|
Ayojjhapura
Ayodhyapura or Ayojjhapura ( or ) was an ancient settlement in central Thailand. It existed before the 14th century and is mentioned in the or ''The Chronicle of the Emerald Buddha'' written in Pali by Brahmarājaprajña in the 15th century and in another Pali chronicle Jinakalamali. Modern scholars suggest ''Ayodhyapura'' was potentially Si Thep, the early center of the Dvaravati civilization, which flourished from the 6th to 11th century. In contrast, some say it was the city in present-day North Thailand, but its exact location is unknown. Ayodhyapura potentially began to decline in the mid-10th century as the Khmer inscription dating to 946 mentioned the Angkorian king Rajendravarman II won over Rāmaññadesa (country of the Mon) and Champa. He later assigned his lineage, Vap Upendra, as the governor of Rāmaññadesa in 949. Earlier, the mentions a battle between Ayodhyapura led by Adītaraj and Yaśodharapura over the Emerald Buddha in the late 9th or early 10th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvaravati
Dvaravati () was a medieval Mon political principality from the 6th century to the 11th century, located in the region now known as central Thailand, and was speculated to be a succeeding state of Lang-chia or Lang-ya-hsiu (). It was described by Chinese pilgrims in the middle of the 7th century as a Buddhist kingdom named ''To-lo-po-ti'' situated to the west of Isanapura (Cambodia), to the east of Sri Ksetra (Burma), and adjoined Pan Pan in the South. Its northern border met ''Jiā Luó Shě Fú'' (), which was speculated to be either ''Kalasapura'', situated along the coast of the Bay of Bengal somewhere between Tavoy and Rangoon, or Canasapura in modern northeast Thailand. Dvaravati sent the first embassy to the Chinese court around 605–616, and then in 756. Text: Dvaravati also refers to a culture, an art style, and a disparate conglomeration of principalities of Mon people. The Mon migrants as maritime traders might have brought the Dvaravati Civilization to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiān
Xiān ( zh, 暹) or Siam () was a confederation of maritime-oriented port polities along the present Bay of Bangkok, including Ayutthaya Kingdom#Pre-Ayutthaya cities, Ayodhya, Suphannabhum, and Phip Phli Kingdom, Phip Phli, as well as Nakhon Si Thammarat Kingdom, Nakhon Si Thammarat (Ligor), which became Siam in the late 13th century. Previous studies suggested that ''Xiān'' in Chinese dynasty records only referred to Sukhothai Kingdom, Sukhothai, but this presupposition has recently been rebutted. Xiān was formed from city-states on the west Chao Phraya River, Chao Phraya plain after the decline of Dvaravati in the 11th century. In 1178, the region was mentioned in the term ''San-lo '', as recorded in the Chinese Lingwai Daida, in which Thai scholars suggest it was plausibly referred to Mueang Chaliang, Chaliang's new center, Si Satchanalai Historical Park, Sawankhalok. Xiān or Siam, which was also recorded as Suphannabhum, Suphan Buri and Nakhon Si Thammarat Kingdom, Nakho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Si Thep Historical Park
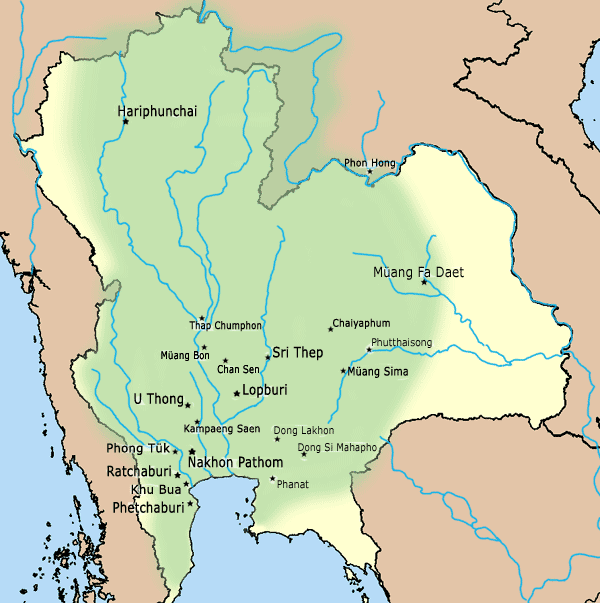
Si Thep Historical Park () is an archaeological site in Thailand's Phetchabun province. It covers the ancient city of Si Thep, a site inhabited from around the third to fifth century CE until the thirteenth century, spanning cultural periods from late prehistory, through Dvaravati, to the golden age of the Khmer Empire. Si Thep was one of the largest known city-states that emerged around the plains of central Thailand in the first millennium, but became abandoned around the time the Thai-speaking cities of Sukhothai and later Ayutthaya emerged as new centres of power in the Chao Phraya River basin. The site gained the attention of modern archaeology in 1904 following surveys by Prince Damrong Rajanubhab, and it was listed as an ancient monument in 1935. The Fine Arts Department has undertaken continued study and excavations of the site, which has also been studied by archaeologists Prince Subhadradis Diskul, H. G. Quaritch Wales and Jean Boisselier, among others. As per hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champa
Champa (Cham language, Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ, چمڤا; ; 占城 or 占婆) was a collection of independent Chams, Cham Polity, polities that extended across the coast of what is present-day Central Vietnam, central and southern Vietnam from approximately the 2nd century CE until 1832. According to History of Champa, earliest historical references found in ancient sources, the first History of Champa#Initial kingdoms, Cham polities were established around the 2nd century, 2nd to 3rd century, 3rd centuries CE, in the wake of Khu Liên's rebellion against the rule of China's Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty, and lasted until when the final Panduranga (Champa), remaining principality of Champa was annexed by Minh Mạng, Emperor Minh Mạng of the Vietnamese Nguyễn dynasty as part of the expansionist Nam tiến policy. The kingdom was known variously as ''Nagaracampa'' (), ''Champa'' (ꨌꩌꨛꨩ) in modern Cham languages, Cham, and ''Châmpa'' () in the Khmer lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city)
Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (, ), or locally and simply Ayutthaya is the capital of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province of Thailand. Ayutthaya was the capital of the Ayutthaya Kingdom. Located on an island at the confluence of the Chao Phraya River, Chao Phraya and Pa Sak River, Pa Sak rivers, Ayutthaya is the birthplace of the founder of Bangkok, Rama I, King Rama I. The ruins of the old city are preserved in the Ayutthaya Historical Park. Etymology The name ''Ayutthaya'' is derived from Sanskrit अयोध्य - Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya and is from the Thai national epic ''Ramakien''; (from Khmer language, Khmer: ''preah'' ព្រះ ) is a prefix for a noun concerning a royal person, and (from Pali: ''nagara'') designates an important or capital city. History Prior to Ayutthaya's traditional founding date, archaeological and written evidence has revealed that Ayutthaya may have existed as early as the late 13th century as a water-borne port town. Further evidence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lopburi
Lopburi (, , ) is the capital city of Lopburi Province in Thailand. It is about northeast of Bangkok. It has a population of 58,000. The town ('' thesaban mueang'') covers the whole ''tambon'' Tha Hin and parts of Thale Chup Son of Mueang Lopburi District, a total area of 6.85 km2. History Chronology The city has a history dating back to the Dvaravati period more than 1,000 years ago.Higham, C., 2014, ''Early Mainland south-east Asia'', Bangkok: River Books Co., Ltd., According to the ''Northern Chronicles,'' Lavo was founded by Phraya Kalavarnadishraj, who came from Takkasila in 648 CE. According to Thai records, Phraya Kakabatr from Takkasila (it is assumed that the city was Tak or Nakhon Chai Si) set the new era, Chula Sakarat in 638 CE, which was the era used by the Siamese and the Burmese until the 19th century. His son, Phraya Kalavarnadishraj founded the city a decade later. Lopburi, or Lavapura as it then was, was under the rule of the rising Angk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavo Kingdom
The Lavo Kingdom () was a political entity (Mandala (Southeast Asian political model), mandala) on the left bank of the Chao Phraya River in the Upper Chao Phraya valley from the end of Dvaravati civilization, in the 7th century, until 1388. The original center of Lavo was Lopburi, Lavapura and was shifted to Ayodhya (Xiān) in the 1080s. However, since both Ayodhya or Xiān and Lavo separately sent embassies to the Chinese court in the late 1200s, these two polities were potentially individual states. Before the 9th century, Lavo, together with other supra-regional settlements, such as Si Thep Historical Park, Si Thep, , Phimai Historical Park, Phimai, Nakhon Pathom, and others were the centers of the Mandala (political model), mandala-style polities of Dvaravati. Due to several circumstances, including climate changes and the invasions of the surrounding polities, several Dvaravati centers lost their prosperity, and the mandalas in the Chao Phraya River, Menam Valley was then s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pa Sak River
The Pa Sak River (, , Pronunciation is a river in central Thailand. The river originates in the Phetchabun Mountains, Dan Sai District, Loei Province, and passes through Phetchabun Province as the backbone of the province. It then passes through the eastern part of Lopburi Province and Saraburi Province, until it joins the Lopburi River northeast of Ayutthaya Island, before it runs into the Chao Phraya River southeast of Ayutthaya near Phet Fortress. It has a length of and drains a watershed of . The annual discharge is . The valley of the Pa Sak through the Phetchabun mountains is a dominant feature of Phetchabun Province. Water levels vary seasonally. To address drought problems in the lower Pa Sak valley, in 1994 the construction of the Pa Sak Cholasit Dam (เขื่อนป่าสักชลสิทธิ์) in Lopburi Province was built. The wide and high dam retains of water. The dam also supplies about 6.7 MW of electricity. Tributaries Tributaries of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wen Dan
Wén Dān ( zh, 文單; ), proposed Bhavapura, was a group of ancient Mon political entities that existed around the 6th–10th centuries CE in the interior of mainland Southeast Asia scattered around the central Mekong Valley in the present-day northeast Thailand. It was mentioned in the Chinese annals of the Tang period (618-907 AD) as a dependency on the trans-Mekong trade route from the ancient city of Chiaochih (jiāo zhǐ 交趾; Giao chỉ; near the present-day Vinh of Vietnam) to India. It sent representatives to China in 717, 750, 753, 771, 779, and 799. Some scholars identify Wen Dan with Bhavapura and believe it was the origin of the united Chenla. However, this theory remains disputed, as some argue that Chenla probably formed in the southern Tonlé Sap Basin, rather than in Northeast Thailand or Southern Laos. Initially, Wen Dan was believed to be Vientiane, but according to the location given in the Chinese annals as well as archaeological evidence, it is supposed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi River
The Chi River (, , ; , ) is the longest river flowing wholly within Thailand. It is long but carries less water than the second longest river, the Mun. The name of the river is "Mae Si" () in the Isan and Lao languages of the region, being transliterated as "Chi" in Bangkok-Thai. In wet seasons there are often flash floods in the floodplain of the Chi River basin. Course The river rises in the Phetchabun mountains, then runs east through the central Isan provinces of Chaiyaphum, Khon Kaen, and Maha Sarakham, then turns south in Roi Et, runs through Yasothon and joins the Mun in the Kanthararom district of Sisaket Province. The river carries approximately of water per annum. The river was an 18th-century migration route for the re-peopling of the Khorat Plateau by ethnic Lao people from the left (east) bank of the Mekong resettling on the right bank. This began in 1718 when the first king of the left bank Kingdom of Champasak, King Nokasad, sent a group of some 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mun River
The Mun River (, , ; , ), sometimes spelled ''Moon River'', is a tributary of the Mekong River. It carries approximately of water per year. Geography The river begins in the Khao Yai National Park area of the Sankamphaeng Range, near Nakhon Ratchasima in northeast Thailand. It flows east through the Khorat Plateau in southern Isan (Nakhon Ratchasima, Buriram, Surin, and Sisaket Provinces) for , until it joins the Mekong at Khong Chiam in Ubon Ratchathani. The Mun River's main tributary is the Chi River, which joins it in the Kanthararom District of Sisaket Province. History Thanks to the Andy Williams hit song, the Mun River was called " Moon River" by US Air Force personnel stationed at Ubon Ratchathani airbase during the Vietnam War. The spelling is still fairly common. The controversial Pak Mun Dam, which is charged with causing environmental damage, is near the river's confluence with the Mekong. Tributaries * Lam Dom Noi *Chi River The Chi River (, , ; , ) is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
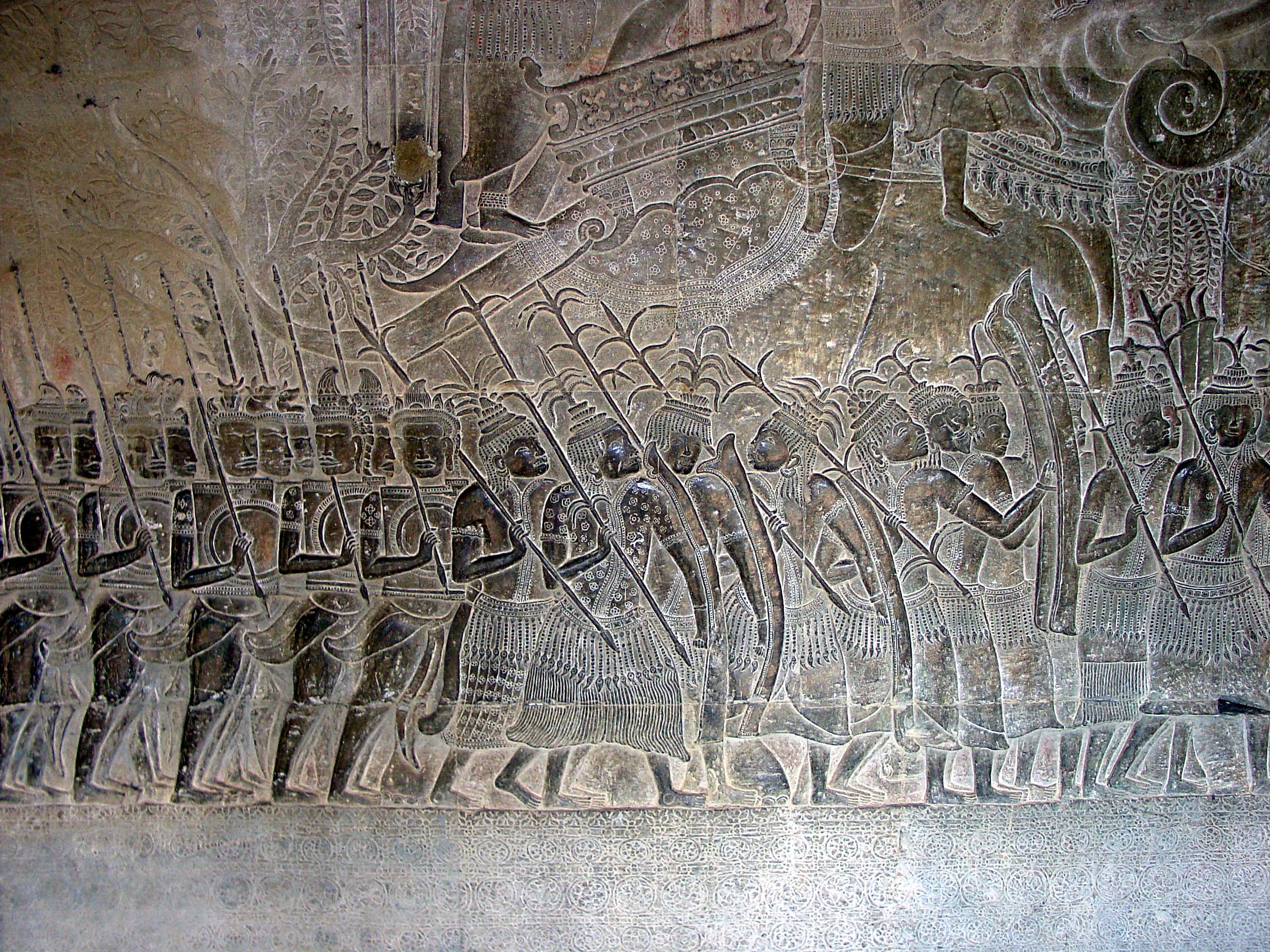
Khmer Empire
The Khmer Empire was an empire in Southeast Asia, centered on Hydraulic empire, hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja (; ) by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilization of Chenla and lasted from 802 to 1431. Historians call this period of History of Cambodia, Cambodian history the Angkor period, after the empire's most well-known capital, Angkor. The Khmer Empire ruled or vassalised most of Mainland Southeast Asia and stretched as far north as southern China. The beginning of the Khmer Empire is conventionally dated to 802, when Khmer people, Khmer prince Jayavarman II declared himself ''chakravartin'' (, a title equivalent to 'emperor') in the Phnom Kulen mountains. Although the end of the Khmer Empire has traditionally been marked with the fall of Angkor to the Siamese Ayutthaya Kingdom in 1431, the reasons for the empire's collapse are still debated amongst scholars. Researchers have determined that a period of strong monsoon rains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |