|
Canavesite
Canavesite, Mg2(HBO3)(CO3)∙5H2O, is a rare carboborate mineral from the abandoned Brosso mine in Italy. Canavesite is a secondary mineral that occurs due to the weathering of ludwigite-magnetite skarn on the surface of mine walls. The physical properties consist of milky-white rosette-like aggregates of elongated transparent fibers shown in figure one.Chao, G.Y., Fliesher, Mandarino, J.A. (1979) New Mineral Names*.,American Mineralogist, 64, 652–659. It has the crystal symmetry of a monoclinic with a diffraction symbol of ''2/mP-/-''. History Giussani & Vighi saw and described boron mineralization in 1964 in a pyrite mine, Brosso, in Italy. They noticed secondary minerals forming between szaibelyite and ludwigite at the point where they come into contact with each other inside magnetite skarns. Years later in 1972 a few members from the Gruppo Mineralogico Lombardo found the first sample of a new unknown mineral around the same location. Since then canavesite has been trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboborate
The borate carbonates are mixed anion compounds containing both borate and carbonate A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid (H2CO3), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word ''carbonate'' may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate g ... ions. Compared to mixed anion compounds containing halides, these are quite rare. They are hard to make, requiring higher temperatures, which are likely to decompose carbonate to carbon dioxide. The reason for the difficulty of formation is that when entering a crystal lattice, the anions have to be correctly located, and correctly oriented. They are also known as carbonatoborates or borocarbonates. Although these compounds have been termed carboborate, that word also refers to the C=B=C5− anion, or CB11H12− anion. This last anion should be called 1-carba-closo-dodecaborate or monocarba-closo-dodecaborate. Some borate carbonates have additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borate Minerals
The borate minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures which include hydroxide or halogen anions.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius Hurlbut, Jr., ''Manual of Mineralogy'', Wiley, 20th ed., 1985 pp. 343 - 347 The (O,OH)4sup>− anion exists as well. Many borate minerals, such as borax, colemanite, and ulexite, are salts: soft, readily soluble, and found in evaporite contexts. However, some, such as boracite, are hard and resistant to weathering, more similar to the silicates. There are over 100 different borate minerals. Vanadates), 09 Silicates: * ''neso-'': insular (from Greek , "island") * ''soro-'': grouped (from Greek , "heap, pile, mound") * ''cyclo-'': rings of (from Greek , "circle") * ''ino-'': chained (from Greek , "fibre", rom Ancient Greek * ''phyllo-'': sheets of (fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usually found associated with other sulfides or oxides in quartz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Minerals
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table) it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and it almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explode as supernovas, much of the magnesium is expelled into the interstellar medium wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate Minerals
Carbonate minerals are those minerals containing the carbonate ion, . Carbonate divisions Anhydrous carbonates *Calcite group: trigonal **Calcite CaCO3 **Gaspéite (Ni,Mg,Fe2+)CO3 **Magnesite MgCO3 **Otavite CdCO3 **Rhodochrosite MnCO3 **Siderite FeCO3 **Smithsonite ZnCO3 **Spherocobaltite CoCO3 *Aragonite group: orthorhombic **Aragonite CaCO3 **Cerussite PbCO3 **Strontianite SrCO3 **Witherite BaCO3 **Rutherfordine UO2CO3 ** Natrite Na2CO3 Anhydrous carbonates with compound formulas *Dolomite group: trigonal **Ankerite CaFe(CO3)2 **Dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 **Huntite Mg3Ca(CO3)4 **Minrecordite CaZn(CO3)2 **Barytocalcite BaCa(CO3)2 Carbonates with hydroxyl or halogen *Carbonate with hydroxide: monoclinic **Azurite Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Hydrocerussite Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 **Malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 **Rosasite (Cu,Zn)2CO3(OH)2 **Phosgenite Pb2(CO3)Cl2 **Hydrozincite Zn5(CO3)2(OH)6 **Aurichalcite (Zn,Cu)5(CO3)2(OH)6 Hydrated carbonates *Hydromagnesite Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2.4H2O *Ikaite CaCO3·6(H2O) *Lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Powder Diffraction
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. There is no universally accepted, strict definition of the bounds of the X-ray band. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York (state), New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware River and Pennsylvania; and on the southwest by Delaware Bay and the state of Delaware. At , New Jersey is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fifth-smallest state in land area; but with close to 9.3 million residents, it ranks List of U.S. states and territories by population, 11th in population and List of U.S. states and territories by population density, first in population density. The state capital is Trenton, New Jersey, Trenton, and the most populous city is Newark, New Jersey, Newark. With the exception of Warren County, New Jersey, Warren County, all of the state's 21 counties lie within the combined statistical areas of New York City or Delaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
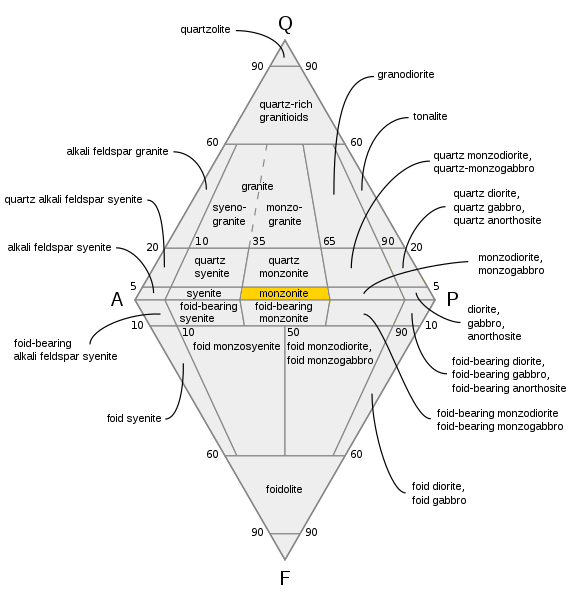
Monzonite
Monzonite is an igneous intrusive rock, formed by slow cooling of underground magma that has a moderate silica content and is enriched in alkali metal oxides. Monzonite is composed mostly of plagioclase and alkali feldspar. Syenodiorite is an obsolescent term for monzonite or for monzodiorite.Le Maitre, R.W., ''Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms'' Cambridge University Press, 2nd ed, pp. 113 Larvikite is a particular form of monzonite. Description Monzonite is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) igneous rock. Such rocks are classified by their relative percentages of quartz, plagioclase, alkali feldspar, and feldspathoid (the QAPF classification). Monzonite is defined as rock having less than 5% quartz in its QAPF fraction and in which alkali feldspar makes up between 35% and 65% of the total feldspar content. If quartz constitutes greater than 5% of the QAPF fraction, the rock is termed a quartz monzonite, while if feldspathoids are present as up to 10% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in the orthorhombic system. They form a parallelogram prism. Hence two pairs of vectors are perpendicular (meet at right angles), while the third pair makes an angle other than 90°. Bravais lattices Two monoclinic Bravais lattices exist: the primitive monoclinic and the base-centered monoclinic. For the base-centered monoclinic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of an oblique rhombic prism;See , row mC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the primitive cell below equals \frac \sqrt of the conventional cell above. Crystal classes The table below or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |