Stent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

 Ureteral stents are used to ensure the patency of a
Ureteral stents are used to ensure the patency of a
 Prostatic stents are placed from the
Prostatic stents are placed from the
 Colon and esophageal stents are a palliative treatment for advanced colon and
Colon and esophageal stents are a palliative treatment for advanced colon and
 Pancreatic and biliary stents provide pancreatic and bile drainage from the
Pancreatic and biliary stents provide pancreatic and bile drainage from the
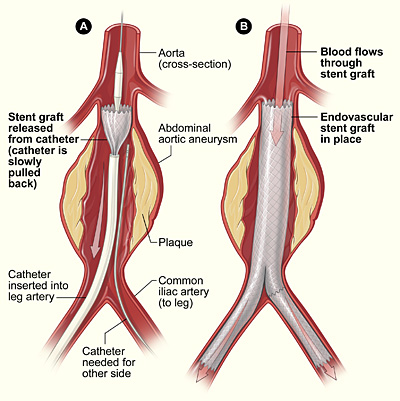 A stent graft or covered stent is type of vascular stent with a fabric coating that creates a contained tube but is expandable like a bare metal stent. Covered stents are used in endovascular surgical procedures such as endovascular aneurysm repair. Stent grafts are also used to treat stenoses in vascular grafts and
A stent graft or covered stent is type of vascular stent with a fabric coating that creates a contained tube but is expandable like a bare metal stent. Covered stents are used in endovascular surgical procedures such as endovascular aneurysm repair. Stent grafts are also used to treat stenoses in vascular grafts and
Coronary Stent
Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe
The Cardiovascular Forum
Stent for Life Initiative
Cobalt Chromium Rapamycin Eluting Coronary Stent System
{{Authority control Implants (medicine) Interventional radiology Medical devices
medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, a stent is a tube usually constructed of a metallic alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
or a polymer. It is inserted into the lumen (hollow space) of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open.
Stenting refers to the placement of a stent. The word "stent" is also used as a verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic f ...
to describe the placement of such a device, particularly when a disease such as atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
has pathologically narrowed a structure such as an artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
.
A stent is different from a shunt. A shunt is a tube that connects two previously unconnected parts of the body to allow fluid to flow between them. Stents and shunts can be made of similar materials, but perform two different tasks.
There are various types of stents used for different medical purposes. Coronary stent
A coronary stent is a tube-shaped device placed in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart, to keep the arteries open in patients suffering from coronary heart disease. The vast majority of stents used in modern interventional ca ...
s are commonly used in coronary angioplasty, with drug-eluting stent
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a tube made of a mesh-like material used to treat atherosclerosis, narrowed arteries in medical procedures both mechanically (by providing a supporting scaffold inside the artery) and pharmacologically (by slowly ...
s being the most common type. Vascular stents are used for peripheral and cerebrovascular disease, while ureteral stents ensure the patency of a ureter.
Prostatic stents can be temporary or permanent and are used to treat conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, urinary retention, inability t ...
. Colon and esophageal stents are palliative treatments for advanced colon and esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weigh ...
. Pancreatic and biliary stents provide drainage from the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, and bile ducts to the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
in conditions such as obstructing gallstones
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
. There are also different types of bare-metal, drug-eluting, and bioresorbable stents available based on their properties.
The term "stent" originates from Charles Stent, an English dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in provi ...
who made advances in denture-making techniques in the 19th century. The use of coronary stents began in 1986 by Jacques Puel and Ulrich Sigwart
Ulrich Sigwart (; born 9 March 1941) is a German retired cardiologist known for his pioneering role in the conception and clinical use of stents to keep blood vessels open, and introducing a non-surgical intervention, alcohol septal ablation fo ...
to prevent vessel closure during coronary angioplasty.
Stent types
By destination organ
Coronary stent

Coronary stent
A coronary stent is a tube-shaped device placed in the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart, to keep the arteries open in patients suffering from coronary heart disease. The vast majority of stents used in modern interventional ca ...
s are placed during a coronary angioplasty. The most common use for coronary stents is in the coronary arteries
The coronary arteries are the arteries, arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the Cardiac muscle, heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any ...
, into which a bare-metal stent, a drug-eluting stent
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a tube made of a mesh-like material used to treat atherosclerosis, narrowed arteries in medical procedures both mechanically (by providing a supporting scaffold inside the artery) and pharmacologically (by slowly ...
, a bioabsorbable stent, a dual-therapy stent (combination of both drug and bioengineered stent), or occasionally a covered stent is inserted.
The majority of coronary stents used today are drug-eluting stents, which release medication to prevent complications such as blood clot formation and restenosis (re-narrowing). Stenting is performed through a procedure called percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), where the cardiologist uses angiography and intravascular ultrasound to assess the blockage in the artery and determine the appropriate size and type of stent. The procedure is typically done in a catheterization clinic, and patients may need to stay overnight for observation. While stenting has been shown to reduce chest pain (angina) and improve survival rates after a heart attack, its effectiveness in stable angina patients has been debated .
Studies have found that most heart attacks occur due to plaque rupture rather than an obstructed artery that would benefit from a stent. Statins, along with PCI/stenting and anticoagulant therapies, are considered part of a broader treatment strategy. Some cardiologists believe that coronary stents are overused, but there is evidence of under-use in certain patient groups like the elderly. Ongoing research continues to explore new types of stents with biocompatible coatings or absorbable materials.
Vascular stent
Vascular stents are a common treatment for advancedperipheral
A peripheral device, or simply peripheral, is an auxiliary hardware device that a computer uses to transfer information externally. A peripheral is a hardware component that is accessible to and controlled by a computer but is not a core compo ...
and cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. Th ...
. Common sites treated with vascular stents include the carotid, iliac, and femoral arteries. Because of the external compression and mechanical forces subjected to these locations, flexible stent materials such as nitinol
Nickel titanium, also known as nitinol, is a metal alloy of nickel and titanium, where the two elements are present in roughly equal atomic percentages. Different alloys are named according to the weight percentage of nickel; e.g., nitinol 55 and ...
are used in many peripheral stents.
Vascular stents made of metals can lead to thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
at the site of treatment or to inflammation scarring. Drug-eluting stent
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a tube made of a mesh-like material used to treat atherosclerosis, narrowed arteries in medical procedures both mechanically (by providing a supporting scaffold inside the artery) and pharmacologically (by slowly ...
s with pharmacologic agents or as drug delivery vehicles have been developed as an alternative to decrease the chances of restenosis.
Because vascular stents are designed to expand inside a blocked artery to keep it open, allowing blood to flow freely, the mechanical properties of vascular stents are crucial for their function: they need to be highly elastic to allow for the expansion and contraction of the stent within the blood vessel, they also need to have high strength and fatigue resistance to withstand the constant physiological load of the arteries, they should have good biocompatibility to reduce the risk of thrombosis and vascular restenosis, and to minimize the body's rejection of the implant.
Vascular stents are commonly used in angioplasty, a surgical procedure that opens blocked arteries and places a stent to keep the artery open. This is a common treatment for heart attacks and is also used in the prevention and treatment of strokes. Over 2 million people receive a stent each year for coronary artery disease alone. Vascular stents can also be used to prevent the rupture of aneurysms in the brain, aorta, or other blood vessels.
Ureteric stent
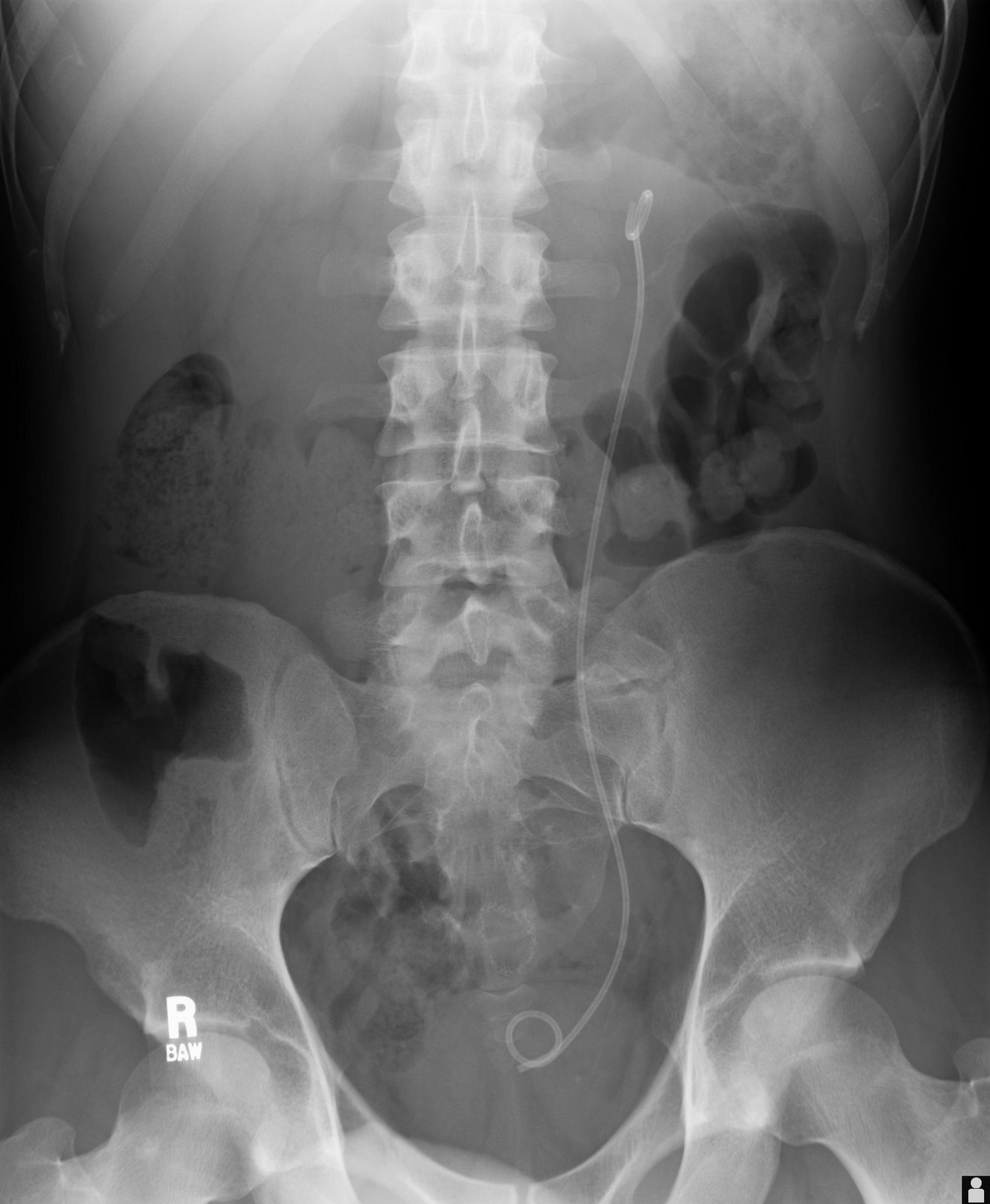
 Ureteral stents are used to ensure the patency of a
Ureteral stents are used to ensure the patency of a ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
, which may be compromised, for example, by a kidney stone
Kidney stone disease (known as nephrolithiasis, renal calculus disease, or urolithiasis) is a crystallopathy and occurs when there are too many minerals in the urine and not enough liquid or hydration. This imbalance causes tiny pieces of cr ...
. This method is sometimes used as a temporary measure to prevent damage to a kidney caused by a kidney stone until a procedure to remove the stone can be performed.
An ureteral stent it is typically inserted using a cystoscope, and one or both ends of the stent may be coiled to prevent movement. Ureteral stents are used for various purposes, such as temporary measures to prevent damage to a blocked kidney until a stone removal procedure can be performed, providing drainage for compressed ureters caused by tumors, and preventing spasms and collapse of the ureter after trauma during procedures like stone removal. The thread attached to some stents may cause irritation but allows for easy removal by pulling gently.
Stents without threads require cystoscopy for removal. Recent developments have introduced magnetic retrieval systems that eliminate the need for invasive procedures like cystoscopy when removing the stent. The use of magnets enables simple extraction without anesthesia and can be done by primary care physicians or nurses rather than urologists. This method has shown high success rates across different patient groups including adults, children, and kidney transplant patients while reducing costs associated with operating room procedures.
Prostatic stent
 Prostatic stents are placed from the
Prostatic stents are placed from the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
through the prostatic and penile urethra to allow drainage of the bladder through the penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate.
The term ''pen ...
. This is sometimes required in benign prostatic hyperplasia
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, urinary retention, inability t ...
.
A prostatic stent is used to keep the male urethra open and allow for the passage of urine in cases of prostatic obstruction and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). There are two types of prostatic stents: temporary and permanent. Permanent stents, typically made of metal coils, are inserted into the urethra to apply constant gentle pressure and hold open sections that obstruct urine flow. They can be placed under anesthesia as an outpatient procedure but have disadvantages such as increased urination, limited incontinence, potential displacement or infection, and limitations on subsequent endoscopic surgical options. On the other hand, temporary stents can be easily inserted with topical anesthesia similar to a Foley catheter, and allow patients to retain volitional voiding. However, they may cause discomfort or increased urinary frequency.
In the US, there is one temporary prostatic stent that has received FDA approval called The Spanner. It maintains urine flow while allowing natural voluntary urination. Research on permanent stents often focuses on metal coil designs that expand radially to hold open obstructed areas of the urethra.
These permanent stents are used for conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), recurrent bulbar urethral stricture (RBUS), or detrusor external sphincter dyssynergia (DESD). The Urolume is currently the only FDA-approved permanent prostatic stent.
Colon and Esophageal stents
 Colon and esophageal stents are a palliative treatment for advanced colon and
Colon and esophageal stents are a palliative treatment for advanced colon and esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weigh ...
.
A colon stent is typically made of flexible metal mesh that can expand and hold open the blocked area, allowing for the passage of stool. Colon stents are used primarily as a palliative treatment for patients with advanced colorectal cancer who are not candidates for surgery. They help relieve symptoms such as abdominal pain, constipation, and bowel obstruction caused by tumors or strictures in the colon.
The placement of a colon stent involves endoscopic techniques similar to esophageal stenting. A thin tube called an endoscope is inserted into the rectum and guided through the colon to locate the blockage. Using fluoroscopy or endoscopic guidance, a guidewire is passed through the narrowed area and then removed after positioning it properly. The stent is then delivered over the guidewire and expanded to keep open the obstructed section of the colon. Complications associated with colon stents include perforation of the intestinal wall, migration or dislodgment of the stent, bleeding, infection at insertion site, or tissue overgrowth around it.
Colon stenting provides several benefits including prompt relief from bowel obstruction symptoms without invasive surgery in many cases. It allows for faster recovery time compared to surgical interventions while providing palliative care for patients with advanced colorectal cancer by improving quality of life and enabling better nutritional intake. However, there are potential risks associated with complications such as migration or obstruction that may require additional procedures or interventions to address these issues effectively.
Pancreatic and biliary stents
 Pancreatic and biliary stents provide pancreatic and bile drainage from the
Pancreatic and biliary stents provide pancreatic and bile drainage from the gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, and bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).
Bile is requ ...
s to the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
in conditions such as ascending cholangitis
Ascending cholangitis, also known as acute cholangitis or simply cholangitis, is inflammation of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria ascending from Ampulla of Vater, its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It ten ...
due to obstructing gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s.
Pancreatic and biliary stents can also be used to treat biliary/pancreatic leaks or to prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis.
In the case of gallstone pancreatitis, a gallstone travels from the gallbladder and blocks the opening to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). This causes a backup of fluid that can travel up both the bile duct and the pancreatic duct. Gallbladder stones can lead to obstruction of the biliary tree via which gallbladder and pancreas enzymes are secreted into the duodenum, causing emergency events such as acute cholecystitis or acute pancreatitis.
In conditions such as ascending cholangitis due to obstructing gallstones, these stents play a crucial role. They help in maintaining the flow of bile and pancreatic juices from the gallbladder, pancreas, and bile ducts to the duodenum1. Biliary stents are often used during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to treat blockages that narrow your bile or pancreatic ducts. In cases of malignant biliary obstruction, endoscopic stent placement is one of the treatment options to relieve the obstruction. Biliary drainage is considered effective, particularly in bile duct conditions that are diagnosed and treated early.
Glaucoma drainage stent
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
drainage stents are recent developments and have been recently approved in some countries. They are used to reduce intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated t ...
by providing a drainage channel.
By properties or function
Bare-metal stent
 A stent graft or covered stent is type of vascular stent with a fabric coating that creates a contained tube but is expandable like a bare metal stent. Covered stents are used in endovascular surgical procedures such as endovascular aneurysm repair. Stent grafts are also used to treat stenoses in vascular grafts and
A stent graft or covered stent is type of vascular stent with a fabric coating that creates a contained tube but is expandable like a bare metal stent. Covered stents are used in endovascular surgical procedures such as endovascular aneurysm repair. Stent grafts are also used to treat stenoses in vascular grafts and fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
s used for hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply ''"'dialysis'"'', is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of Kidney dialys ...
.
Bioresorbable stent
A bioresorbable stent is a tube-like device made from a material that can release a drug to prevent scar tissue growth. It is used to open and widen clogged heart arteries and then dissolves or is absorbed by the body. Unlike traditional metal stents, bioresorbable stents can restore normal vessel function, avoid long-term complications, and enable natural reconstruction of the arterial wall. Metal-based bioresorbable scaffolds include iron, magnesium, zinc, and their alloys. Magnesium-based scaffolds have been approved for use in several countries around the world and show promising clinical results in delivering against the drawbacks of permanent metal stents. However, attention has been given to reducing the rate of magnesium corrosion through alloying and coating techniques. Clinical research shows that resorbable scaffolds offer comparable efficacy and safety profiles to traditional drug-eluting stents (DES). The Magmaris resorbable magnesium scaffold has reported favorable safety outcomes similar to thin-strutted DES in patient populations. The Absorb naturally dissolving stent has also shown low rates of major adverse cardiac events when compared to DES. Imaging studies demonstrate that these naturally dissolving stents begin to dissolve between six months to two years after placement in the artery.Drug-eluting stent
Drug-eluting stents (DES) are specialized medical devices used to treat coronary artery disease and peripheral artery disease. They release a drug that inhibits cellular growth into the blocked or narrowed arteries, reducing the risk of blockages. DES are commonly placed using percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), a minimally invasive procedure performed via catheter. These stents have shown clear advantages over older bare-metal stents, improving patient outcomes and quality of life for cardiac patients. With over 90% of stents used in PCI procedures being drug-eluting as of 2023, DES have become the standard choice for interventional cardiologists. DES gradually release drugs that prevent restenosis and thrombosis within the treated arteries, addressing common complications associated with previous treatments. While risks such as clot formation and bleeding exist, studies have demonstrated superior efficacy compared to bare-metal stents in reducing major adverse cardiac events like heart attacks and repeat revascularization procedures. Long-term outcomes are still being studied due to their relatively recent introduction; however, DES have revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease by significantly improving patient outcomes and enhancing their quality of life.Etymology
The currently accepted origin of the word ''stent'' is that it derives from the name of an Englishdentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in provi ...
, Charles Thomas Stent (1807–1885), notable for his advances in the field of denture-making. He was born in Brighton
Brighton ( ) is a seaside resort in the city status in the United Kingdom, city of Brighton and Hove, East Sussex, England, south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age, R ...
, England, on October 17, 1807, was a dentist in London, and is most famous for improving and modifying the denture base of the gutta-percha
Gutta-percha is a tree of the genus ''Palaquium'' in the family Sapotaceae, which is primarily used to create a high-quality latex of the same name. The material is rigid, naturally biologically Chemically inert, inert, resilient, electrically n ...
, creating the stent's compounding that made it practical as a material for dental impressions.
Others attribute the noun ''stent'' to Jan F. Esser, a Dutch plastic surgeon who in 1916 used the word to describe a dental impression compound invented in 1856 by Charles Stent, whom Esser employed to craft a form for facial reconstruction. The full account is described in the ''Journal of the History of Dentistry''. According to the author, from the use of Stent's compound as a support for facial tissues evolved the use of a stent to hold open various body structures.
The verb form "stenting" was used for centuries to describe the process of stiffening garments (a usage long obsolete, per the ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
''), and some believe this to be the origin. According to the Merriam Webster Third New International Dictionary, the noun evolved from the Middle English verb , shortened from 'to stretch', which in turn came from Latin , the past participle of 'to stretch out'.
The first (self-expanding) "stents" used in medical practice in 1986 by Ulrich Sigwart
Ulrich Sigwart (; born 9 March 1941) is a German retired cardiologist known for his pioneering role in the conception and clinical use of stents to keep blood vessels open, and introducing a non-surgical intervention, alcohol septal ablation fo ...
in Lausanne were initially called "Wallstents" after their inventor, Hans Wallstén.
Julio Palmaz ''et al.'' created a balloon-expandable stent that is currently used.
History
The first use of a coronary stent is typically attributed to andUlrich Sigwart
Ulrich Sigwart (; born 9 March 1941) is a German retired cardiologist known for his pioneering role in the conception and clinical use of stents to keep blood vessels open, and introducing a non-surgical intervention, alcohol septal ablation fo ...
, who implanted a stent into a patient in Toulouse, France, in 1986. That stent was used as a scaffold to prevent a vessel from closing and to avoid restenosis
Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis, a narrowing of a blood vessel, leading to restricted blood flow. Restenosis usually pertains to an artery or other large blood vessel that has become narrowed, received treatment to clear the blockage, and ...
in coronary surgery—a condition where scar tissue grows within the stent and interferes with vascular flow. Shortly thereafter, in 1987, Julio Palmaz (known for patenting a balloon-expandable stent ) and Richard Schatz implanted their similar stent into a patient in Germany.
Though several doctors have been credited with the creation of the stent, the first FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
-approved stent in the U.S. was created by Richard Schatz and coworkers. Named the Palmaz-Schatz (Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical technologies corporation headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Its common stock is a c ...
), it was developed in 1987.
To further reduce the incidence of restenosis, the drug-eluting stent
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a tube made of a mesh-like material used to treat atherosclerosis, narrowed arteries in medical procedures both mechanically (by providing a supporting scaffold inside the artery) and pharmacologically (by slowly ...
was introduced in 2003. Research has led to general stent design changes and improvements since that time. Bioresorbable scaffolds have also entered the market, though a large-scale clinical trial showed higher acute risks compared to drug-eluding stents. As a result, the FDA issued an official warning for their use in 2013, and research on the design and performance optimisation of stents is ongoing.
See also
* * * * *References
External links
Coronary Stent
Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe
The Cardiovascular Forum
Stent for Life Initiative
Cobalt Chromium Rapamycin Eluting Coronary Stent System
{{Authority control Implants (medicine) Interventional radiology Medical devices