|
Balaustion Quinquelobum
''Balaustion quinquelobum'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is low-growing to fairly erect shrub with narrowly egg-shaped or narrowly oblong to linear leaves, and white or pale pink flowers with 18 to 25 stamens. Description ''Balaustion quinquelobum'' is a low-growing or fairly erect shrub that typically grows to high and wide, the flowering branchlets with usually one pair of flowers. Its leaves are narrowly egg-shaped or narrowly oblong to linear, mostly long and wide, the lower surface keeled near the tip with usually one or two rows of oil glands each side of the midvein. The flowers are in diameter on a peduncle long, each flower on a pedicel long. The floral tube is long and wide and is distinctively five-lobed. The sepals are broadly egg-shaped, long, wide and reddish, sometimes with a whitish border. The petals are white or pale pink, long, with 18 to 25 stamens. Flowering has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbara Lynette Rye
Barbara Lynette Rye is an Australian botanist born in 1952. Barbara Rye has been associated with the Western Australian Herbarium, where her work as a taxonomist has been the source of many new descriptions of plants. The number of taxa recorded as described by women authors is historically very low, of the terrestrial plant species this amount is around three percent, yet in analysis published in 2019 Rye is amongst the ten most prolific women taxonomists. Born in Perth, Western Australia, she spent her childhood investigating the local flora and fauna of the Southwest Australia region, a biodiversity hotspot, and later began studies at the University of Western Australia. Barbara Rye entered the fields of zoology and botany, taking a special interest in genetics and evolutionary biology. The first description of a new species was a ''Darwinia'', a genus of the family Myrtaceae that Rye investigated for her doctoral thesis, separating '' Darwinia capitellata'' from a more widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welbungin
Welbungin is a small town located just off the Koorda–Southern Cross road from Perth in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia. Land was reserved in the area for a town hall as early as 1915 but it was not until the extension of the railway line from Mount Mashall to Lake Brown was planned to pass close by and that a station would be established in 1921 that the local primary producers association began to campaign for a town to be gazetted. The area was also known locally as Polkinghome's Corner but was gazetted in 1923 as Welbunging. The spelling was later changed to its current spelling in 1944. The name of the town is Aboriginal in origin and was first recorded in 1889 by early surveyors after the name of a nearby hill. In 1932 the Wheat Pool of Western Australia announced that the town would have two grain elevators, each fitted with an engine, installed at the railway siding. The surrounding areas produce wheat and other cereal crops. The town is a receival sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Described In 2022
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria to produce sugars from carbon dioxide and water, using the green pigment chlorophyll. Exceptions are parasitic plants that have lost the genes for chlorophyll and photosynthesis, and obtain their energy from other plants or fungi. Most plants are multicellular, except for some green algae. Historically, as in Aristotle's biology, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi. Definitions have narrowed since then; current definitions exclude fungi and some of the algae. By the definition used in this article, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (green plants), which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants (hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, conifers and other gymnosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Western Australia
The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,842 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,030 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genus, genera from 211 Family (biology), families; there are also 1,335 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority. History Indigenous Australians have a long history with the flora of Western Australia. They have for over 50,000 years obtained detailed information on most plants. The information includes its uses as sources for food, shelter, tools and medicine. As Indigenous Australians passed the knowledge along orally or by example, most of this information has been lost, along many of the names they gave the flora. It was not until Europeans started to explore Western Australia that systematic written de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Biodiversity, Conservation And Attractions (Western Australia)
The Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) is the Government of Western Australia, Western Australian government department responsible for managing lands and waters described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'', the ''Rottnest Island Authority Act 1987'', the ''Swan and Canning Rivers Management Act 2006'', the ''Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority Act 1998'', and the ''Zoological Parks Authority Act 2001'', and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The Department reports to the Minister for Environment and the Minister for Tourism. DBCA was formed on 1 July 2017 by the merger of the Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW), the Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority, the Zoological Parks Authority and the Rottnest Island Authority. The former DPaW became the Parks and Wildlife Service. Status Parks and Wildlife Service The Formerly Department of Parks and Wildlife. the Parks and Wildlife Servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallee Bioregion
Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeography, biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive ''Eucalyptus'' mallee (habit), mallee vegetation. It has an area of . About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Mallee region has a complex shape with tortuous boundaries, but may be roughly approximated as the triangular area south of a line from Bruce Rock, Western Australia, Bruce Rock to Eyre, Western Australia, Eyre, but not within 40 kilometres (25 mi) of the south coast, except at its eastern limits. It has an area of about 79000 square kilometres (31000 mi2), making it about a qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
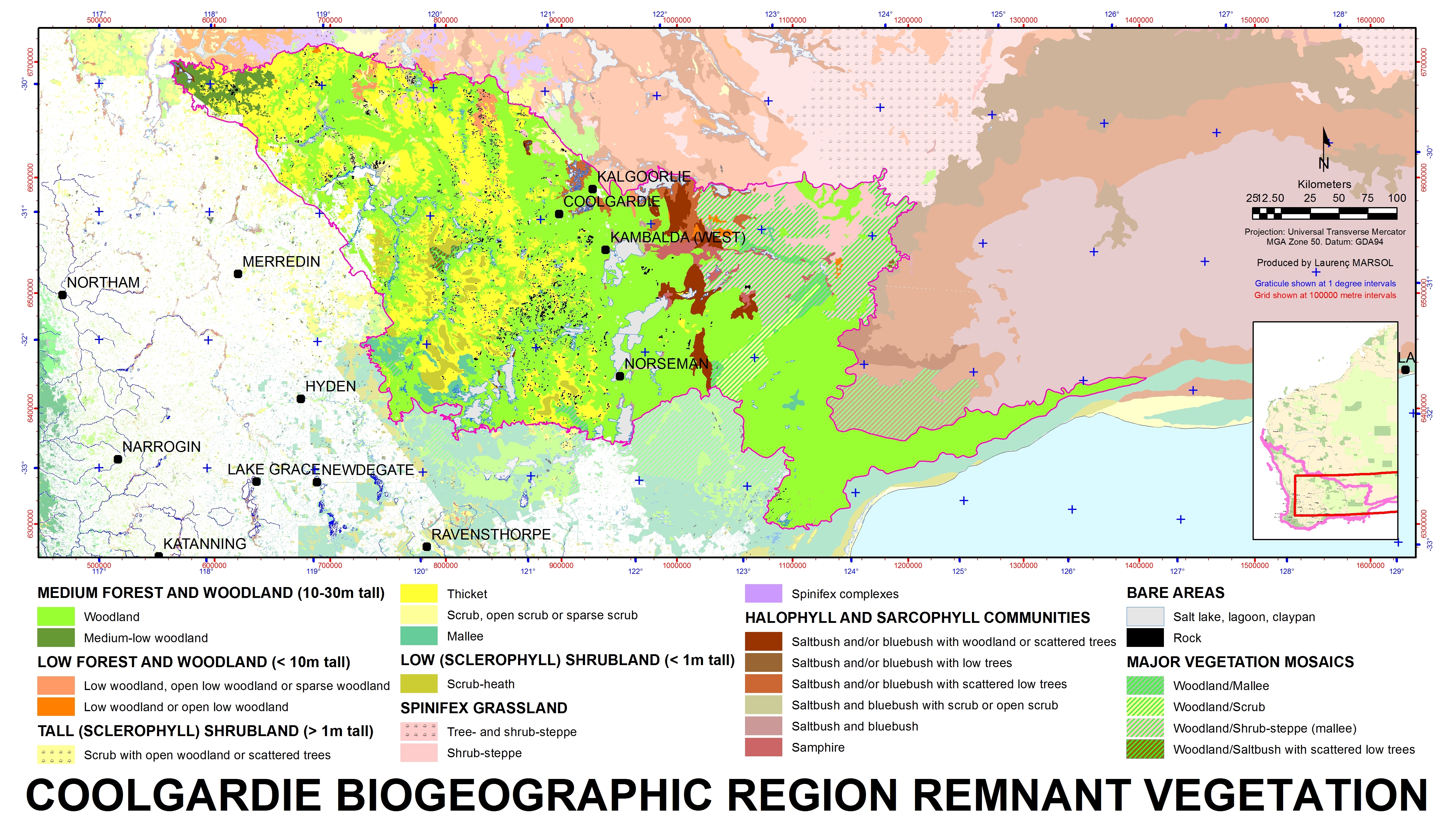
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake King
Lake King is a town in the eastern Wheatbelt region of Western Australia, from Perth along State Route 40 between Ravensthorpe and Newdegate. As of 2016, the town had a population of 95. The 2011 census recorded both the population of the town and the surrounding area for a population of 332. Lake King is named after a nearby lake which in turn was named after the Surveyor General of Western Australia, Henry Sandford King, by Marshall Fox, District Surveyor (Narrogin). In 1926, following completion of an initial land classification survey of the Lake King district that defined 230,000 acres as suitable for settlement, a large official inspection party was led by Surveyor General John Percy Camm, Sydney Stubbs ( MLA Wagin), Edwin Wilkie Corboy (MLA Yilgan), and James Cornell ( MLC South Province). The area was surveyed and access roads built during 1927, and land released in 1928 at prices from 4/6 to 16/- per acre. The town struggled through the Great Depression but thri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Grace
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a depression (geology), basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Cross, Western Australia
Southern Cross is a town in Western Australia, 371 kilometres (230.5 miles) east of state capital Perth on the Great Eastern Highway. It was founded in 1888 after gold prospectors Richard Greaves and Ted Paine during their October 1887 expedition successfully found gold, and gazetted in 1890. It is the major town and administrative centre of the Shire of Yilgarn. At the , Southern Cross had a population of 680. The town of Southern Cross is one of the many towns that run along the Goldfields Water Supply Scheme pipeline from Mundaring to Kalgoorlie, engineered by C. Y. O'Connor, and as a consequence is an important location on the Golden Pipeline Heritage Trail. A succession of gold rushes in the Yilgarn region near Southern Cross in 1887, at Coolgardie in 1892, and at Kalgoorlie in 1893 caused a population explosion in the barren and dry desert centre of Western Australia. It is named after the Southern Cross constellation, and the town's streets are named after const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrtaceae
Myrtaceae (), the myrtle family, is a family of dicotyledonous plants placed within the order Myrtales. Myrtle, pōhutukawa, bay rum tree, clove, guava, acca (feijoa), allspice, and eucalyptus are some notable members of this group. All species are woody, contain essential oils, and have flower parts in multiples of four or five. The leaves are evergreen, alternate to mostly opposite, simple, and usually entire (i.e., without a toothed margin). The flowers have a base number of five petals, though in several genera, the petals are minute or absent. The stamens are usually very conspicuous, brightly coloured, and numerous. Evolutionary history Scientists hypothesize that the family Myrtaceae arose between 60 and 56 million years ago (Mya) during the Paleocene era. Pollen fossils have been sourced to the ancient supercontinent Gondwana. The breakup of Gondwana during the Cretaceous period (145 to 66 Mya) geographically isolated disjunct taxa and allowed for rapid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |