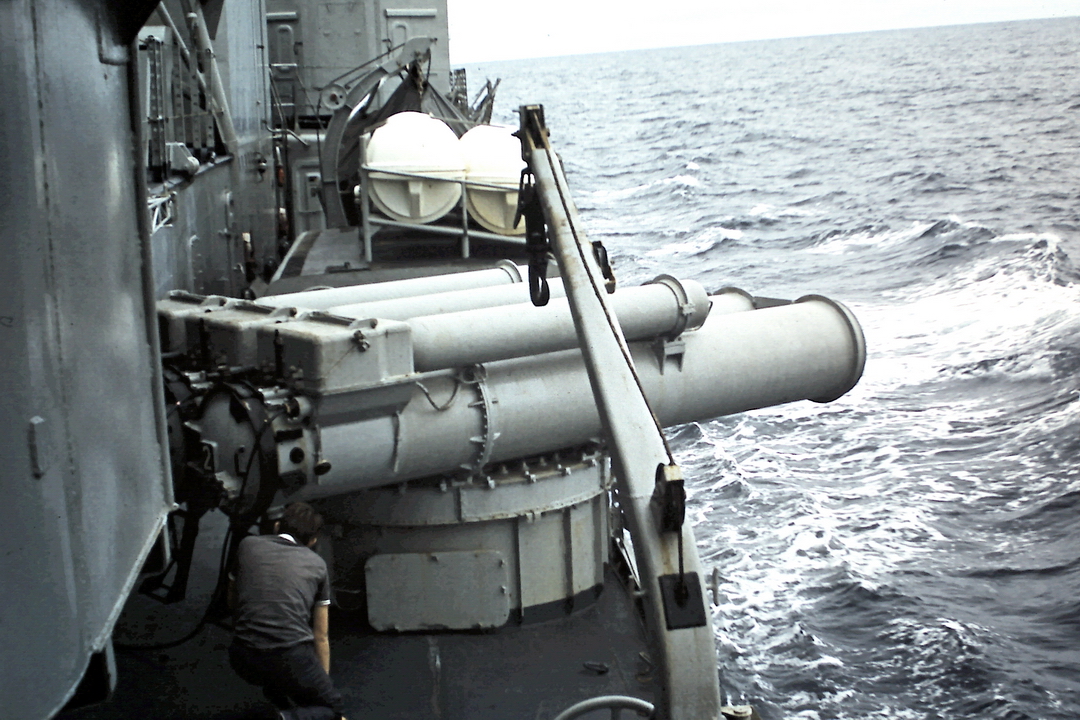 The German Type 212 submarine uses a new development of the water ram expulsion system, which ejects the torpedo with water pressure to avoid acoustic detection.
The German Type 212 submarine uses a new development of the water ram expulsion system, which ejects the torpedo with water pressure to avoid acoustic detection.
''The Fleet Type Submarine Online 21-Inch Submerged Torpedo Tubes'' United States Navy Restricted Ordnance Pamphlet 1085, June 1944''Torpedo tubes of German U-Boats''
{{Authority control Torpedoes
torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such ...
es.
 There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboard surface vessels. Deck-mounted torpedo launchers are usually designed for a specific type of torpedo, while submarine torpedo tubes are general-purpose launchers, and are often also capable of deploying mines and cruise missile
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided missile that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large payload over long distances with high precision. Modern cru ...
s. Most modern launchers are standardized on a diameter for light torpedoes (deck mounted aboard ship) or a diameter for heavy torpedoes (underwater tubes), although torpedoes of other classes and diameters have been used.
Submarine torpedo tube
A submarine torpedo tube is a more complex mechanism than a torpedo tube on a surface ship, because the tube has to accomplish the function of moving the torpedo from the normal atmosphericpressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
within the submarine into the sea at the ambient pressure of the water around the submarine. Thus a submarine torpedo tube operates on the principle of an airlock
An airlock is a room or compartment which permits passage between environments of differing atmospheric pressure or composition, while minimizing the changing of pressure or composition between the differing environments.
An airlock consist ...
.
Torpedo tube operation

 #Open the breech door in the torpedo room. Load the torpedo into the tube.
#Hook up the wire-guide connection and the torpedo power cable.
#Shut and lock the breech door.
#Turn on power to the torpedo. A minimum amount of time is required for torpedo warmup. Fire control programs are uploaded to the torpedo.
#Flood the torpedo tube. This may be done manually or automatically, from sea or from tanks, depending on the class of submarine. The tube must be vented during this process to allow for complete filling and eliminate air pockets which could escape to the surface or cause damage when firing.
#Open the equalizing
#Open the breech door in the torpedo room. Load the torpedo into the tube.
#Hook up the wire-guide connection and the torpedo power cable.
#Shut and lock the breech door.
#Turn on power to the torpedo. A minimum amount of time is required for torpedo warmup. Fire control programs are uploaded to the torpedo.
#Flood the torpedo tube. This may be done manually or automatically, from sea or from tanks, depending on the class of submarine. The tube must be vented during this process to allow for complete filling and eliminate air pockets which could escape to the surface or cause damage when firing.
#Open the equalizing valve
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or Slurry, slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically Pip ...
to equalize pressure in the tube with ambient sea pressure.
#Open the muzzle door. If the tube is set up for Impulse Mode the slide valve will open with the muzzle door. If Swim Out Mode is selected, the slide valve remains closed. The slide valve allows water from the ejection pump to enter the tube.
#When the launch command is given and all interlocks are satisfied, the water ram operates, thrusting a large volume of water into the tube at high pressure, which ejects the torpedo from the tube with considerable force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
. Modern torpedoes have a safety mechanism that prevents activation of the torpedo unless the torpedo senses the required amount of G-force
The g-force or gravitational force equivalent is a Specific force, mass-specific force (force per unit mass), expressed in Unit of measurement, units of standard gravity (symbol ''g'' or ''g''0, not to be confused with "g", the symbol for ...
.
#The power cable
A power cable is an electrical cable used specifically for transmission of electric energy, electrical power. It is an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together in a single bundle with an insulator (electricity), insu ...
is severed at launch. However, if a guidance wire is used, it remains connected through a drum of wire in the tube. Torpedo propulsion systems vary but electric torpedoes swim out of the tube on their own and are of a smaller diameter. Torpedoes with diameter and fuel-burning engines usually start outside the tube.
#Once outside the tube the torpedo begins its run toward the target as programmed by the fire-control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a hum ...
. Attack functions are programmed but with wire guided weapons, certain functions can be controlled from the ship.
#For wire-guided torpedoes, the muzzle door must remain open because the guidance wire is still connected to the inside of the breech door to receive commands from the submarine's fire-control system. A wire cutter on the inside of the breech door is activated to release the wire and its protective cable. These are drawn clear of the ship prior to shutting the muzzle door.
#The drain cycle is a reverse of the flood cycle; water is returned to the boat's tanks and can be moved as necessary. The tube must be vented to completely drain the tube since it is usually by gravity.
#Open the breech door and remove the remnants of the torpedo power cable and the guidance wire basket. The tube must be wiped dry to prevent a buildup of slime. This process is called "diving the tube" and tradition dictates that "ye who shoots, dives".
#Shut and lock the breech door.
Spare torpedoes are stored behind the tube in racks.
Speed is a desirable feature of a torpedo loading system, but safety is paramount. There are various manual and hydraulic handling systems for loading torpedoes into the tubes. Prior to the , US SSBNs utilized manual block and tackle which took about 15 minutes to load a tube. SSNs prior to the used a hydraulic system that was much faster and safer in conditions where the ship needed to maneuver.
 The German Type 212 submarine uses a new development of the water ram expulsion system, which ejects the torpedo with water pressure to avoid acoustic detection.
The German Type 212 submarine uses a new development of the water ram expulsion system, which ejects the torpedo with water pressure to avoid acoustic detection.
See also
*List of torpedoes by name
__NOTOC__
The list of torpedoes by name includes all torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on ...
References
External links
''The Fleet Type Submarine Online 21-Inch Submerged Torpedo Tubes'' United States Navy Restricted Ordnance Pamphlet 1085, June 1944
{{Authority control Torpedoes