|
Caribosiren
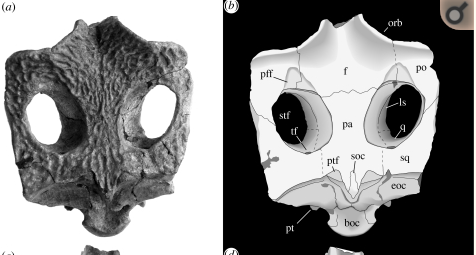
''Caribosiren'' is an extinct genus of mammal which existed in what is now Puerto Rico during the late Oligocene (Chattian). Fossils have been recovered from the San Sebastián Limestone The San Sebastián Formation is a geologic formation in Puerto Rico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Oligocene period. It was primarily deposited as limestone in a marine environment, but some localities with a significant amount of ter .... References Dugongidae Oligocene sirenians Fossil taxa described in 1959 Prehistoric placental genera {{Paleo-sirenian-stub Fossils of Puerto Rico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Sebastián Limestone
The San Sebastián Formation is a geologic formation in Puerto Rico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Oligocene period. It was primarily deposited as limestone in a marine environment, but some localities with a significant amount of terrestrial fauna appear to have been deposited in a deltaic environment. It contains some of the earliest fossils of terrestrial Caribbean vertebrates, including chinchilloid rodents and ''Eleutherodactylus'' frogs. In addition, taxa that are no longer known from the Caribbean, such as gavialid crocodilians Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchi ... and geomyoid rodents, have also been recovered from the formation. Vertebrate paleofauna Based on the Paleobiology Database: Cartilaginous fish Amphibians Reptiles Mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dugongidae
Dugongidae is a Family (biology), family in the Order (biology), order of Sirenia. The family has one surviving species, the dugong (''Dugong dugon''), one recently Extinction, extinct species, Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas''), and a number of extinct Genus, genera known from fossil records. Dugongidae's body weight ranges from 217 to 307 kg for juveniles, 334 to 424 kg for subadults, and 435 to 568.5 kg for adults. Oral temperatures for individual dugongs is determined from 24° to 34.2 °C. Heart rate readings are from 40 to 96 bpm and vary between individual dugongs. Respiration rate during the out-of-water phase is from 1 to 33. Taxonomy * Family Dugongidae ** Genus extinction, †''Anisosiren'' ** Genus †''Caribosiren'' ** Genus †''Indosiren'' ** Genus †''Lentiarenium'' ** Genus †''Kaupitherium'' ** Genus †''Paralitherium'' ** Genus †''Priscosiren'' ** Genus †''Prohalicore'' ** Genus †''Sirenavus'' ** Subfamily †Halitheriinae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
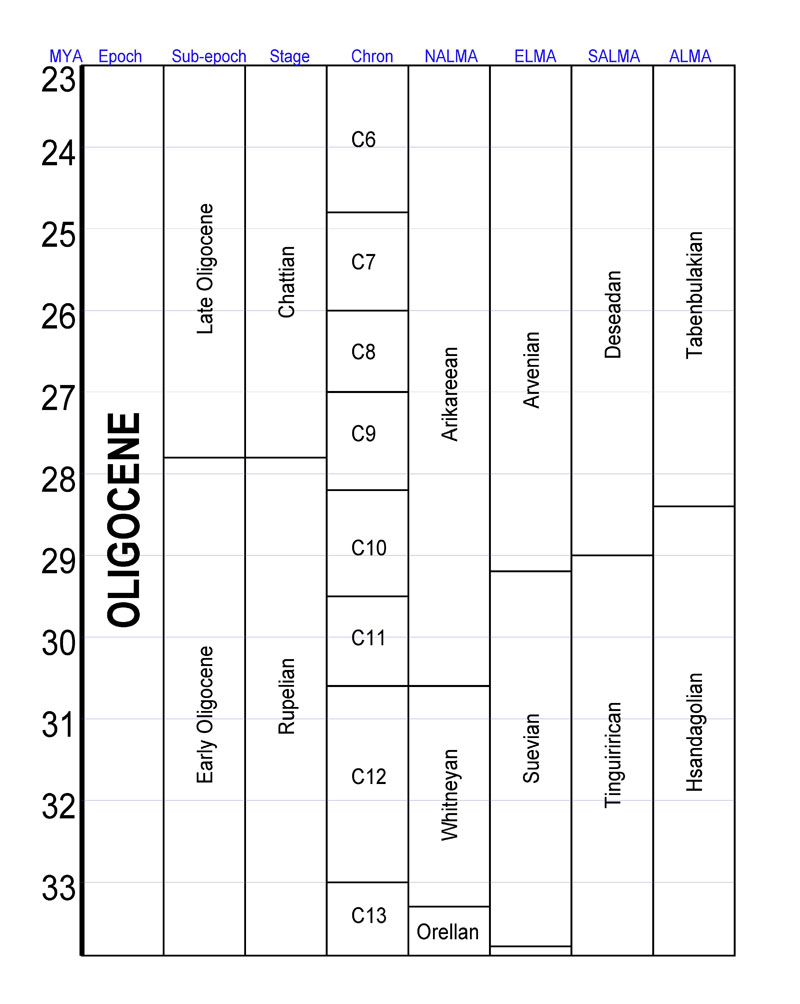
Late Oligocene
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale The geologic time scale or geological time scale (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochron ..., the younger of two age (geology), ages or upper of two stage (stratigraphy), stages of the Oligocene epoch (geology), Epoch/Series (stratigraphy), Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (stage), Aquitanian (the lowest stage of the Miocene). Stratigraphic definition The Chattian was introduced by Austrian palaeontologist Theodor Fuchs in 1894. Fuchs named the stage after the Chatti, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe.Berry, Edward W"The Mayence Basin, a Chapter of Geologic History" ''The Scientific Monthly'', Vol. 16, No. 2, February 1923. pp. 114. Retrieved March 18, 2020. The original type locality (geology), type l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological Type (biology), type wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or specimens). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name with that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles, middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors Genetic divergence, diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 Neontology#Extant taxon, extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 Order (biology), orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, Mole (animal), moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the Artiodactyl, even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including Felidae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States under the designation of Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth. Located about southeast of Miami, Miami, Florida between the Dominican Republic in the Greater Antilles and the United States Virgin Islands, U.S. Virgin Islands in the Lesser Antilles, it consists of the eponymous main island and numerous smaller islands, including Vieques, Puerto Rico, Vieques, Culebra, Puerto Rico, Culebra, and Isla de Mona, Mona. With approximately 3.2 million Puerto Ricans, residents, it is divided into Municipalities of Puerto Rico, 78 municipalities, of which the most populous is the Capital city, capital municipality of San Juan, Puerto Rico, San Juan, followed by those within the San Juan–Bayamón–Caguas metro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattian
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (the lowest stage of the Miocene). Stratigraphic definition The Chattian was introduced by Austrian palaeontologist Theodor Fuchs in 1894. Fuchs named the stage after the Chatti, a Germanic tribe.Berry, Edward W"The Mayence Basin, a Chapter of Geologic History" ''The Scientific Monthly'', Vol. 16, No. 2, February 1923. pp. 114. Retrieved March 18, 2020. The original type locality was near the German city of Kassel. The base of the Chattian is at the extinction of the foram genus ''Chiloguembelina'' (which is also the base of foram biozone P21b). An official GSSP for the Chattian Stage was ratified in October of 2016. The top of the Chattian Stage (which is the base of the Aquitanian Stage, Miocene Series and Neogene System) is at the first appeara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene Sirenians
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion of gras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1959
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Placental Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |