Vaginal Artery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The vaginal artery is an
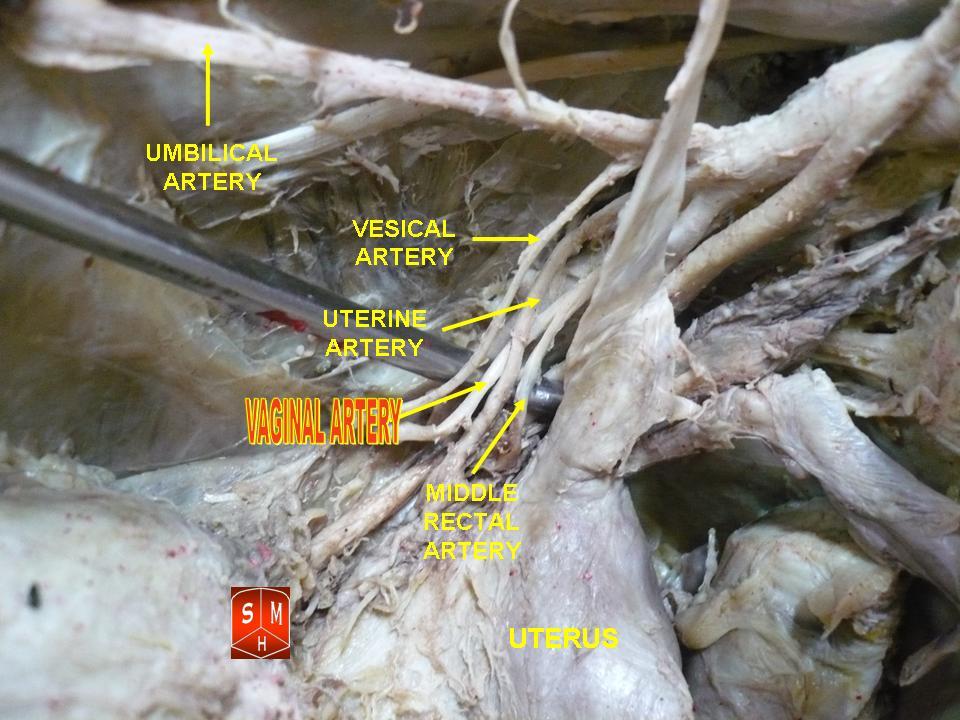 The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the uterine artery, but the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the term for blood supply to the
The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the uterine artery, but the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the term for blood supply to the
artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
in females that supplies blood to the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
and the base of the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
.
Structure
 The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the uterine artery, but the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the term for blood supply to the
The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the uterine artery, but the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the term for blood supply to the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
coming from the uterine artery.
The vaginal artery is frequently represented by two or three branches. These descend to the vagina, supplying its mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
. They anastomose with branches from the uterine artery. It can send branches to the bulb of the vestibule, the fundus of the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
, and the contiguous part of the rectum
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces temporarily. The adult ...
.
Function
The vaginal artery supplies oxygenatedblood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
to the muscular wall of the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
, along with the uterine artery and the internal pudendal artery
The internal pudendal artery is one of the three pudendal arteries. It branches off the internal iliac artery, and provides blood to the external genitalia.
Structure
The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk ...
. It also supplies the cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
, along with the uterine artery.
Other animals
Inhorses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
, the vaginal artery may haemorrhage after birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
, which can cause death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose sh ...
.
See also
* Uterine arteryReferences
External links
* - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery" {{Authority control Arteries of the abdomen Vagina