|
Balloon Angioplasty
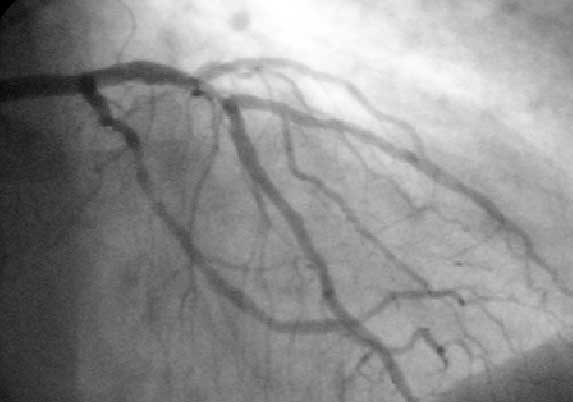
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter (a balloon catheter) is passed over a guide-wire into the narrowed vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously. Uses and indications Coronary angioplasty A coronary angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure to treat the stenotic (narrowed) coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary heart disease. These stenotic segments of the corona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimally Invasive Procedure
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive, and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as ''open surgery''. Incisions made during open surgery can sometimes leave large wounds that may be painful and take a long time to heal. Advancements in medical technologies have enabled the development and regular use of minimally invasive procedures. For example, endovascular aneurysm repair, a minimally invasive surgery, has become the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the US as of 2003. The procedure involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. Interventional radiologists were the forerunners of minimally invasive procedures. Using imaging techniques, radiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unstable Angina
In dynamical systems instability means that some of the outputs or internal states increase with time, without bounds. Not all systems that are not stable are unstable; systems can also be marginally stable or exhibit limit cycle behavior. In structural engineering, a structural beam or column can become unstable when excessive compressive load is applied. Beyond a certain threshold, structural deflections magnify stresses, which in turn increases deflections. This can take the form of buckling or crippling. The general field of study is called structural stability. Atmospheric instability is a major component of all weather systems on Earth. Instability in control systems In the theory of dynamical systems, a state variable in a system is said to be unstable if it evolves without bounds. A system itself is said to be unstable if at least one of its state variables is unstable. In continuous time control theory, a system is unstable if any of the roots of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include edema, leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetic nephropathy, diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as essential hypertension, primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to non-specific lifestyle and Genetics, genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, overweight, excess body weight, smoking, physical inactivity and Alcohol (drug), alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary hypertension, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Artery Stenosis
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is the narrowing of one or both of the renal arteries, most often caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. This narrowing of the renal artery can impede blood flow to the target kidney, resulting in renovascular hypertension – a secondary type of high blood pressure. Possible complications of renal artery stenosis are chronic kidney disease and coronary artery disease. Signs and symptoms Most cases of renal artery stenosis are asymptomatic, and the main problem is high blood pressure that cannot be controlled with medication. Decreased kidney function may develop if both kidneys do not receive adequate blood flow, furthermore some people with renal artery stenosis present with episodes of flash pulmonary edema. Cause Renal artery stenosis is most often caused by atherosclerosis which causes the renal arteries to harden and narrow due to the build-up of plaque. This is known as atherosclerotic renovascular disease, which accounts f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Bypass
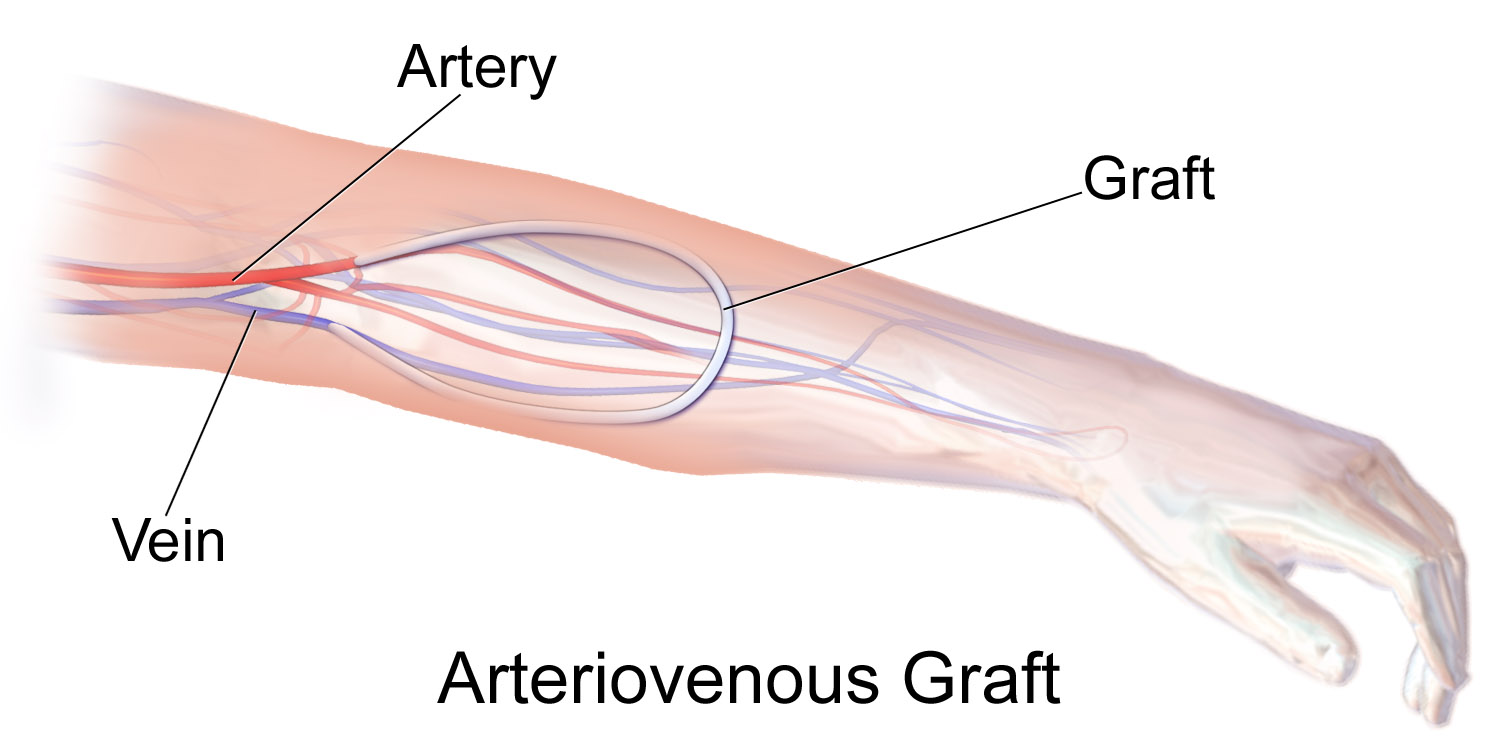
A vascular bypass is a surgical procedure performed to redirect blood flow from one area to another by reconnecting blood vessels. Often, this is done to bypass around a diseased artery, from an area of normal blood flow to another relatively normal area. It is commonly performed due to inadequate blood flow (ischemia) caused by atherosclerosis, as a part of organ transplantation, or for vascular access in hemodialysis. In general, someone's own vein (autograft) is the preferred graft material (or conduit) for a vascular bypass, but other types of grafts such as polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon), polyethylene terephthalate (Dacron), or a different person's vein (allograft) are also commonly used. Arteries can also serve as vascular grafts. A surgeon sews the graft to the source and target vessels by hand using surgical suture, creating a surgical anastomosis. Common bypass sites include the heart (coronary artery bypass surgery) to treat coronary artery disease, and the legs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudication
Claudication is a medical term usually referring to impairment in walking, or pain, discomfort, numbness, or tiredness in the legs that occurs during walking or standing and is relieved by rest. The perceived level of pain from claudication can be mild to extremely severe. Claudication is most common in the calves but it can also affect the feet, thighs, hips, buttocks, or arms. The word ''claudication'' comes . Claudication that appears after a short amount of walking may sometimes be described by US medical professionals by the number of typical city street blocks that the patient can walk before the onset of claudication. Thus, "one-block claudication" appears after walking one block, "two-block claudication" appears after walking two blocks, etc. The term ''block'' would be understood more exactly locally but is on the order of 100 meters (328 feet). Types Intermittent vascular Intermittent vascular (or arterial) claudication (Latin: ''claudicatio intermittens'') mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atherectomy
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive technique for removing atherosclerosis from blood vessels within the body. It is an alternative to angioplasty for the treatment of peripheral artery disease, but the studies that exist are not adequate to determine whether it is superior to angioplasty. It has also been used to treat coronary artery disease, albeit without evidence of superiority to angioplasty. Uses Atherectomy is used to treat stenosis, narrowing in artery, arteries caused by peripheral artery disease and coronary artery disease. Controversy The use of atherectomy instead of or in addition to angioplasty remains an area of controversy, as atherectomy typically involves the use of more costly disposable devices, and clear evidence to justify its use is lacking. Atherectomy has high physician reimbursement relative to angioplasty alone. According to the New York Times, ‘Medical device makers have bankrolled a cottage industry of doctors and clinics that perform artery-clearin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stent
In medicine, a stent is a tube usually constructed of a metallic alloy or a polymer. It is inserted into the Lumen (anatomy), lumen (hollow space) of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open. Stenting refers to the placement of a stent. The word "stent" is also used as a verb to describe the placement of such a device, particularly when a disease such as atherosclerosis has pathology, pathologically narrowed a structure such as an artery. A stent is different from a shunt (medical), shunt. A shunt is a tube that connects two previously unconnected parts of the body to allow fluid to flow between them. Stents and shunts can be made of similar materials, but perform two different tasks. There are various types of stents used for different medical purposes. Coronary stents are commonly used in coronary angioplasty, with drug-eluting stents being the most common type. Vascular stents are used for peripheral and cerebrovascular disease, while ureteral stents ensure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular disorder that causes abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms. When narrowing occurs in the heart, it is called coronary artery disease (CAD), and in the brain, it is called cerebrovascular disease. Peripheral artery disease most commonly affects the legs, but other arteries may also be involved, such as those of the arms, neck, or kidneys. Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a form of peripheral vascular disease. Vascular refers to the arteries and veins within the body. PAD differs from peripheral veinous disease. PAD means the arteries are narrowed or blocked—the vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood as it moves from the heart to other parts of the body. Peripheral veinous disease, on the other hand, refers to problems with veins—the vessels that bring the blood back to the heart. The classic symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |