Pudendal nerve on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The pudendal nerve is the main
 The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the
The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the
 A pudendal nerve block, also known as a ''saddle nerve block'', is a
A pudendal nerve block, also known as a ''saddle nerve block'', is a
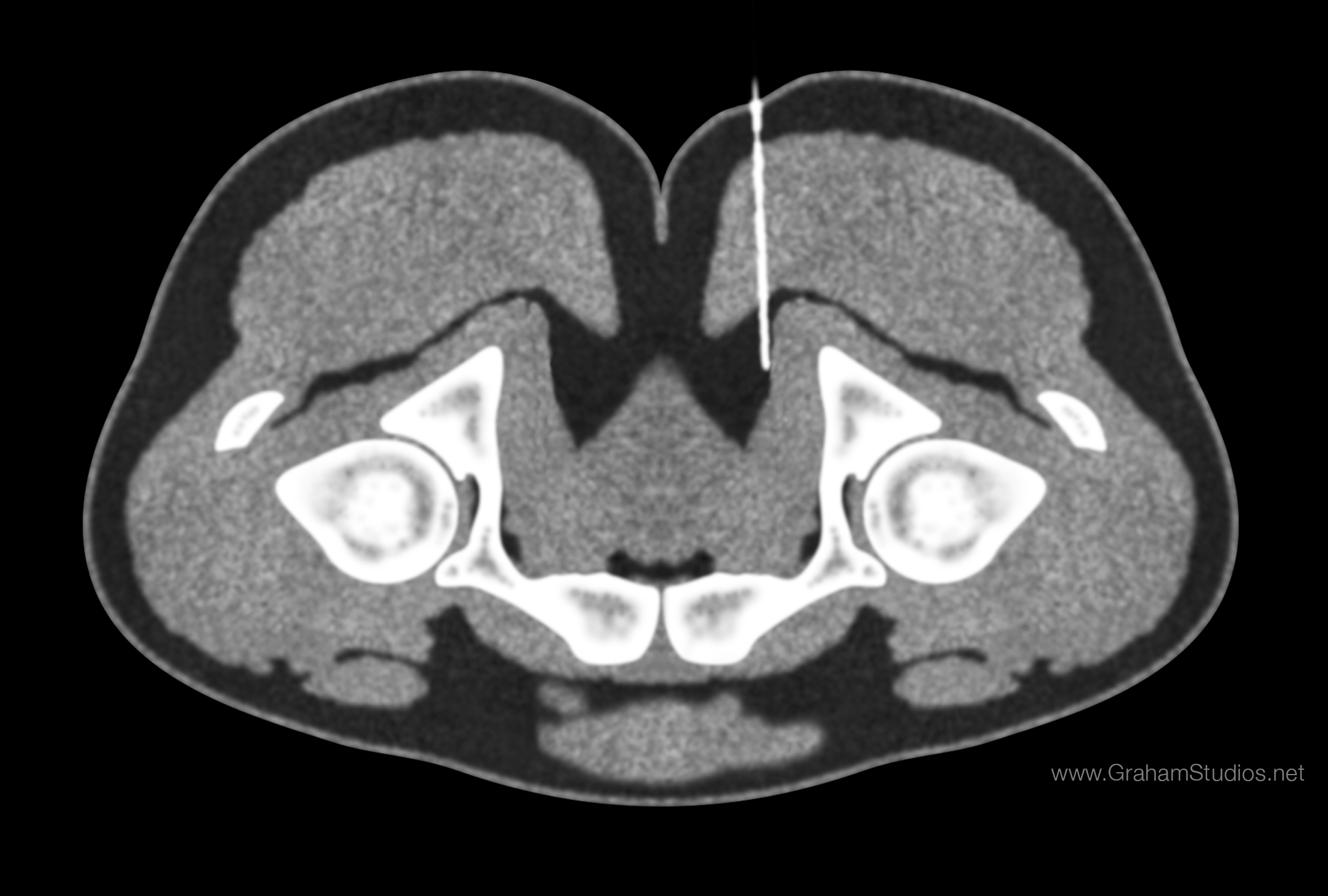 The pudendal nerve is difficult to visualize on routine CT or MR imaging, however under CT guidance, a needle may be placed adjacent to the pudendal neurovascular bundle. The
The pudendal nerve is difficult to visualize on routine CT or MR imaging, however under CT guidance, a needle may be placed adjacent to the pudendal neurovascular bundle. The
File:Gray829.png, The male pelvis, showing the pudendal nerve (centre right)
File:Grant 1962 214.png, Schematic showing the structures innervated by the pudendal nerve
File:Grant 1962 215.png, Diagram of the course of the pudendal nerve in the male pelvis
Diagnosis and treatment at www.nervemed.com
www.pudendal.com
{{good article Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso Sexual anatomy
nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
of the perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
. It is a mixed (motor and sensory) nerve and also conveys sympathetic autonomic fibers. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter.
If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, loss of sensation or fecal incontinence
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms, encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents—including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. FI is a sign or a symptom ...
may result. The nerve may be temporarily anesthetized, called pudendal anesthesia or pudendal block.
The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836.
Structure
Origin
 The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the
The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament
The sacrotuberous ligament (great or posterior sacrosciatic ligament) is situated at the lower and back part of the pelvis. It is flat, and triangular in form; narrower in the middle than at the ends.
Structure
It runs from the sacrum (the lowe ...
and the coccygeus muscle
The coccygeus muscle or ischiococcygeus is a muscle of the pelvic floor located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament.
Structure
The coccygeus muscle is posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous liga ...
. The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root join to form the lower cord, and these in turn unite to form the pudendal nerve proper just proximal to the sacrospinous ligament
The sacrospinous ligament (small or anterior sacrosciatic ligament) is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the i ...
. The three roots are derived from the ventral rami of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th sacral spinal nerves, with the primary contribution coming from the 4th.
Course and relations
The pudendal nerve passes between thepiriformis muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the buttock, gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group.
The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, ...
and coccygeus (ischiococcygeus) muscles and leaves the pelvis through the lower part of the greater sciatic foramen
The greater sciatic foramen is an opening (:wikt:foramen, foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament, sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies ...
. It crosses over the lateral part of the sacrospinous ligament
The sacrospinous ligament (small or anterior sacrosciatic ligament) is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the i ...
and reenters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen. After reentering the pelvis, it accompanies the internal pudendal artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.
Structure
The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk ...
and internal pudendal vein upwards and forwards along the lateral wall of the ischiorectal fossa, being contained in a sheath of the obturator fascia termed the pudendal canal, along with the internal pudendal blood vessels.
Branches
Inside the pudendal canal, the nerve divides into branches, first giving off the inferior rectal nerve, then theperineal nerve
The perineal nerve is a nerve of the pelvis. It arises from the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. It gives superficial branches to the skin, and a deep branch to muscles. It supplies the skin and muscles of the perineum. Its latency is tes ...
, before continuing as the dorsal nerve of the penis
The dorsal nerve of the penis is the deepest of three divisions of the pudendal nerve; it accompanies the internal pudendal artery along the Ischium#Structure, ramus of the ischium; it then runs forward along the margin of the inferior ramus of t ...
(in males) or the dorsal nerve of the clitoris
The dorsal nerve of the clitoris is a nerve in females that branches off the pudendal nerve to innervate the clitoris. The nerve is important for female sexual pleasure, and it may play a role in clitoral erections.
It travels from below the inf ...
(in females).
Nucleus
The nerve is a major branch of thesacral plexus
In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar verteb ...
, with fibers originating in Onuf's nucleus in the sacral region of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
.
Variation
The pudendal nerve may vary in its origins. For example, the pudendal nerve may actually originate in thesciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
. Consequently, damage to the sciatic nerve can affect the pudendal nerve as well. Sometimes dorsal rami of the first sacral nerve contribute fibers to the pudendal nerve, and even more rarely .
Function
The pudendal nerve has both motor (control of muscles) and sensory functions. It also carries sympathetic autonomic fibers (but notparasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
fibers).
Sensory
The pudendal nerve supplies sensation to thepenis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
in males, and to the clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. Th ...
in females, which travels through the branches of both the dorsal nerve of the penis
The dorsal nerve of the penis is the deepest of three divisions of the pudendal nerve; it accompanies the internal pudendal artery along the Ischium#Structure, ramus of the ischium; it then runs forward along the margin of the inferior ramus of t ...
and the dorsal nerve of the clitoris
The dorsal nerve of the clitoris is a nerve in females that branches off the pudendal nerve to innervate the clitoris. The nerve is important for female sexual pleasure, and it may play a role in clitoral erections.
It travels from below the inf ...
. The posterior scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin ...
in males and the labia majora
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora (: labium majus), also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent Anatomical terms of location, longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis ...
in females are also supplied, via the posterior scrotal nerves (males) or posterior labial nerves (females). The pudendal nerve is one of several nerves supplying sensation to these areas., page=Neurovascular Bundles of the Perineum Branches also supply sensation to the anal canal
The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional s ...
. By providing sensation to the penis and the clitoris, the pudendal nerve is responsible for the afferent component of penile erection and clitoral erection
Clitoral erection (also known as clitoral tumescence or female erection) is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm.
Clitoral erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular ...
.
Motor
Branchesinnervate
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called ...
muscles of the perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
and the pelvic floor
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function, and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and ...
; namely, the bulbospongiosus
The bulbospongiosus muscles (in older texts bulbocavernosus and, for female muscle, constrictor cunni) are a subgroup of the superficial muscles of the perineum. They have a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. ...
and the ischiocavernosus
The ischiocavernosus muscle (erectores penis ''or'' erector clitoridis in older texts) is a muscle just below the surface of the perineum, present in both men and women.
Structure
It arises by tendinous and fleshy fibers from the inner surface of ...
muscles respectively, the levator ani
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.
It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the ...
muscle (including the Iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus, puborectalis
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis.
It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the ...
and either pubovaginalis in females or puboprostaticus in males) the external anal sphincter (via the inferior anal branch), and male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
or female external urethral sphincter.
As it functions to innervate the external urethral sphincter it is responsible for the tone of the sphincter mediated via acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
release. This means that during periods of increased acetylcholine release the skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are a ...
in the external urethral sphincter contracts, causing urinary retention. Whereas in periods of decreased acetylcholine release the skeletal muscle in the external urethral sphincter relaxes, allowing voiding of the bladder to occur. (Unlike the internal sphincter muscle, the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle, therefore it is under voluntary control of the somatic nervous system
The somatic nervous system (SNS), also known as voluntary nervous system, is a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that links brain and spinal cord to skeletal muscles under conscious control, as well as to sensory receptors in the skin ...
.)
It is also responsible for ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
.
Clinical significance
The pudendal nerve may be tested by elicitation of the anocutaneous reflex ("anal wink").Anesthesia
 A pudendal nerve block, also known as a ''saddle nerve block'', is a
A pudendal nerve block, also known as a ''saddle nerve block'', is a local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sense, sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. ...
technique used in an obstetric
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgic ...
procedure to anesthetize the perineum during labor
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
. In this procedure, an anesthetic agent such as lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anae ...
is injected through the inner wall of the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
about the pudendal nerve. Abnormal loss of sensation in the same region as a medical symptom is also sometimes termed saddle anesthesia
Saddle anesthesia is a loss of sensation ( anesthesia) restricted to the area of the buttocks, perineum and inner surfaces of the thighs.
Asymmetric saddle anesthesia is frequently associated with the spine-related injury cauda equina syndrom ...
.
Damage
The pudendal nerve can be compressed or stretched, resulting in temporary or permanentneuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
. Injury to the pudendal nerve manifests more as sensory problems (pain or alteration/loss of sensation) rather than loss of muscle control. Irreversible nerve injury may occur when nerves are stretched by 12% or more of their normal length. If the pelvic floor is over-stretched, acutely (e.g. prolonged or difficult childbirth) or chronically (e.g. chronic straining during defecation
Defecation (or defaecation) follows digestion and is the necessary biological process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid metabolic waste, waste material known as feces (or faeces) from the digestive tract via the anus o ...
caused by constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The Human feces, stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the ...
), the pudendal nerve is vulnerable to stretch-induced neuropathy. After repeated traction of the pudendal nerve, it starts to be replaced by fibrous tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesode ...
with subsequent loss of function. Pudendal nerve entrapment, also known as ''Alcock canal syndrome'', is neuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuo ...
in the distribution of the pudendal nerve. It is caused by entrapment of the nerve. The condition is estimated to have a prevalence of 1 in 100000, and is sometimes associated with professional cycling
Cycling, also known as bicycling or biking, is the activity of riding a bicycle or other types of pedal-driven human-powered vehicles such as balance bikes, unicycles, tricycles, and quadricycles. Cycling is practised around the world fo ...
. Systemic diseases such as diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
and multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
can damage the pudendal nerve via demyelination or other mechanisms. A pelvic tumor (most notably a large sacrococcygeal teratoma
Sacrococcygeal teratoma (SCT) is a type of tumor known as a teratoma that develops at the base of the coccyx (tailbone) and is thought to be primarily derived from remnants of the primitive streak. Sacrococcygeal teratomas are Benign tumor, benign ...
), or surgery to remove the tumor, can also cause permanent damage.
Unilateral pudendal nerve neuropathy inconsistently causes fecal incontinence
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms, encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents—including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. FI is a sign or a symptom ...
in some, but not others. This is because crossover innervation of the external anal sphincter occurs in some individuals. There is significant overlap of the innervation of the external anal sphincter from the pudendal nerves of both sides. This allows partial re-innervation from the opposite side after nerve injury.
Imaging
 The pudendal nerve is difficult to visualize on routine CT or MR imaging, however under CT guidance, a needle may be placed adjacent to the pudendal neurovascular bundle. The
The pudendal nerve is difficult to visualize on routine CT or MR imaging, however under CT guidance, a needle may be placed adjacent to the pudendal neurovascular bundle. The ischial spine
The ischial spine is part of the posterior border of the body of the ischium bone of the pelvis. It is a thin and pointed triangular eminence, more or less elongated in different subjects.
Structure
The pudendal nerve travels close to the ischia ...
, an easily identifiable structure on CT, is used as the level of injection. A spinal needle is advanced via the gluteal muscles
The gluteal muscles, often called glutes, are a group of three muscles which make up the gluteal region commonly known as the buttocks: the gluteus maximus muscle, gluteus maximus, gluteus medius muscle, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscl ...
and advanced within several millimeters of the ischial spine. Contrast (X-ray dye) is then injected, highlighting the nerve in the canal and allowing for confirmation of correct needle placement. The nerve may then be injected with cortisone
Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enzyme corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase ...
and local anesthetic to confirm and also treat chronic pain of the external genitalia (known as vulvodynia in females), pelvic and anorectal pain.
Nerve latency testing
The time taken for a muscle supplied by the pudendal nerve to contract in response to an electrical stimulus applied to the sensory and motor fibers can be quantified. Increased conduction time (terminal motor latency) signifies damage to the nerve. 2 stimulating electrodes and 2 measuring electrodes are mounted on the examiner's gloved finger ("St Mark's electrode").History
The term pudendal comes fromLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
', meaning external genitals, derived from , meaning "parts to be ashamed of". The pudendal canal is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Alcock documented the existence of the canal and pudendal nerve in a contribution about iliac arteries in Robert Bentley Todd's "The Cyclopaedia of Anatomy and Physiology".
Additional images
See also
* Neurogenic bladder * Pudendal neuralgia *Sacral plexus
In human anatomy, the sacral plexus is a nerve plexus which provides motor and sensory nerves for the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis. It is part of the lumbosacral plexus and emerges from the lumbar verteb ...
* Inferior rectal nerve
* Perineal nerve
The perineal nerve is a nerve of the pelvis. It arises from the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. It gives superficial branches to the skin, and a deep branch to muscles. It supplies the skin and muscles of the perineum. Its latency is tes ...
* Dorsal nerve of the penis
The dorsal nerve of the penis is the deepest of three divisions of the pudendal nerve; it accompanies the internal pudendal artery along the Ischium#Structure, ramus of the ischium; it then runs forward along the margin of the inferior ramus of t ...
* Dorsal nerve of the clitoris
The dorsal nerve of the clitoris is a nerve in females that branches off the pudendal nerve to innervate the clitoris. The nerve is important for female sexual pleasure, and it may play a role in clitoral erections.
It travels from below the inf ...
* Pudendal canal
References
External links
* - "Inferior view of female perineum, branches of the internal pudendal artery." * * *Diagnosis and treatment at www.nervemed.com
www.pudendal.com
{{good article Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso Sexual anatomy