|
Uterine Artery
The uterine artery is an artery that supplies blood to the uterus in females. Structure The uterine artery usually arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It travels to the uterus, crossing the ureter anteriorly, to the uterus by traveling in the cardinal ligament. It travels through the parametrium of the inferior broad ligament of the uterus. It commonly anastomoses (connects with) the ovarian artery. The uterine artery is the major blood supply to the uterus and enlarges significantly during pregnancy. Branches and organs supplied * round ligament of the uterus * ovary ("ovarian branches") * uterus ( arcuate vessels) * vagina ( Vaginal branches of uterine artery) * uterine tube ("tubal branch") Anatomical variants Uterine artery can arise from the first branch of inferior gluteal artery. It can also arise as the 2nd or 3rd branch from the inferior gluteal artery. On the other hand, uterine artery can be first branch from internal iliac artery bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Artery
The ovarian artery is an artery that supplies oxygenated blood to the ovary in females. It arises from the abdominal aorta below the renal artery. It can be found within the suspensory ligament of the ovary, anterior to the ovarian vein and ureter. Structure The ovarian arteries are paired structures that arise from the abdominal aorta, usually at the level of L2. After emerging from the aorta, the artery travels within the suspensory ligament of the ovary and enters the mesovarium. The ovarian arteries are the corresponding arteries in the female to the testicular artery in the male. They are shorter than the testicular arteries, as the testicular arteries courses through the abdominal wall to the external scrotum. The origin and course of the first part of each artery are the same as those of the testicular artery, but on arriving at the upper opening of the lesser pelvis the ovarian artery passes inward, between the two layers of the ovariopelvic ligament and of the bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Artery
The uterine artery is an artery that supplies blood to the uterus in females. Structure The uterine artery usually arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It travels to the uterus, crossing the ureter anteriorly, to the uterus by traveling in the cardinal ligament. It travels through the parametrium of the inferior broad ligament of the uterus. It commonly anastomoses (connects with) the ovarian artery. The uterine artery is the major blood supply to the uterus and enlarges significantly during pregnancy. Branches and organs supplied * round ligament of the uterus * ovary ("ovarian branches") * uterus ( arcuate vessels) * vagina ( Vaginal branches of uterine artery) * uterine tube ("tubal branch") Anatomical variants Uterine artery can arise from the first branch of inferior gluteal artery. It can also arise as the 2nd or 3rd branch from the inferior gluteal artery. On the other hand, uterine artery can be first branch from internal iliac artery bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Leiomyomata
Uterine fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, fibromyoma or fibroids, are benign smooth muscle tumors of the uterus, part of the female reproductive system. Most people with fibroids have no symptoms while others may have painful or heavy periods. If large enough, they may push on the bladder, causing a frequent need to urinate. They may also cause pain during penetrative sex or lower back pain. Someone can have one uterine fibroid or many. It is uncommon but possible that fibroids may make it difficult to become pregnant. The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unclear. However, fibroids run in families and appear to be partly determined by hormone levels. Risk factors include obesity and eating red meat. Diagnosis can be performed by pelvic examination or medical imaging. Treatment is typically not needed if there are no symptoms. NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, and paracetamol (acetaminophen) may help with pain. According to The Mayo Clinic, NSAIDs may help relieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Artery Embolization
Uterine artery embolization (UAE, uterine fibroid embolization, or UFE) is a procedure in which an interventional radiologist uses a catheter to deliver small particles that block the blood supply to the uterine body. The procedure is primarily done for the treatment of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis. Compared to surgical treatment for fibroids such as a hysterectomy, in which a woman's uterus is removed, uterine artery embolization may be beneficial in women who wish to retain their uterus. Other reasons for uterine artery embolization are postpartum hemorrhage and uterine arteriovenous malformations. Medical uses Uterine fibroids are the most common type of benign uterine tumor and are composed of smooth muscle. They often cause bulk-related symptoms, which can be characterized by back pain, heaviness in the pelvic area, abdominal bloating. Uterine artery embolization may be done to treat bothersome bulk-related symptoms as well as abnormal or heavy uterine bleeding due to ute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
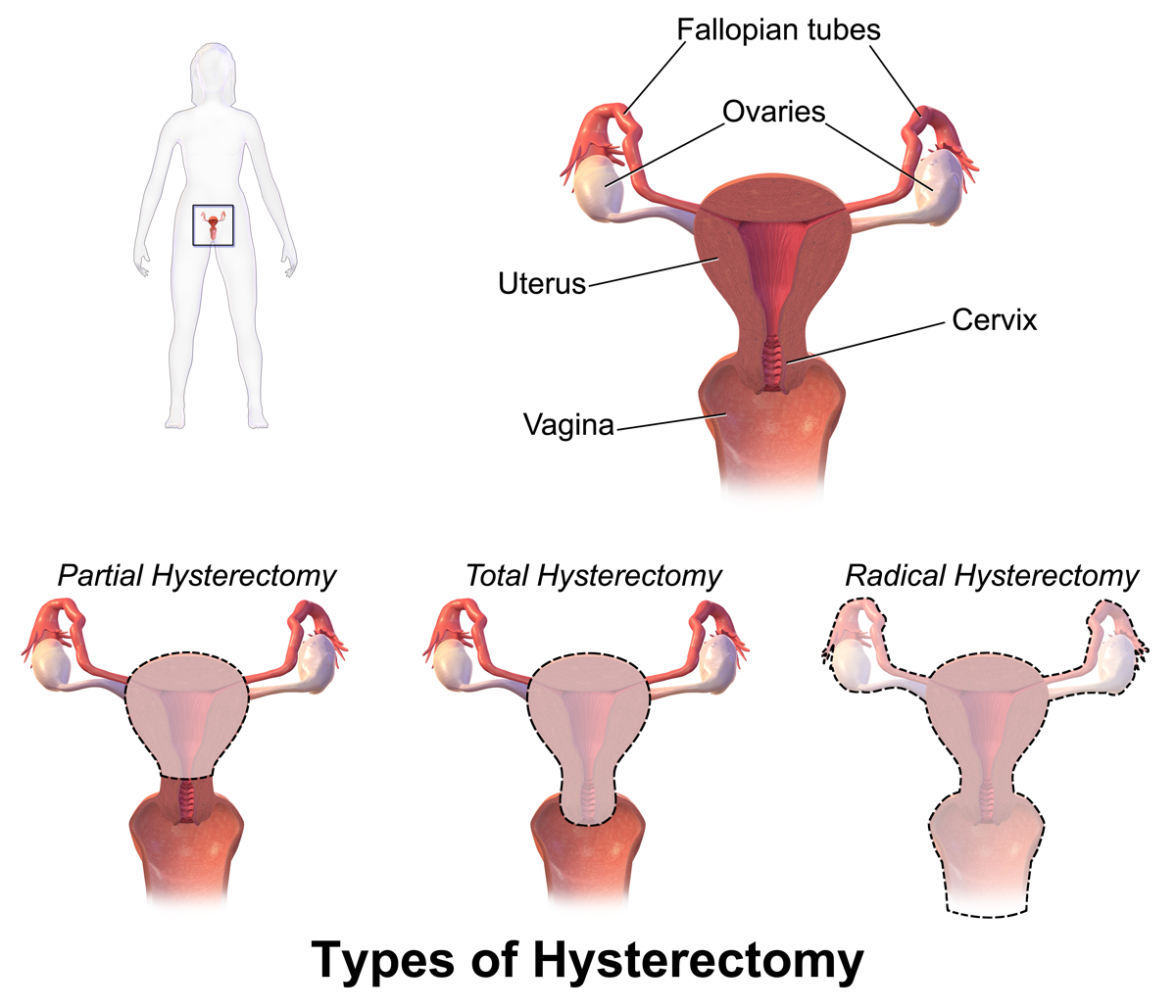
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus and cervix. Supracervical hysterectomy refers to removal of the uterus while the cervix is spared. These procedures may also involve removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy), fallopian tubes ( salpingectomy), and other surrounding structures. The term “partial” or “total” hysterectomy are lay-terms that incorrectly describe the addition or omission of oophorectomy at the time of hysterectomy. These procedures are usually performed by a gynecologist. Removal of the uterus is a form of sterilization, rendering the patient unable to bear children (as does removal of ovaries and fallopian tubes) and has surgical risks as well as long-term effects, so the surgery is normally recommended only when other treatment options are not available or have failed. It is the second most commonly performed gynecological surgical procedure, after cesarean section, in the United States. Nearly 68 percent were performed for conditions such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
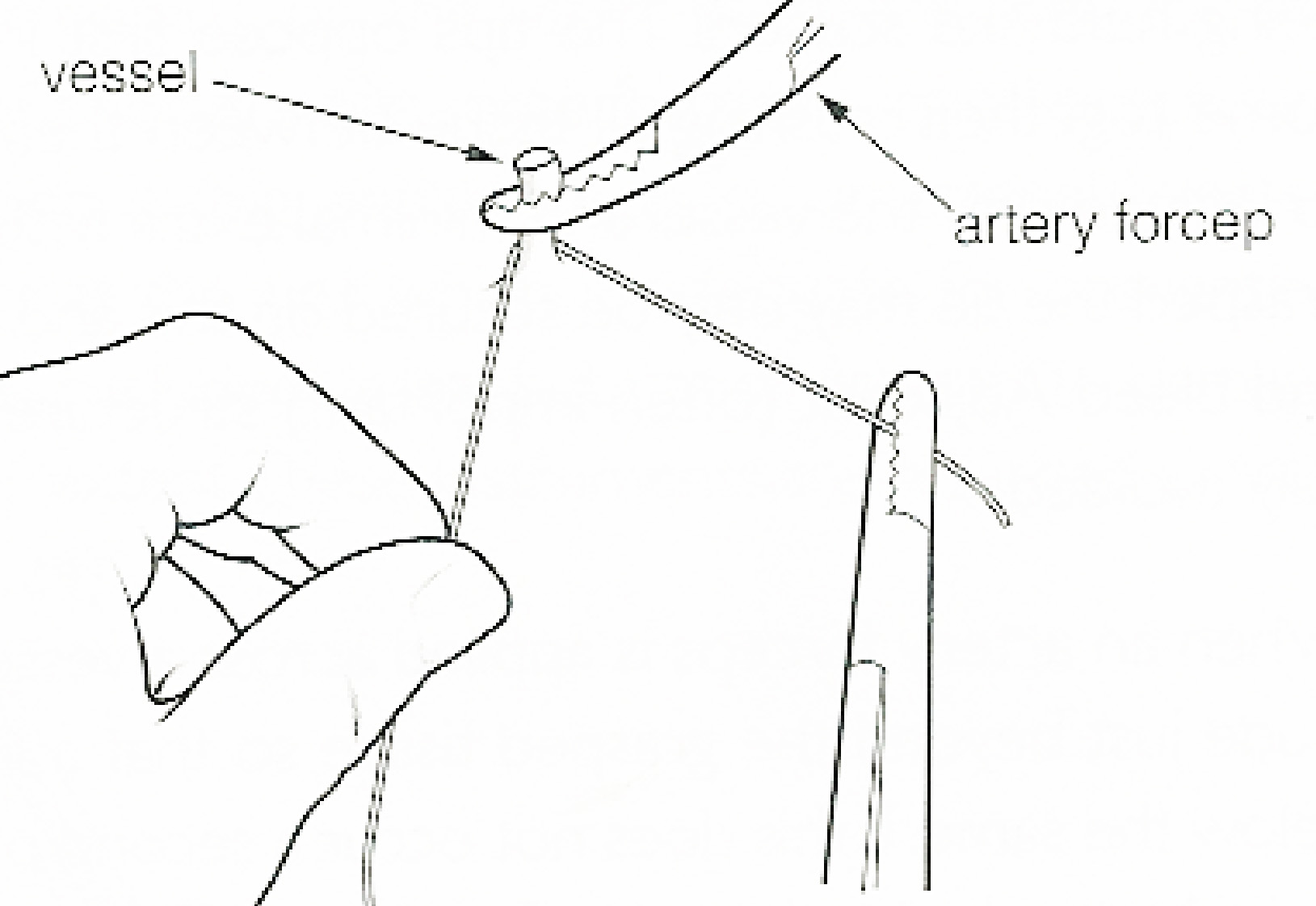
Ligature (medicine)
In surgery or medical procedure, a ligature consists of a piece of thread (Surgical suture, suture) tied around an anatomical structure, usually a blood vessel, another hollow structure (e.g. urethra) or an accessory skin tag to shut it off. History The principle of ligation is attributed to Hippocrates and Galen. In Surgery in Ancient Rome, ancient Rome, ligatures were used to treat Hemorrhoid, hemorrhoids. Spanish Muslim doctor Al-Zahrawi described the procedure around the year 1000 in his book ''Kitab al-Tasrif''. The concept of a ligature was reintroduced some 500 years later by Ambroise Paré and first performed by him in the village of Damvillers. It finally found its modern use in 1870–1880, made popular by Jules-Émile Péan. Procedure With a blood vessel the surgeon will clamp the vessel perpendicular to the axis of the artery or vein with a hemostat, then secure it by ligating it; i.e. using a piece of suture around it before dividing the structure and releasing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Branches Of Uterine Artery
The uterine artery supplies branches to the cervix uteri and others which descend on the vagina; the latter anastomose with branches of the vaginal arteries and form with them two median longitudinal vessels—the vaginal branches of uterine artery (or azygos arteries of the vagina)—one of which runs down in front of and the other behind the vagina In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag .... References Arteries of the abdomen {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Vessels Of Uterus
The arcuate vessels of the uterus are a component of the blood supply of the uterus. They are arteries and veins that branch from the uterine arteries and veins, respectively, with additional anastomoses from the ovarian arteries and veins, and penetrate and assume a circumferential course in the myometrium. They have also been called helicine branches of the uterus (or helicine arterioles), as they are spiral-shaped, but they should not be confused with the spiral arteries that penetrate the endometrium The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The funct ... in the inner uterus. The radial arteries branch off from the arcuate artery through the myometrium. References Arteries of the abdomen {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Ligament Of The Uterus
The round ligament of the uterus is a ligament that connects the uterus to the labia majora. It originates at the junction of the uterus and uterine tube. It passes through the inguinal canal to insert at the labium majus. The two round ligaments of uterus develop from the gubernaculum; they are the female homologue of the male gubernaculum testis. Structure The round ligament of the uterus originates at the uterine horns, in the parametrium. The round ligament exits the pelvis via the deep inguinal ring. It passes through the inguinal canal to reach the labium majus, inserting into the fibro-fatty substance of the labium majus. Blood supply The round ligament is supplied by the artery of the round ligament of uterus, also known as ''Sampson's artery''. Development The round ligament develops from the gubernaculum which attaches the gonad to the labioscrotal swellings in the embryo. Function The round ligament of uterus acts to hold the uterus anterior-ward to in antef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anastomosis
An anastomosis (, : anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (such as the foramen ovale in a fetus' heart) or abnormal (such as the patent foramen ovale in an adult's heart); it may be acquired (such as an arteriovenous fistula) or innate (such as the arteriovenous shunt of a metarteriole); and it may be natural (such as the aforementioned examples) or artificial (such as a surgical anastomosis). The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology, geology, and geography. Etymology Anastomosis: medical or Modern Latin, from Greek ἀναστόμωσις, anastomosis, "outlet, opening", Greek ana- "up, on, upon", stoma "mouth" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Ligament Of The Uterus
The broad ligament of the uterus is the wide fold of peritoneum that connects the sides of the uterus to the walls and floor of the pelvis. Structure Subdivisions Contents The contents of the broad ligament include the following: * Reproductive ** uterine tubes (or fallopian tube) ** ovary (some sources consider the ovary to be on the broad ligament, but not in it.) * vessels ** ovarian artery (in the suspensory ligament) ** uterine artery (in reality, travels in the cardinal ligament) * ligaments ** ovarian ligament ** round ligament of uterus ** suspensory ligament of the ovary (Some sources consider it a part of the broad ligament, while other sources just consider it a "termination" of the ligament.) Relations The peritoneum surrounds the uterus like a flat sheet that folds over its fundus (uterus), fundus, covering it anteriorly and posteriorly; on the sides of the uterus, this sheet of peritoneum comes in direct contact with itself, forming the double layer of perito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parametrium
The parametrium is the fibrous and fatty connective tissue that surrounds the uterus. This tissue separates the supravaginal portion of the cervix from the bladder. The parametrium lies in front of the cervix and extends laterally between the layers of the broad ligaments. It connects the uterus to other tissues in the pelvis. It is different from the perimetrium, which is the outermost layer of the uterus. The uterine artery and ovarian ligament are located in the parametrium. An associated form of pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder, is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, mainly the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no ... is inflammation of the parametrium known as parametritis. References * External links Mammal female reproductive system {{genitourinary-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |