|
Bladder (other)
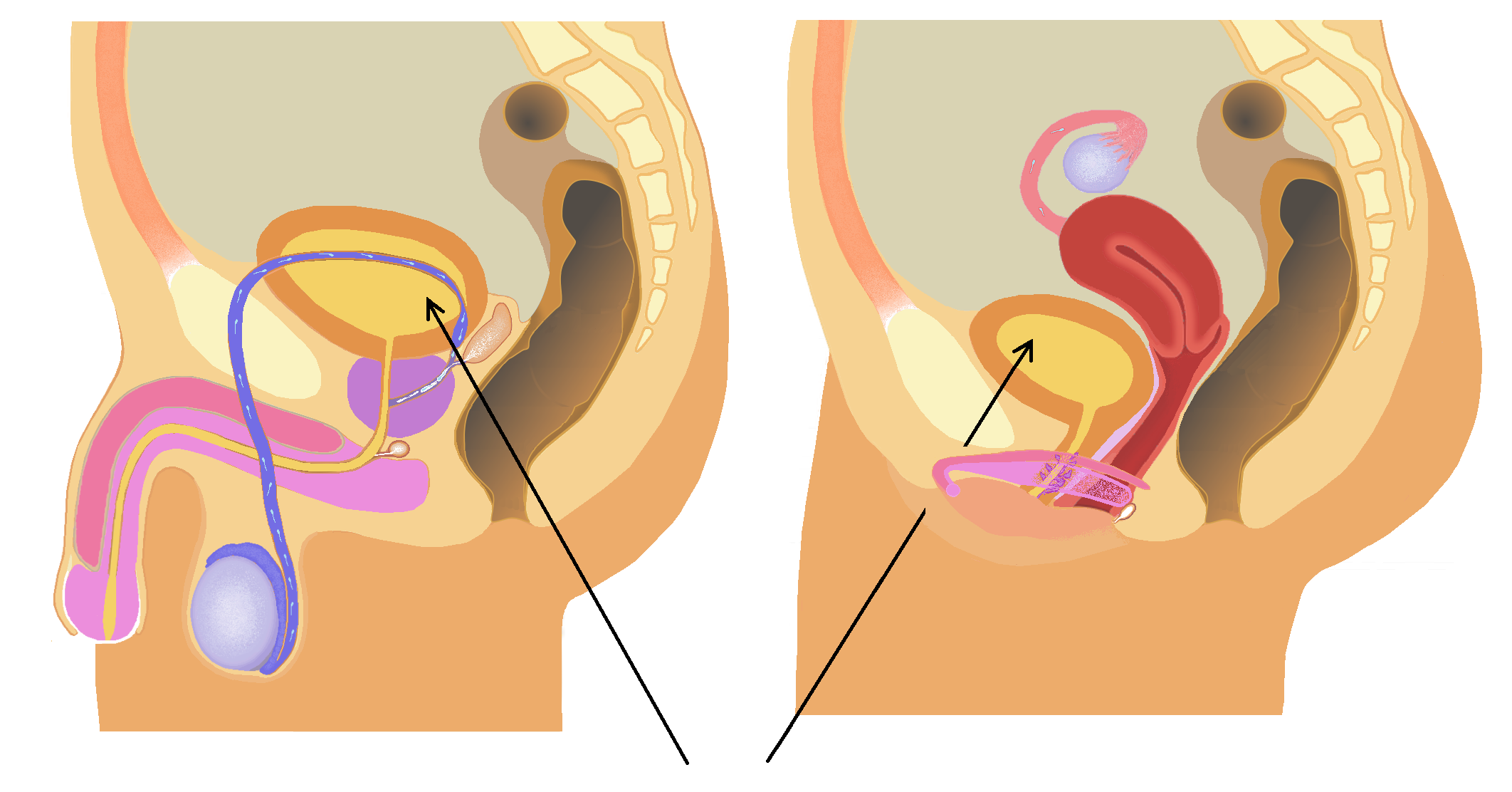
The bladder is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary System
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes (in the form of urine) exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination ( voiding). The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra. Urine is formed in the kidneys through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates many by-products that are rich in nitrogen and must be cleared from the bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine. These by-products are expelled from the body during urination, which is the primary method for excreting water-soluble chemicals from the body. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (known as lant) was also used for gunpowder production, household cleaning, tanning of leather and dye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * Agnatha, jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * Gnathostomata, jawed vertebrates, which include: ** Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish (sharks, Batoidea, rays, and Chimaeriformes, ratfish) ** Euteleostomi, bony vertebrates, which include: *** Actinopterygii, ray-fins (the majority of living Osteichthyes, bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant taxon, Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only Extant taxon, extant member. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollow Organ
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerves that innervate the parenchyma, the blood vessels that oxygenate and nourish it and carry away its metabolic wastes, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccygeus muscle. The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesical Nervous Plexus
The vesical nervous plexus arises from the forepart of the pelvic plexus. The nerves composing it are numerous, and contain a large proportion of spinal nerve fibers. They accompany the vesicle arteries, and are distributed to the sides and fundus of the bladder. Numerous filaments also pass to the seminal vesicles and vas deferens; those accompanying the vas deferens join, on the spermatic cord, with branches from the spermatic plexus The spermatic plexus (or testicular plexus) is derived from the renal plexus, receiving branches from the aortic plexus. It accompanies the internal spermatic artery to the testis A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive .... Additional images File:Gray838.png, The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses. References External links {{Authority control Nerve plexus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesical Venous Plexus
The vesical plexus envelops the lower part of the bladder and the base of the prostate and communicates with the pudendal and prostatic plexuses. It is drained, by means of several vesical veins, into the internal iliac veins. References External links Anatomy at umich.edu Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep External Pudendal Artery
The deep external pudendal artery (deep external pudic artery) is one of the pudendal arteries that is more deeply seated than the superficial external pudendal artery, passes medially across the pectineus and the adductor longus muscles; it is covered by the fascia lata, which it pierces at the medial side of the thigh, and is distributed, in the male, to the integument of the scrotum and perineum, in the female to the labia majora; its branches anastomose with the scrotal or labial branches of the perineal artery. Additional Images File:Thigh arteries schema.svg, Schema of the arteries arising from the external iliac and femoral arteries See also * Internal pudendal artery The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk ... References External links * () Arteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Pudendal Artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia. Structure The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It is smaller in the female than in the male. Path It arises from the anterior division of internal iliac artery. It runs on the lateral pelvic wall. It exits the pelvic cavity through the greater sciatic foramen, inferior to the piriformis muscle, to enter the gluteal region. It then curves around the sacrospinous ligament to enter the perineum through the lesser sciatic foramen. It travels through the pudendal canal with the internal pudendal veins and the pudendal nerve. Branches The internal pudendal artery gives off the following branches: The deep artery of clitoris is a branch of the internal pudendal artery and supplies the clitoral crura. Another branch of the internal pudendal arter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
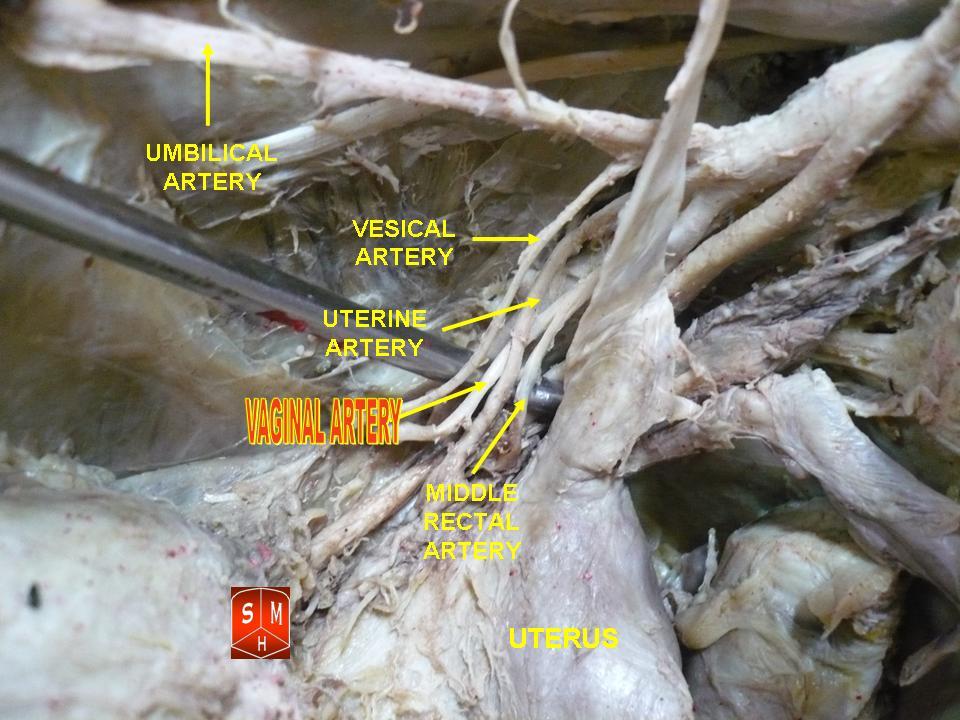
Vaginal Artery
The vaginal artery is an artery in females that supplies blood to the vagina and the base of the bladder. Structure The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the uterine artery, but the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the term for blood supply to the vagina coming from the uterine artery. The vaginal artery is frequently represented by two or three branches. These descend to the vagina, supplying its mucous membrane. They anastomose with branches from the uterine artery. It can send branches to the bulb of the vestibule, the fundus of the bladder, and the contiguous part of the rectum. Function The vaginal artery supplies oxygenated blood to the muscular wall of the vagina, along with the uterine artery and the internal pudendal artery. It also supplies the cervix, along with the uterine artery. Other animals In horses, the vaginal artery may haemorrhage after birth, which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |