|
Bion 8
Bion 8 or Kosmos 1887 (in Russian: ''Бион 8'', ''Космос 1887'') was a Bion satellite. Mission Bion 8 carried a payload of biological and radiation physics experiments from nine countries. The landing was several hundred miles from the expected recovery site, which resulted in considerable difficulties. The biological payload on the spacecraft included 2 monkeys, 10 rats, fruit flies, grasshoppers, beetles, guppies, Hynobiidae, Chlorella ciliate, newts and corn. More than 50 NASA-sponsored scientists were involved in conducting the 33 American experiments on board. One of these experiments, a study of radiation levels in the space environment, did not require the use of any biological subjects. The United States conducted only one experiment on the primates flown on the biosatellite. The remaining American experiments were performed on tissue samples from five of the flight rats. A number of these experiments were extensions of the studies conducted on the Spacel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Life Sciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific study of life – such as microorganisms, plants, and animals including human beings. This science is one of the two major branches of natural science, the other being physical science, which is concerned with non-living matter. Biology is the overall natural science that studies life, with the other life sciences as its sub-disciplines. Some life sciences focus on a specific type of organism. For example, zoology is the study of animals, while botany is the study of plants. Other life sciences focus on aspects common to all or many life forms, such as anatomy and genetics. Some focus on the micro-scale (e.g. molecular biology, biochemistry) other on larger scales (e.g. cytology, immunology, ethology, pharmacy, ecology). Another major branch of life sciences involves understanding the mindneuroscience. Life sciences discoveries are helpful in improving the quality and standard of life a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophilidae
The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes species called fruit flies, although they are more accurately referred to as vinegar or pomace flies. Another distantly related family of flies, Tephritidae, are true fruit flies because they are frugivorous, and include apple maggot flies and many pests. The best known species of the Drosophilidae is ''Drosophila melanogaster'', within the genus ''Drosophila'', also called the "fruit fly." ''Drosophila melanogaster'' is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. Many fundamental biological mechanisms were discovered first in ''D. melanogaster.'' The fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, '' Drosophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million near the end of its existence, it was the second most-populous communist government, communist and Eastern Bloc country in Europe. It was also where the Warsaw Pact was founded. The largest city and capital was Warsaw, followed by the industrial city of Łódź and cultural city of Kraków. The country was bordered by the Baltic Sea to the north, the Soviet Union to the east, Czechoslovak Socialist Republic, Czechoslovakia to the south, and East Germany to the west. The Polish People's Republic was a unitary state with a Marxist–Leninist government established in the country after the Red Army's takeover of Polish territory from Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), German occupation in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-51-B
STS-51-B was the 17th flight of the NASA Space Shuttle program and the seventh flight of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. The launch of ''Challenger'' on April 29, 1985, was delayed by 2 minutes and 18 seconds, due to a launch processing failure. ''Challenger'' was initially rolled out to the pad to launch on the STS-51-E mission. The shuttle was rolled back when a timing issue emerged with the TDRS-B satellite. When STS-51-E was canceled, ''Challenger'' was remanifested with the STS-51-B payloads. The shuttle landed successfully on May 6, 1985, after a week-long mission. Crew Crew seat assignments Mission insignia The mission insignia features the ''Challenger'' with her payload doors open, to show the onboard Spacelab 3. The orbiter rides over the American flag. The seven crewmembers are represented by the 7 stars on the patch, that indirectly refer to the Mercury Seven as a nod to their legacy. Behind the orbiter, the contours of Pegasus can be seen, as a refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
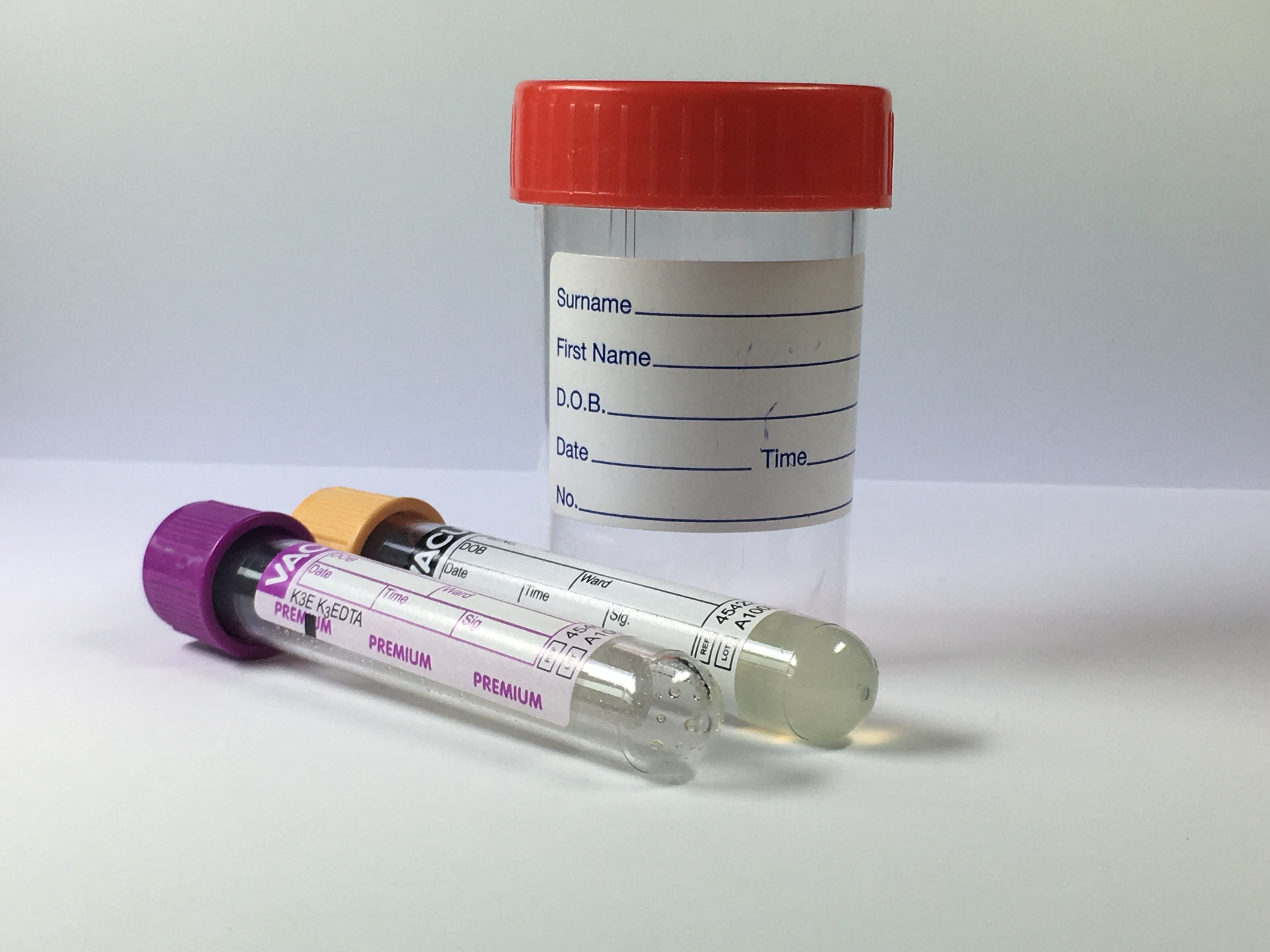
Sampling (medicine)
In medicine, sampling is gathering of matter from the body to aid in the process of a medical diagnosis and/or evaluation of an indication (medicine), indication for treatment, further medical tests or other procedures. In this sense, the sample is the gathered matter, and the sampling tool or sampler is the person or material to collect the sample. Sampling is a prerequisite for many medical tests, but generally not for medical history, physical examination and radiologic tests. By sampling technique * Obtaining excretions or materials that leave the body anyway, such as urine, Feces, stool, sputum, or vomitus, by direct collection as they exit. A sample of saliva can also be collected from the mouth. * Surgery#Types of surgery, Excision (cutting out), a surgical method for the removal of solid or soft tissue samples. * Puncture (also called ''centesis'') followed by aspiration is the main method used for sampling of many types of tissues and body fluids. Examples are thoracoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Environment
Space environment is a branch of astronautics, aerospace engineering and space physics that seeks to understand and address conditions existing in space that affect the design and operation of spacecraft. A related subject, space weather, deals with dynamic processes in the solar-terrestrial system that can give rise to effects on spacecraft, but that can also affect the atmosphere, ionosphere and geomagnetic field, giving rise to several other kinds of effects on human technologies. Effects on spacecraft can arise from radiation, space debris and meteoroid impact, upper atmospheric drag and spacecraft charging, spacecraft electrostatic charging. Various mitigation strategies have been adopted. Radiation Radiation in space usually comes from three main sources: # The Van Allen radiation belts # Solar proton events and solar energetic particles; and # Galactic cosmic rays. For long-duration missions, the high doses of radiation can damage electronic components and solar cells. A maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes: * ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, and Gamma ray, gamma radiation (γ) * ''particle radiation'' consisting of particles of non-zero rest energy, such as alpha radiation (α), beta radiation (β), proton radiation and neutron radiation * ''acoustics, acoustic radiation'', such as ultrasound, sound, and seismic waves, all dependent on a physical transmission medium * ''gravitational radiation'', in the form of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime Radiation is often categorized as either ''ionizing radiation, ionizing'' or ''non-ionizing radiation, non-ionizing'' depending on the energy of the radiated particles. Ionizing radiation carries more than 10 electron volt, electron volts (eV), which is enough to ionize atoms and molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
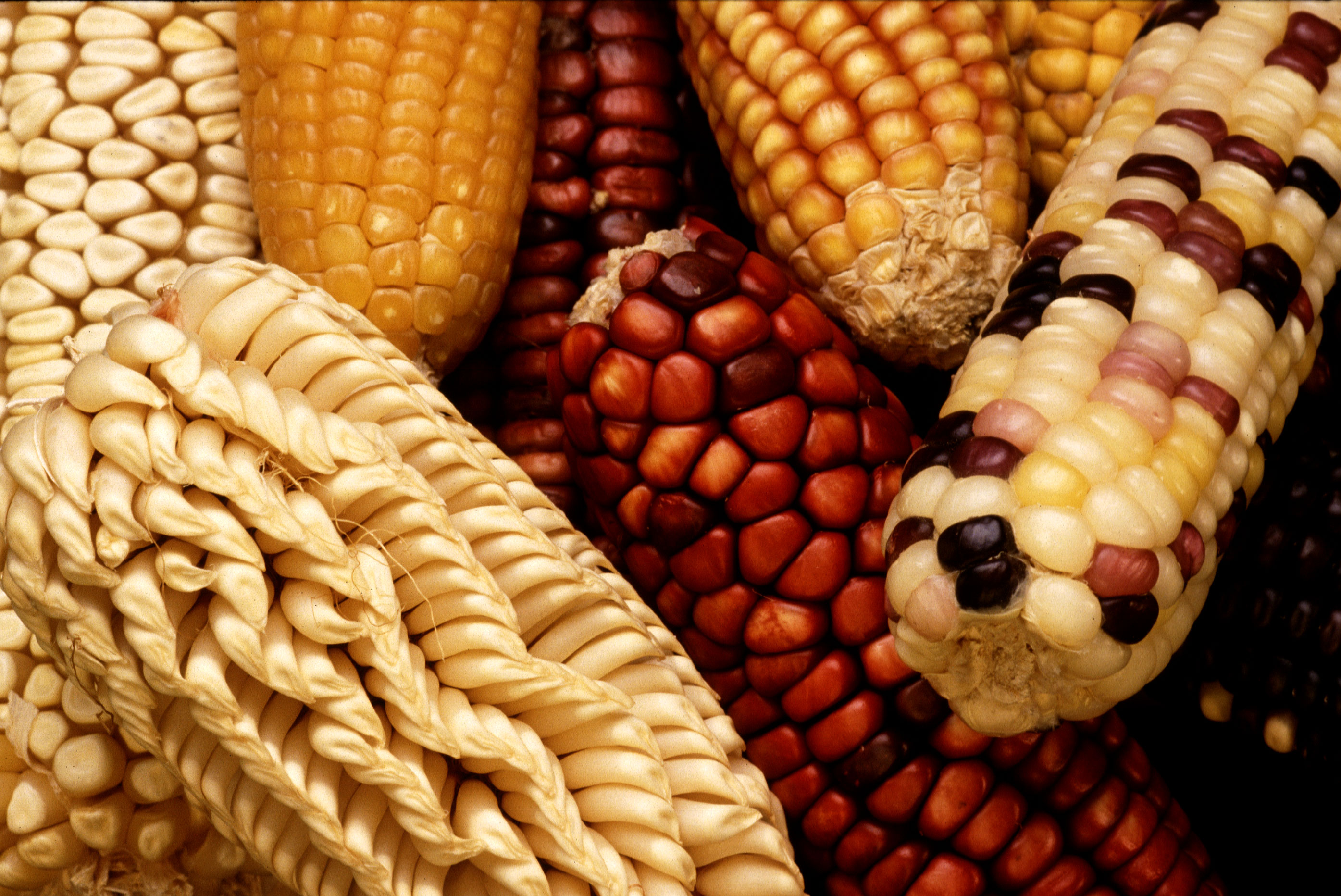
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newt
A newt is a salamander in the subfamily Pleurodelinae. The terrestrial juvenile phase is called an eft. Unlike other members of the family Salamandridae, newts are semiaquatic, alternating between aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Not all aquatic salamanders are considered newts, however. More than 100 known species of newts are found in North America, Europe, North Africa and Asia. Newts metamorphose through three distinct developmental life stages: aquatic larva, terrestrial juvenile (eft), and adult. Adult newts have lizard-like bodies and return to the water every year to breed, otherwise living in humid, cover-rich land habitats. Newts are threatened by habitat loss, habitat fragmentation, fragmentation and pollution. Several species are endangered, and at least one species, the Yunnan lake newt, has become extinct recently. Etymology The Old English name of the animal was , (of unknown origin), resulting in Middle English ; this word was transformed irregularly into , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorella
''Chlorella'' is a genus of about thirteen species of single- celled or colonial green algae of the division Chlorophyta. The cells are spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are without flagella. Their chloroplasts contain the green photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll-a and -b. In ideal conditions cells of ''Chlorella'' multiply rapidly, requiring only carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and a small amount of minerals to reproduce. The name ''Chlorella'' is taken from the Greek χλώρος, ''chlōros/ khlōros'', meaning green, and the Latin diminutive suffix -''ella'', meaning small. German biochemist and cell physiologist Otto Heinrich Warburg, awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1931 for his research on cell respiration, also studied photosynthesis in ''Chlorella''. In 1961, Melvin Calvin of the University of California received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his research on the pathways of carbon dioxide assimilation in plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
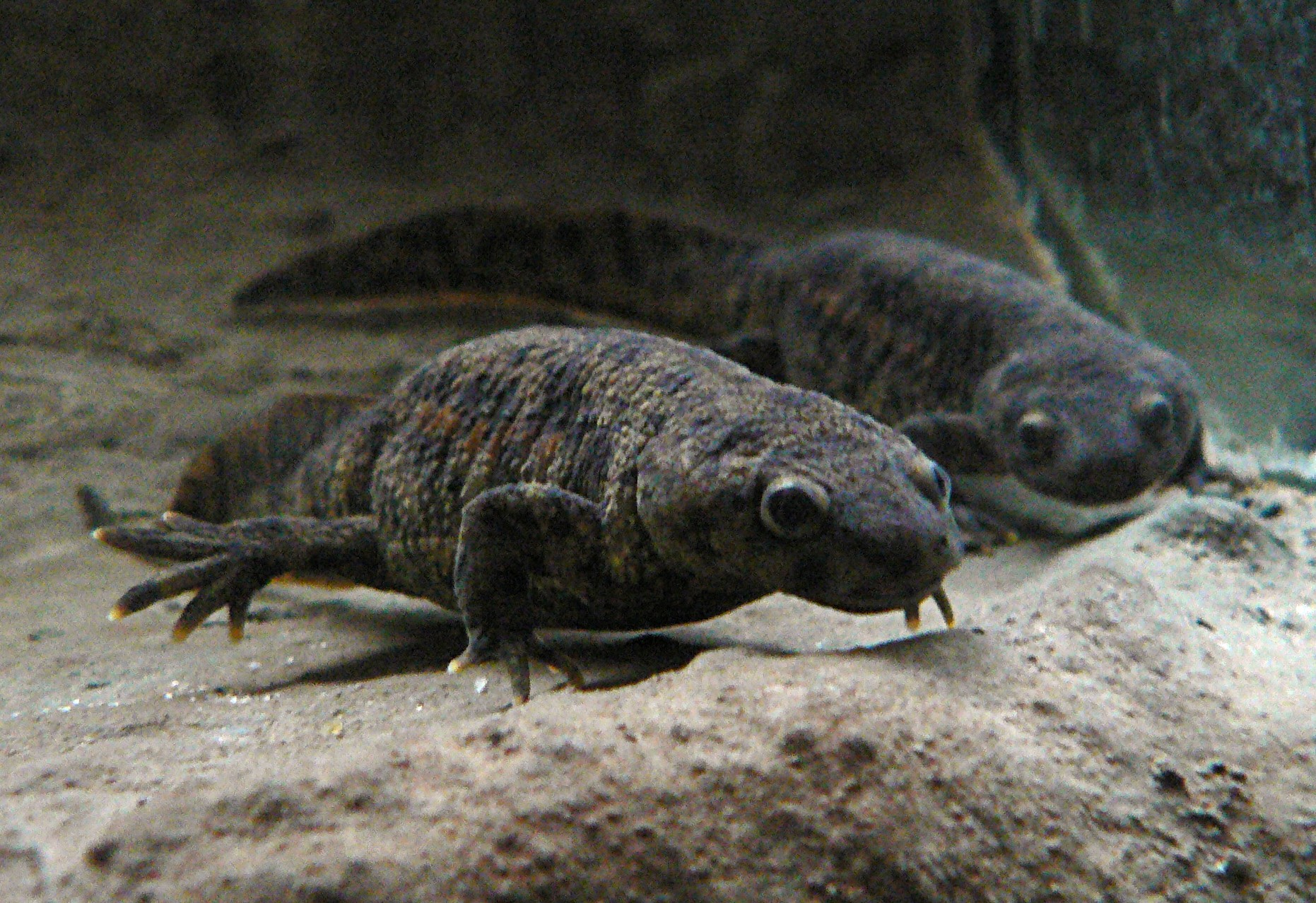
Asiatic Salamander
The Asiatic salamanders (family Hynobiidae) are primitive salamanders found all over Asia, and in European Russia. They are closely related to the giant salamanders (family Cryptobranchidae), with which they form the suborder Cryptobranchoidea. About half of hynobiids currently described are endemic to Japan, but their range also covers parts of China, Russia, Afghanistan and Iran. Hynobiid salamanders practice external fertilization, or spawning. And, unlike other salamander families which reproduce internally, male hynobiids focus on egg sacs rather than females during breeding. The female lays two egg sacs at a time, each containing up to 70 eggs. Parental care is common. A few species have very reduced lungs, or no lungs at all. Larvae can sometimes have reduced external gills if they live in cold and very oxygen-rich water. Fossils of hynobiids are known from the Miocene to the present in Asia and Eastern Europe, though fossils of Cryptobranchoids more closely related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |