|
San Sebastián Limestone
The San Sebastián Formation is a geologic formation in Puerto Rico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Oligocene period. It was primarily deposited as limestone in a marine environment, but some localities with a significant amount of terrestrial fauna appear to have been deposited in a deltaic environment. It contains some of the earliest fossils of terrestrial Caribbean vertebrates, including chinchilloid rodents and ''Eleutherodactylus'' frogs. In addition, taxa that are no longer known from the Caribbean, such as gavialid crocodilians Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchi ... and geomyoid rodents, have also been recovered from the formation. Vertebrate paleofauna Based on the Paleobiology Database: Cartilaginous fish Amphibians Reptiles Mamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (stratigraphy)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleutherodactylus
''Eleutherodactylus'' is a genus of frogs in the family Eleutherodactylidae.Hedges, S. B., W. E. Duellman, and M. P. Heinicke . 2008. New World direct-developing frogs (Anura: Terrarana): molecular phylogeny, classification, biogeography, and conservation. Zootaxa 1737: 1-182. Many of the 200 species of the genus are commonly known as "rain frogs" or "robber frogs", due to their sharp, high-pitched, insect-like calls. They are found from the southern United States south to Central America, and reach their greatest diversity in the Caribbean. Species endemic to Puerto Rico are often referred to as coquís, of which the best-known species is the common coquí (''E. coqui''), which is both a national symbol of Puerto Rico and a notorious invasive species in Hawaii. Two ''Eleutherodactylus'' species, '' E. limbatus'' and '' E. iberia'', are among the smallest known frogs, measuring only 8.5 mm in length (only slightly larger than ''Paedophryne amauensis'', which measures arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
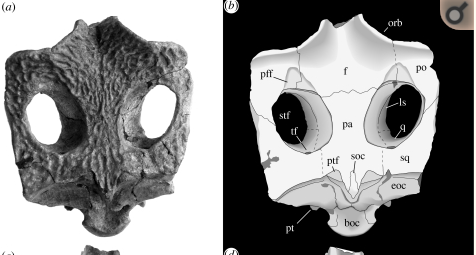
Pleurodira
The Pleurodira are one of the two living suborders of turtles, the other being the Cryptodira. The division between these two suborders represents a very deep evolutionary divide between two very different types of turtles. The physical differences between them, although anatomical and largely internal, are nonetheless significant, and the zoogeographic implications of them are substantial. The Pleurodira are known more commonly as the side-necked turtles and the name Pleurodira quite literally translates to side neck, whereas the Cryptodira are known as hidden-necked turtles. The Pleurodira turtles are currently restricted to freshwater habitats in the Southern Hemisphere, largely to Australia, South America, and Africa. Within the Pleurodira, three living families are represented: Chelidae, also known as the Austro-South American side-necked turtles, the Pelomedusidae, also known as the African mud terrapins, and the Podocnemididae, also known as the American side-neck rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelomedusidae
:''Alternatively, "Pelomedusidae" may refer to the Pelomedusoidea. See below for details.'' Pelomedusidae is a family of freshwater turtles endemic to sub-Saharan Africa, including Madagascar, São Tomé, and the Seychelles (although this population may have been introduced by humans). They range in size from in carapace length, and are generally roundish in shape. They are unable to fully withdraw their heads into their shells, instead drawing them to the side and folding them beneath the upper edge of their shells, hence are called African side-necked turtles. The family contains two living genera, '' Pelomedusa'' and '' Pelusios''. They are distinguished from their closest relatives by a hinge in the front section of the plastron.Obst, Fritz Jürgen (1998): elomedusinae ''In:'' Cogger, H.G., & Zweifel, R.G. (eds.): ''Encyclopedia of Reptiles and Amphibians'': 112-113. San Diego: Academic Press. . Pelomedusids spends most of their time in the mud at the bottom of rivers or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aktiogavialis
''Aktiogavialis'' is an extinct genus of crocodylian that lived from the Oligocene until the Miocene in what is now the Caribbean The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America .... Two species have been described: ''Aktiogavialis puertoricensis'' from the Middle Oligocene of Puerto Rico and ''Aktiogavialis caribesi'' from the Huayquerian of the Late Miocene of Venezuela. As a typical Gavialidae, gavialoid, ''Aktiogavialis'' followed the standard crocodilian body plan. An elongated, squat quadrupedal body terminated in a long, laterally flattened tail at one end, and a specialized, narrow snout at the other. As with the other members of its family, the snout of ''Aktiogavialis'' was extremely long and narrow, tapering into a thin structure past the orbit (anatomy), eye sockets. Bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |